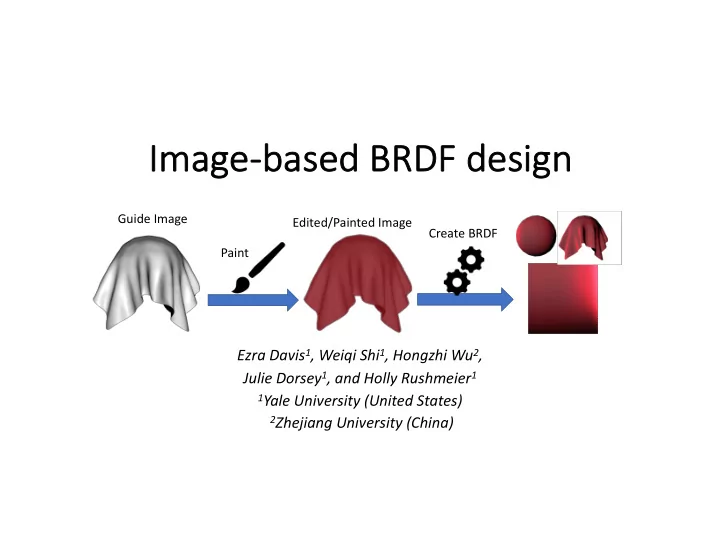

Im Imag age-ba base sed BR d BRDF de F desi sign Guide Image Edited/Painted Image Create BRDF Paint Ezra Davis 1 , Weiqi Shi 1 , Hongzhi Wu 2 , Julie Dorsey 1 , and Holly Rushmeier 1 1 Yale University (United States) 2 Zhejiang University (China)
Problem Definition • Artists/Designers need to specify materials for rendering digital scenes or creating new physical products. We consider the subproblem of specifying bidirectional reflectance distribution functions (BRDFs). Virtual – Games/Film [1] Physical – Product Design [2]
Problem Definition: Conventional methods • Conventional methods often do not provide much control for the artist • Can be limited by being defined by fixed analytic functions to control features such as highlights
Problem Definition: Conventional methods Things you can’t model with simple approach: [3] [4]
Problem Definition: Measured BRDFs • Richer varieties of materials can be captured from physical materials • Takes time to measure • Requires physical samples • Hard to edit by artists Measured materials in the MERL database [5]
Problem Definition: Our Approach Guide Image Edited/Painted Image Create BRDF Paint
Background: Current Design Systems
Background: Current Design Systems Can be powerful and general, but extraordinarily complex and indirect! [6] [7]
Previous Work: Gaussian Material Synthesis • Uses Disney’s “Principled” shader • Navigate parameter variations by example • Gaussian Material Synthesis Zsolnai-Feher et al. ACM TOG 2018
Previous Work: BRDF-Shop Paint highlights onto BRDF • BRDF-Shop: creating physically correct • bidirectional reflectance distribution functions, Colbert et al. Computer Graphics and Applications, 2006
Previous Work: The Lit Sphere • Use a painted sphere to shade an object by its normals • The Lit Sphere: A Model for Capturing NPR Shading from Art, Sloan et al., Graphics Interface, 2001
Our image-based BRDF design system Dense BRDF Guide Sparse BRDF Painted Calculate Calculate Paint
Our image-based BRDF design system
Our System: Select object Allows design in context for the user • Allows associating normal/light/view • direction for calculations (Or Custom)
Our System: Set light position • Light direction • Allows associating normal/light/view direction for calculations
Our System: Download guide image Provide an image that can be • imported to any image editor
Our System: Paint image Any type of editing allowed: Paint on image • Paint on an image layer • Adjust contrast • Set colors in different • ranges.
Our System: Upload painted image
BRDF format Incident Theta Incident Phi Reflected Theta Normal Reflected Phi Theta Phi
Sparse BRDF Reconstruction Reconstruct Create Sparse from same angle BRDF
Sparse BRDF Reconstruction Reconstruct from Create Sparse different angle BRDF
Dense BRDF reconstruction Sparse BRDF Dense BRDF PCA Reconstruction
Dense BRDF Reconstruction • Our method based on Nielsen et al. paper for reconstructing measured BRDFs from few samples On Optimal, Minimal BRDF Sampling for Reflectance Acquisition. Nielsen et al., Siggraph Asia 2015
User Experiences • All of the people that used the interface would be willing to use this method (though one artist preferred traditional parametric BRDF creation) • Some users like resulting image more than their painting
Limitations No textures Limited by BRDF tables in database (Spatially Varying BRDFs)
Future work • Use larger database of measured BRDFs • Alternate reconstruction methods • Use natural images instead of just painted ones
Future work • How to present lighting direction? • How is high dynamic range input (e.g. specular highlights) obtained from a low dynamic range image? • What other refinements and feedback should we offer? (e.g. “blurring” the BRDF)
Image-based BRDF design
Questions and Comments
Image sources • [1] https://all3dp.com/1/best-20-3d-animation-software/ • [2] Photo-realistic Rendering of Metallic Car Paint from Image-Based Measurements. Rump et al., Eurographics 2008 • [3] https://jsouguan.en.made-in-china.com/product/fjdmsYwSkTcv/China- Magic-Color-Interference-Powder-Violet-Iridescent-Pearl-Pigment-for- Paint.html • [4] https://www.trurofabrics.com/shot-silk-taffeta-fabric-purple- orange.html • [5] A data-driven reflectance model. Matusik et al., Siggraph 2003 • [6] https://lesterbanks.com/2013/12/cinema-4d-creating-node-based- materials-and-shaders-using-cmnodes/ • [7] http://www.design-corps.co.uk/tag/slate-material-editor/
BRDF format Incident Theta Incident Phi Reflected Theta Normal Reflected Phi Theta Phi
Recommend
More recommend