Interaction-based knowledge evolution Small team (three permanent - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
mOeX mOeX The heterogeneity problem Cultural knowledge evolution Interaction-based knowledge evolution Small team (three permanent researchers); ome ( ) Euzenat J er LIG team common to INRIA and UGA; Worldwide
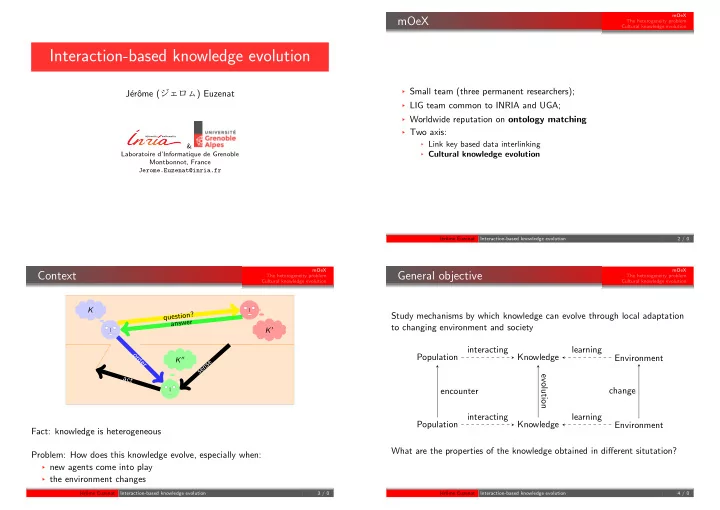
mOeX mOeX The heterogeneity problem Cultural knowledge evolution Interaction-based knowledge evolution § Small team (three permanent researchers); ome ( ジェロ ㇺ ) Euzenat J´ erˆ § LIG team common to INRIA and UGA; § Worldwide reputation on ontology matching § Two axis: § Link key based data interlinking & § Cultural knowledge evolution Laboratoire d’Informatique de Grenoble Montbonnot, France Jerome.Euzenat@inria.fr J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 2 / 0 mOeX mOeX Context General objective The heterogeneity problem The heterogeneity problem Cultural knowledge evolution Cultural knowledge evolution K question? Study mechanisms by which knowledge can evolve through local adaptation answer to changing environment and society K 1 interacting learning o Population Knowledge Environment r d K 2 e e s r n e s a evolution c t encounter change interacting learning Population Knowledge Environment Fact: knowledge is heterogeneous What are the properties of the knowledge obtained in different situtation? Problem: How does this knowledge evolve, especially when: § new agents come into play § the environment changes J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 3 / 0 J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 4 / 0
mOeX mOeX Knowledge interpretation Knowledge interpretation The heterogeneity problem The heterogeneity problem Cultural knowledge evolution Cultural knowledge evolution ě ě polygone planar polygone polygone 多 形 ” ” K K quadrilat` ere triangle triangle quadrangle quadrilat` ere triangle 三 角 形 四 邊 形 losange rectangle rectangle simple complexe losange rectangle 菱 形 矩 形 isocelle ď convexe concave 梯 形 carr´ e carr´ e ď carr´ e K triangle ? carr´ e K triangle ? triangle K carr´ e ) triangle K carr´ e ) J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 5 / 0 J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 5 / 0 mOeX mOeX Approach: Cultural knowledge evolution Relevant questions The heterogeneity problem The heterogeneity problem Cultural knowledge evolution Cultural knowledge evolution Adaptation: § How do agent populations adapt their knowledge representation to their environment and to other populations? § Natural evolution (Darwin): variation-selection-transmission; § Cultural evolution (Cavalli Sforza, Richerson): applied to culture Evolution: (knowhow, society structure, language) § How must this knowledge evolve when the environment changes and § Experimental cultural language evolution (Axelrod, Steels): multi-agent new populations are encountered? simulation § To what extent the environment and society constrain (formal) knowledge representation? ñ Cultural knowledge evolution: applied to knowledge Diversity: § How can agents preserve knowledge diversity and is this diversity beneficial? J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 6 / 0 J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 7 / 0
mOeX mOeX Alignment repair game Alignment repair game The heterogeneity problem The heterogeneity problem Cultural knowledge evolution Cultural knowledge evolution ” ” all all all all K ” K K K large large white black black small white black black small K white K black small K small large K large K white K black small K small large K large white black white black small large small large square triangle square triangle small large small large square triangle square triangle ” ” △ � classOf( � ) ? classOf( △ ) ? black black black black J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 8 / 0 J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 8 / 0 mOeX mOeX Adaptation operators Experimental questions The heterogeneity problem The heterogeneity problem Cultural knowledge evolution Cultural knowledge evolution addjoin ě K black add 1. Does the process converge? ě delete 2. How different adaptation operators compare? K ” ” replace small 3. How do they compare to baselines? white small large black ď r e 4. Can operators improve away from the initial situation? fi n e K refine ě 5. Can this start from scratch? ě K △ J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 9 / 0 J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 10 / 0
mOeX mOeX Convergence and operators Initial success rate and F-measure The heterogeneity problem The heterogeneity problem Cultural knowledge evolution Cultural knowledge evolution F - measure { Success rate 1 1 0 . 8 0 . 8 Success rate 0 . 6 0 . 6 0 . 4 0 . 4 0 . 2 0 . 2 0 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 Games Games delete replace refine add addjoin refadd operator=add; #agents=4; #games=2000; #runs=1 operator=del,repl,add,addjoin,refine,refadd; #agents=4; #games=10000; #runs=10 J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 11 / 0 J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 12 / 0 mOeX mOeX Initial results Further exploration The heterogeneity problem The heterogeneity problem Cultural knowledge evolution Cultural knowledge evolution Success Inc. Sem. Sem. Sem. Operator Size rate degree Precision F-measure Recall Conv. 1. Altering ontologies reference 86 1.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1 2. Learning ontologies and alignments initial 54 0.24 0.34 0.11 0.20 0.89 - 6 0.99 0.0 1.0 0.13 0.07 445 delete 3. Involving several populations 11 0.99 0.01 0.99 0.21 0.12 1478 replace 4. Modifying the environment 33 0.98 0.14 0.80 0.52 0.39 1396 add 5. Maintaining several representations 20 0.99 0.02 0.96 0.37 0.23 1133 refine 6. Using different selective pressure 23 0.99 0.10 0.84 0.43 0.29 1004 addjoin 41 0.99 0.09 0.86 0.62 0.48 1266 7. Playing games with heterogeneous agents refadd Alcomo 28 0.43 0.0 0.21 0.26 0.33 - 8. . . . LogMap 29 0.51 0.0 0.24 0.26 0.29 - operator=del,repl,add,addjoin,refine,refadd; #agents=4; #games=10000; #runs=10 J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 13 / 0 J´ erˆ ome Euzenat Interaction-based knowledge evolution 14 / 0
http://mOeX.inria.fr Jerome . Euzenat @ inria . fr
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.