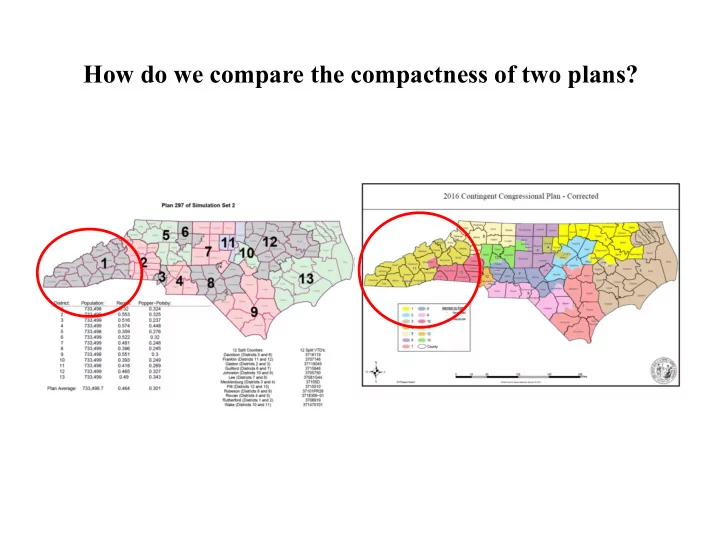

How do we compare the compactness of two plans?
Measuring District Compactness: Reock Score
Measuring District Compactness: Polsby-Popper Score
State Courts: 1) Obligated to follow federal law 2) Obligated to enforce state laws
Federal Courts: 1) Obligated to follow federal law 2) Not empowered to enforce state laws
Equal Protection Clause (Article I, Section 19): “No person shall be denied the equal protection of the laws.” “these clauses provide significant constraints against governmental conduct that disfavors certain groups of voters or creates barriers to the free ascertainment and expression of the will of the People…” (Common Cause v. Lewis 2019)
Free Speech Clause (Article I, Section 14): “Freedom of speech and of the press are two of the great bulwarks of liberty and therefore shall never be restrained…” “[T]he North Carolina Constitution affords a direct cause of action for damages against government officers in their official capacity for speech violations, even though federal law does not” (Common Cause v. Lewis 2019)
Free Election Clause (Article I, Section 10): “All elections shall be free.” Common Cause v. Lewis (2019): “Elections are not free when partisan actors have tainted future elections by specifically and systematically designing the contours of the election districts for partisan purposes and a desire to preserve power.”
Partisan Intent: Thomas Hofeller’s Draft Plans
Partisan Intent: Thomas Hofeller’s Draft Plans
Thousands of Non-Partisan Computer-Simulated Maps:
Computer Simulation Algorithm:
Common Cause v. Lewis (2019) July 15-26, 2019: Trial in Raleigh, North Carolina September 3, 2019: Court strikes down House and Senate District Maps; Orders Legislature to draw new non-partisan maps September 10, 2019: Legislature draws new maps by randomly selecting from Chen computer-simulated districting maps
Legislature Uses Lottery Machine to Randomly Select Computer-Simulated Maps
Legislature’s New Remedial House Map (Sept. 2019)
Why did the NC General Assembly use a lottery machine?
League of Women Voters of Michigan v. Ruth Johnson (2018)
League of Women Voters of Michigan v. Ruth Johnson (2018)
League of Women Voters of Michigan v. Ruth Johnson (2018)
League of Women Voters of Michigan v. Ruth Johnson (2018)
Redistricting Reform in Michigan: - Michigan referendum process: Initiated Constitutional Amendment - Voters Not Politicians writes Proposal 2 Gather 315,654 signatures within 180 days, at least 120 days before Nov 2018 election (10% of electorate in Gubernatorial election) Voters approved Proposal 2 by 61% - 39% in Nov 2018
Michigan Independent Citizens Redistricting Commission: - 13 Michigan voters (4 Republicans, 4 Democrats, 5 independents) - Commission draws Michigan’s Congressional, House, and Senate maps - Commission must follow constitutional criteria in drawing districts
Michigan Independent Citizens Redistricting Commission:
Example of how California’s Redistricting Commission Solicited Public Feedback on Communities of Interest (2011):
Using Crowdsourced Maps to Describe Communities of Interest:
Recommend
More recommend