I (1) 2 r B has a curly field pa=ern, it is into the - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
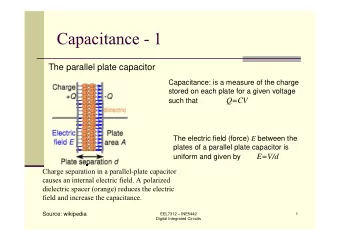
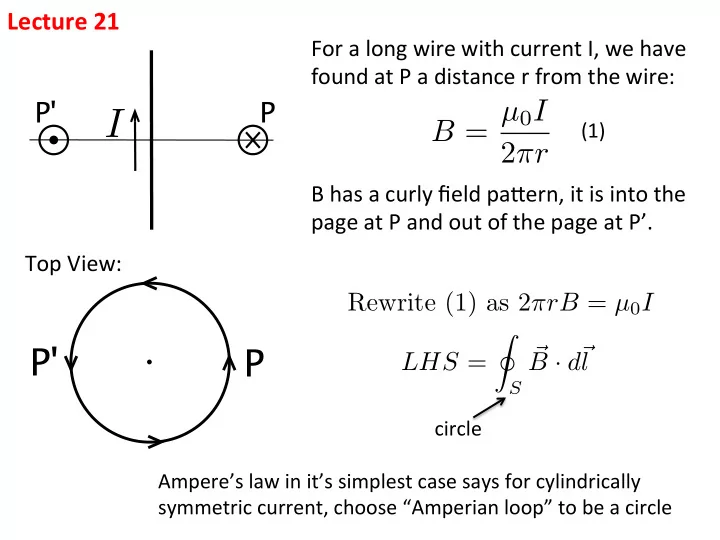
Lecture 21 For a long wire with current I, we have found at P a distance r from the wire: P' P B = 0 I I (1) 2 r B has a curly field
Lecture ¡21 ¡ For ¡a ¡long ¡wire ¡with ¡current ¡I, ¡we ¡have ¡ found ¡at ¡P ¡a ¡distance ¡r ¡from ¡the ¡wire: ¡ P' P B = µ 0 I I (1) ¡ 2 π r B ¡has ¡a ¡curly ¡field ¡pa=ern, ¡it ¡is ¡into ¡the ¡ page ¡at ¡P ¡and ¡out ¡of ¡the ¡page ¡at ¡P’. ¡ ¡ Top ¡View: ¡ Rewrite (1) as 2 π rB = µ 0 I I P' P B · d ~ ~ LHS = l S circle ¡ Ampere’s ¡law ¡in ¡it’s ¡simplest ¡case ¡says ¡for ¡cylindrically ¡ symmetric ¡current, ¡choose ¡“Amperian ¡loop” ¡to ¡be ¡a ¡circle ¡
Ampere’s ¡law ¡in ¡it’s ¡simplest ¡case ¡says ¡for ¡cylindrically ¡ symmetric ¡current, ¡choose ¡“Amperian ¡loop” ¡to ¡be ¡a ¡circle ¡ I Bdl = µ 0 I S S Denote: ¡ I B ? at P. Let S be the circular loop, LHS = B ? dl = 2 π rB ? RHS = µ 0 I S = µ 0 I I S = current enclosed by S
Long, ¡thick ¡wire: ¡Assume ¡current ¡density ¡is ¡uniform. ¡ NotaMons: ¡ for r < R , where B = B ? B ?? B ? r for r > R , where B = B ?? R Define: J = ∆ I I ∆ A = π R 2 J π r 2 � � r < R : 2 π rB ? = µ 0 B ∴ B ? ∝ r µ 0 I 2 π R r > R : 2 π rB ?? = µ 0 I ∴ B ?? ∝ 1 r R r
Coaxial ¡Cable ¡(example ¡problem): ¡ Let I in = I out = I 0 Find: B ? at D , where r = r 3 . Hint: Ampere’s Law I LHS = Bdl = 2 π r 3 B L RHS = µ 0 I L = µ 0 JA ring b → r 3 I 0 " A ring # J = b → r 3 ∴ RHS = µ 0 I A ring A ring b → a b → a A ring r 1 → r 2 = π r 2 2 − π r 2 1
Discussion ¡on ¡example ¡problem ¡ Given: Total current I 0 flows through a long conductor with a hole. ◆ 2 ✓ R = A 1 A hole = π 2 4 A cyl = π R 2 = A 1 A 0 = Area of conduction medium = A cyl − A hole = 3 A 1 4
Assume I 0 flows out of the page, current density is constant. J = I 0 A 0 I hole = J A 1 Magnitude: I cyl = JA, 4 I cyl = I 0 A 1 = 4 (out) ¡ 3 I 0 A 0 I hole = I 0 A 1 4 = 1 (into) ¡ 3 I 0 A 0 Find: ¡B ¡at ¡P ¡ B = B cyl − Bhole µ 0 I hole B cyl = µ 0 I cyl B hole = x − R � � 2 π 2 π x 2
Solenoid ¡Discussion ¡ LHS = 0 + 0 + 0 + B ? d RHS = µ 0 I S = µ 0 ∆ dI N LHS = RHS = B ? d = µ 0 L dI N ∴ B ? = µ 0 L I
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.