Indifferentiable Authenticated Encryption Pooya Farshim Manuel - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Indifferentiable Authenticated Encryption Pooya Farshim Manuel Barbosa (Porto) (CNRS & ENS) Indifferentiable Authenticated Encryption Pooya Farshim Manuel Barbosa (Porto) (CNRS & ENS) Hash Functions long & short
Indifferentiable Authenticated Encryption Pooya Farshim Manuel Barbosa (Porto) (CNRS & ENS)
Indifferentiable Authenticated Encryption Pooya Farshim Manuel Barbosa (Porto) (CNRS & ENS)
Hash Functions long & short & SHA arbitrary random-looking
Hash Functions long & short & SHA arbitrary random-looking Provably security not always possible.
Random Oracles long & short & SHA arbitrary random-looking
Random Oracles long & short & Random Function arbitrary random-looking
Random Oracles long & short & Random Oracle arbitrary random-looking
Random Oracles are Practical Provable Security for Many Simple & Efficient Protocols ๏ Public-Key Enc. (OAEP, ECIES) ๏ Signatures (PSS, FDH) ๏ TLS 1.3 ๏ Symmetric schemes Ideal Hash ๏ ….
This Talk
This Talk Encryption
This Talk Ideal Hash Encryption
This Talk Ideal Hash Inherit all strengths Encryption
This Talk Ideal Hash Inherit all strengths Ideal Encryption
This Talk Random Ideal Hash Function Inherit all strengths Ideal Encryption
This Talk Random Ideal Hash Function Inherit all strengths Ideal Encryption What Object?
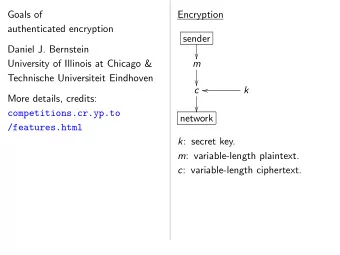
Authenticated Encryption
Authenticated Encryption 1. K ↞ Gen(1 λ ) 2. C ← Enc( K,N,A,M, ! ) | C |=| M | + ! 3. M / ⟘ ← Dec( K,N,A,C, ! )
Authenticated Encryption 1. K ↞ Gen(1 λ ) 2. C ← Enc( K,N,A,M, ! ) | C |=| M | + ! 3. M / ⟘ ← Dec( K,N,A,C, ! ) Security says: under an unknown random key K ๏ Nothing about messages leaks ๏ Cannot forge new valid ciphertexts
Simplifying 1. K ↞ Gen(1 λ ) 2. C ← Enc( K,M ) | C |=| M | + ! 3. M / ⟘ ← Dec( K,C )
Simplifying 1. K ↞ Gen(1 λ ) 2. C ← Enc( K,M ) | C |=| M | + ! 3. M / ⟘ ← Dec( K,C ) A Keyed Injection
Ideal Encryption
Ideal Encryption Hash
Ideal Encryption Hash Function
Ideal Encryption Ideal Hash Hash Function
Ideal Encryption Ideal Hash Hash Random Function
Ideal Encryption Ideal Hash Hash Random Function Cipher
Ideal Encryption Ideal Hash Hash Random Function Cipher Keyed Permutation
Ideal Encryption Ideal Hash Hash Random Function Ideal Cipher Cipher Keyed Permutation
Ideal Encryption Ideal Hash Hash Random Function Random Ideal Cipher Cipher Keyed Permutation
Ideal Encryption Ideal Hash Hash Random Function Random Ideal Cipher Cipher Keyed Permutation Encryption
Ideal Encryption Ideal Hash Hash Random Function Random Ideal Cipher Cipher Keyed Permutation Encryption Keyed Injection
Ideal Encryption Ideal Hash Hash Random Function Random Ideal Cipher Cipher Keyed Permutation Ideal Encryption Encryption Keyed Injection
Ideal Encryption Ideal Hash Hash Random Function Random Ideal Cipher Cipher Keyed Permutation Ideal Encryption Encryption Random Keyed Injection
Ideal Encryption Ideal Hash Hash Random Function Random Ideal Cipher Cipher Keyed Permutation Ideal Encryption Encryption Random Keyed Injection New Ideal Model
Encryption Random Ideal Hash Function Inherit all strengths Ideal Encryption What Object?
Encryption Random Ideal Hash Function Inherit all strengths Random Ideal Encryption Keyed Injection
Encryption Random Ideal Hash Function Inherit all strengths Random Ideal Encryption Keyed Injection
Encryption Random Ideal Hash Function Inherit Indifferentiability all strengths Random Ideal Encryption Keyed Injection
Indifferentiability C RO is “as good as” iEnc:
Indifferentiability C RO is “as good as” iEnc: ≈ iEnc C RO
Indifferentiability C RO is “as good as” iEnc: , RO ≈ iEnc C RO
Indifferentiability C RO is “as good as” iEnc: , RO ≈ iEnc , RO C RO
Indifferentiability C RO is “as good as” iEnc: , RO ≈ iEnc , S iEnc C RO
Indifferentiability C RO is “as good as” iEnc: , RO ≈ iEnc , S iEnc C RO C RO iEnc S D
Indifferentiability C RO is “as good as” iEnc: , RO ≈ iEnc , S iEnc C RO C RO iEnc S D Unified Attack Surface
Indifferentiability C RO is “as good as” iEnc: , RO ≈ iEnc , S iEnc C RO C RO iEnc S Keys can be under adversarial control D Unified Attack Surface
Why Indifferentiability? Theorem [MRH04]: If C RO is indifferentiable from iEnc, then it is secure in many adversarial environments in the RO model.
Why Indifferentiability? Theorem [MRH04]: If C RO is indifferentiable from iEnc, then it is secure in many adversarial environments in the RO model. AE, MRAE, & RAE
Why Indifferentiability? Theorem [MRH04]: If C RO is indifferentiable from iEnc, then it is secure in many adversarial environments in the RO model. AE, MRAE, & RAE KDM Security RKA Security Leakage Resilience Committing Encryption Deduplication
Why Indifferentiability? Theorem [MRH04]: If C RO is indifferentiable from iEnc, then it is secure in many adversarial environments in the RO model. AE, MRAE, & RAE KDM Security RKA Security Leakage Resilience Committing Encryption Deduplication Combined Models Unforeseen Models
Why Indifferentiability? Theorem [MRH04]: If C RO is indifferentiable from iEnc, then it is secure in many adversarial environments in the RO model. AE, MRAE, & RAE KDM Security RKA Security Leakage Resilience Committing Encryption Deduplication Combined Models Unforeseen Models Single stage
So… Are there any indifferentiable encryption schemes out there?
Generic Composition [NRS14] N M A N M A N M A N M A F L F L F L F L F L F L F L IV IV IV IV E K E K E K E K scheme scheme scheme scheme A1 A2 A3 A4 C T C T C T C T N M A N M A N M A N M A F L F L F L F L F L F L F L F L T T IV IV IV IV E K E K E K E K scheme scheme scheme scheme A5 A6 A7 A8 C T C T C C
Generic Composition [NRS14] N M A N M A N M A N M A F L F L F L F L F L F L F L IV IV IV IV E K E K E K E K scheme scheme scheme scheme A1 A2 A3 A4 C T C T C T C T N M A N M A N M A N M A F L F L F L F L F L F L F L F L T T IV IV IV IV E K E K E K E K scheme scheme scheme scheme A5 A6 A7 A8 C T C T C C Enc-then-Mac
Generic Composition [NRS14] N M A N M A N M A N M A F L F L F L F L F L F L F L IV IV IV IV E K E K E K E K scheme scheme scheme scheme A1 A2 A3 A4 C T C T C T C T N M A N M A N M A N M A F L F L F L F L F L F L F L F L T T IV IV IV IV E K E K E K E K scheme scheme scheme scheme A5 A6 A7 A8 C T C T C C Enc-then-Mac Mac-then-Enc
Generic Composition [NRS14] SIV N M A N M A N M A N M A F L F L F L F L F L F L F L IV IV IV IV E K E K E K E K scheme scheme scheme scheme A1 A2 A3 A4 C T C T C T C T N M A N M A N M A N M A F L F L F L F L F L F L F L F L T T IV IV IV IV E K E K E K E K scheme scheme scheme scheme A5 A6 A7 A8 C T C T C C Enc-then-Mac Mac-then-Enc
Attack on Enc-then-Mac N M A F L F L IV E K scheme A5 C T
Attack on Enc-then-Mac Construction : Changing K does not affect T N M A iEnc : Random Injection: changing K will change T F L F L IV E K scheme A5 C T
Attack on Enc-then-Mac Construction : Changing K does not affect T N M A iEnc : Random Injection: changing K will change T F L F L IV Interpretation : Related-Key Attacks E K scheme A5 C T
General Attacks Algo. AE ( K, N, A, M, τ ) Algo. AD ( K, N, A, C, τ ) ( est 0 , est 1 ) ← I e ( K, N, A, M, τ ) ( dst 0 , dst 1 ) ← I d ( K, N, A, C, τ ) ( K 0 , N 0 , M 0 , τ 0 ) ← E H ( K 0 , N 0 , C 0 , τ 0 ) ← D H 0 ( est 0 ) 0 ( dst 0 ) C 0 ← E ( K 0 , N 0 , ε , M 0 , τ 0 ) M 0 ← D ( K 0 , N 0 , ε , C 0 , τ 0 ) C ← E H M ← D H 1 ( C 0 , est 1 ) 1 ( M 0 , dst 1 ) return C return M A template for generic composition. Two types of attacks based on how information flows.
Attacks: Specifics Schemes OCB [Rog et al.] Deoxys [JNP15] ’ ’ M � M 1 M 1 M m M m M � M � M � X 1, 1 1, m ∆ 0, 1 X � X � 0, 0 0, 0 0, 4 0, 5 -1, 1 X 1 X m S S S S -1, 4 -1, 5 2, 1 2, m ... S Y 1 Y m Y � Y � -1, 2 0, 0 0, 0 0, 4 0, 5 1, 1 1, m 0, 2 ∆ Y ’ ’ C 1 C 1 C m C m C � C � C � C � L R ∆ ⊕ 0 Z 1 Z l -1 Z l 0, 6 ∆ ⊕ 1 0, 6 i +2, l − 1 i +2, 1 i +2, l ∆ ⊕ 2 0, 6 ∆ ⊕ 3 ... ∆ i 0, 6 ∆ ⊕ 4 0, 6 ∆ ⊕ 5 0, 6 ∆ ⊕ 6 Z 1 Z l -1 Z l 10* 0, 6 ∆ ⊕ 7 i +2, l − 1 i +2, 1 i +2, 0 0, 6 ... ∆ i * * L R AEZ [HKR17]
Indifferntius
So… Any indifferentiable encryption schemes?
Feistel
Feistel L RO 1 RO 2 RO 3 R
Feistel L RO 1 RO 2 RO 3 R 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Permutation
Feistel L RO 1 RO 2 RO 3 R 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 9 10 10 11 11 12 12 13 13 14 14 Permutation
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.