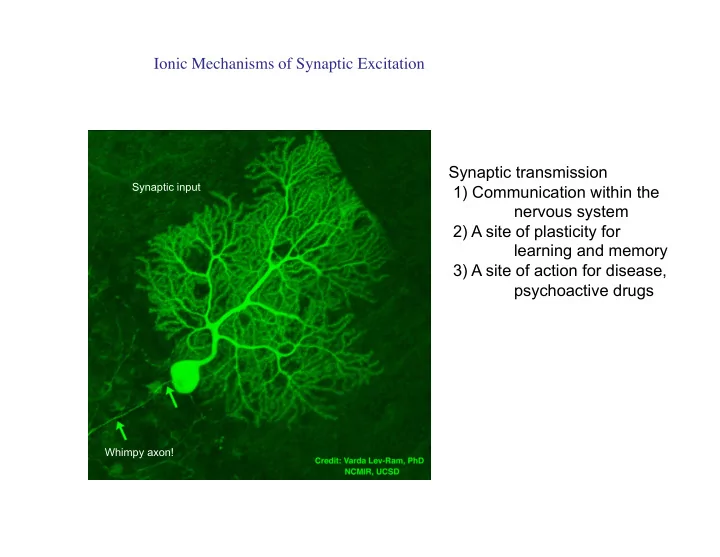

Ionic Mechanisms of Synaptic Excitation � Synaptic transmission Synaptic input 1) Communication within the nervous system 2) A site of plasticity for learning and memory 3) A site of action for disease, psychoactive drugs Whimpy axon!
Crayfish NMJ as a model for human brain synapses Neuromuscular Innervation Uni-terminal Multi-terminal Uni-neuronal Poly-neuronal Excitation Only Inhibition Often no APs Mammals Arthropods See Synapse Tutorial on class web site for review
Crayfish NMJ preparation
Example Data
Map Muscle Innervation Patterns (Also better distinguish number of axons in nerve 3 ) Synaptic Integration See G-PRIME for example of- Muscle Innervation - Cross Correlation
EPSP trying to reach AP threshold Synaptic integration Axon Hillock Dendrite spatial and temporal
Space constant important Time constant important Spatial summation Temporal summation
Synaptic Inhibition Two flavors: Algebraic Summation Shunting How do they work?
Synaptic Inhibition Stimulation of inhibitory nerve blocks AP production
Presynaptic inhibition � Presynaptic inhibition � reduces transmitter � release �
Types of Chemical Synaptic Transmission direct, fast indirect, ~slow
Action Potentials can arise from subthreshold depolarizations if they are not spontaneous
Stimulate presynaptic axon
Steps in ionotropic chemical synaptic transmission
Excitation: Conductance increase (resistance decrease): Channels in membrane open Membrane potential goes towards Vrev (Equil. Pot)
Vrev = Eion Results if EPSP were due to only Na + or K +
Isyn= g ACh (V m -V rev ) (Vm-Vrev)= Driving force Depolarizing because of large Na driving force -60 mV
Conductance change due to multiple ions
Inhibition: Conductance increase (resistance decrease): Membrane potential goes towards Vrev (Equil. Pot)
Most common fast transmittters Proof of Neurotransmitter Identity?? Presence Action Release Pharmacological Congruence Synthetic/packaging machinery
Release of Transmitter Snake Neuromuscular Junction Model
EM section of NMJ Freeze-fracture of NMJ
Brain Synapse Few vesicles at each synaptic site
Recommend
More recommend