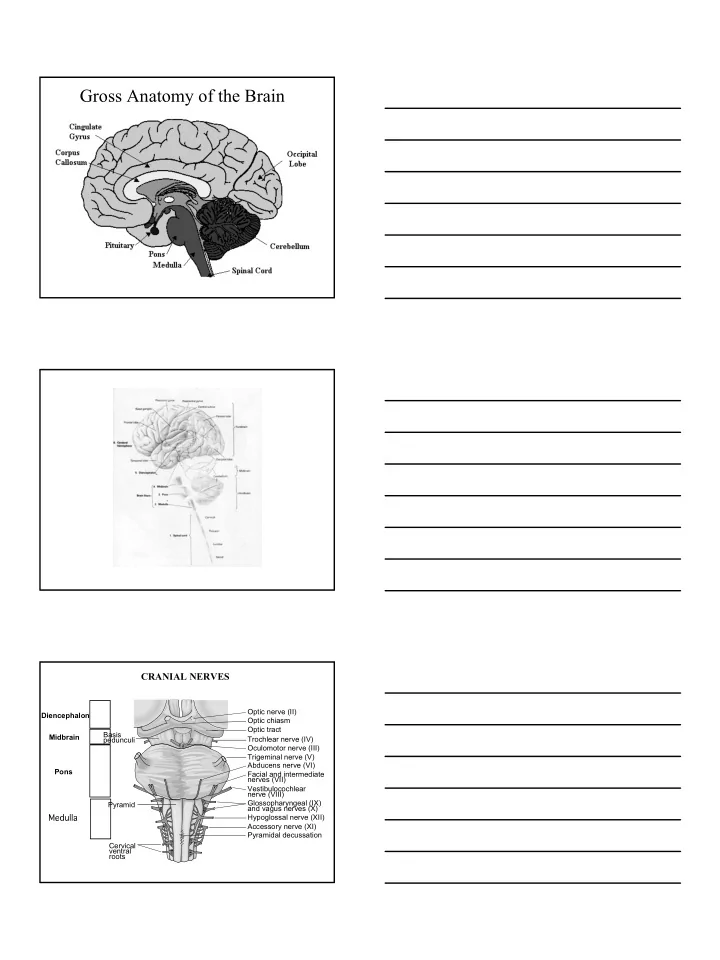

Gross Anatomy of the Brain CRANIAL NERVES Optic nerve (II) Diencephalon Optic chiasm Optic tract Basis Midbrain pedunculi Trochlear nerve (IV) Oculomotor nerve (III) Trigeminal nerve (V) Abducens nerve (VI) Pons Facial and intermediate nerves (VII) Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) Glossopharyngeal (IX) Pyramid and vagus nerves (X) Hypoglossal nerve (XII) Accessory nerve (XI) Pyramidal decussation Cervical ventral roots 1
CRANIAL NERVES Diencephalon Lateral geniculate body Optic Inferior colliculus nerve (II) Trochlear nerve (IV) Midbrain Oculomotor nerve (III) Basis pedunculi Cerebellar peduncles: Trigeminal Superior nerve (V) Middle Pons Abducens nerve (VI) Inferior Facial and intermediate nerves (VII) Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) Pyramid Olive Glossopharyngeal (IX) Medulla and vagus nerves (X) Hypoglossal nerve (XII) Spinal accessory Cervical nerve (XI) ventral roots CRANIAL NERVE NUCLEI Mesencephalic trigeminal Motor Afferent nucleus (N. V) Edinger-Westphal nucleus (N. III) Special visceral General General and special visceral Oculomotor somatic General somatic nucleus (N. III) General visceral Special somatic Trochlear nucleus (N. IV) III III Midbrain V IV Trigeminal motor nucleus (N. V) Principal sensory trigeminal nucleus V Abducens nucleus (N. VI) (N. V) V Facial motor VI VIII Pons nucleus (N. VII) Vestibular nuclei V, VII, VII IX, X VIII (N. VIII) Superior (N. VII) Inferior (N. IX) IX VII IX Salivatory Cochlear nucleus XII nucleus Medulla (N. VIII) X Nucleus ambiguus (N. IX, X) IX, X Hypoglossal nucleus (N. XII) Solitary nucleus (N. VII, IX, X) Dorsal motor nucleus of vagus (N. X) Spinal cord XI Spinal trigeminal Accessory nucleus (N. XI) nucleus (V, VII, IX, X) CRANIAL NERVE NUCLEI Afferent : Somatic Visceral Special somatic Visceral Somatic afferent (VIII) General somatic afferent (V, VII, IX, X) General and special visceral afferent (VII, IX, X) Sulcus limitans General visceral motor (III, VII, IX, X) Special visceral motor (V, VII, IX, X, XI) General somatic motor (III, IV, VI, XII) 2
CRANIAL NERVE NUCLEI Section through superior colliculus Mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus (V) Edinger- Westphal nucleus (III) Oculomotor nucleus (III) Section through inferior colliculus Mesencephalic Trochlear trigeminal nucleus (IV) nucleus (V) CRANIAL NERVE NUCLEI Section through middle cerebellar peduncle Mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus (V) Vestibular nuclei (VIII) Principal sensory trigeminal nucleus (V) Motor trigeminal nucleus (V) Section through cochlear nuclei and the trapezoid body Abducens nucleus (VI) Cochlear nuclei (VIII) Vestibular nuclei (VIII) Spinal trigeminal nucleus (V) Facial motor nucleus (VII) BRAIN STEM RETICULAR FORMATION MLF ICP Parvocellular Magnocellular ML PYR 3
BRAIN STEM DEVELOPMENT BRAIN STEM DEVELOPMENT Sulcus limitans A B Alar plate Basal plate C Special somatic afferent General and special General visceral afferent visceral motor General somatic Special afferent visceral motor General somatic motor D Hypoglossal Vestibular nucleus (VIII) nucleus (XII) Solitary nucleus (VII, IX, X) Dorsal motor Spinal nucleus of trigeminal vagus (X) nucleus (V, VII, IX, X) Nucleus ambiguus (X) MOVEMENT CONTROL Basal Motor ganglia areas Non- motor areas Cerebellum Brain stem motor nuclei Spinal interneurons Motor neurons Movement 4
MOVEMENT CONTROL A Ventral corticospinal tract B Lateral corticospinal tract 6 6 4 4 3,1,2 Internal capsule Internal capsule Reticular and vestibular Red nucleus nuclei (magnocellular part) Rubrospinal Medial tract brain stem pathways Pyramidal decussation Lateral corticospinal Ventral corticospinal tract tract Ascending dorsal column – medial lemniscal pathway to primary sensory cortex Somatic sensory cortex Toe (postcentral gyrus) Leg Trunk SENSORY Forearm and hand area Cerebral cortex CONTROL Face Lateral sulcus Internal capsule Thalamus Ventral posterior lateral nucleus Third ventricle Midbrain Medial lemniscus Pons Medial lemniscus Medulla Gracile nucleus Cuneate nucleus Spinal trigeminal Medulla nucleus Sensory decussation Gracile fascicle Dorsal root Cuneate fascicle ganglion Spinal cord AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Sympathetic Projections of Projections of Parasympathetic division sympathetic parasympathetic division division division Ciliary ganglion Eye III Midbrain Lacrimal and Pterygopalatine and submaxillary ganglion Pons salivary glands VII Medulla Otic ganglion IX Superior cervical X ganglion Bronchi Esophagus Cranial Middle cervical nerves and lungs Cervical ganglion Inferior cervical ganglion Piloerector Heart muscle Artery Celiac ganglion Thoracic Liver Sweat Stomach glands Pancreas Adrenal medulla Small intestine Lumbar Large intestine, rectum Sacral Pelvic nerve Bladder leading to pelvic ganglia Sypathetic Superior Inferior chain mesenteric mesenteric Reproductive ganglion ganglion organs 5
NORADRENERGIC SYSTEM A6 / locus ceruleus A A7 A5 B CTX T HF C PT Cerebellum CC Th CTX S OB F EC DT AO RF Spinal cord CT LC BS A H DOPAMINERGIC SYSTEM A Caudate Corpus and putamen callosum Cerebellum Anterior Lateral Hippocampus cingulate septum cortex Prefrontal cortex Habenula A10 Striatum Locus ceruleus A8 Lateral parabrachial nucleus A9 Pyriform Central Entorhinal Nucleus cortex nucleus cortex accumbens (amygdala) B Olfactory bulb Thalamus A16 A13 A11 A15 Spinal cord Retina A14 A12 Pituitary A17 Median eminence SEROTONERGIC SYSTEM Cerebellum Cerebral cortex Cingulate bundle HF B7 Th CD B8 B6 B2 B4 B3 B9 B5 B1 H External Medial forebrain capsule bundle Serotonergic innervation 6
CHOLINERGIC SYSTEM Caudate Fornix and putamen Hi Ha Th OB LDT DBv BM VTA IPN PPT LH A RF MaPo Cholinergic system HISTAMINERGIC SYSTEM A Tuberomammillary nucleus B Cerebral cortex Cingulate cortex Thalamus Septum Amygdala Hypothalamus Tuberomammillary Histaminergic innervation nucleus DOPAMINERGIC SYNAPSE Presynaptic dopaminergic neuron IP 3 Ca 2+ D 3 D 3 DAG PKC PIP 2 AC Cortical or – + mesolimbic target (D 2 , D 3 , D 4 ) (D 1 , D 5 ) neuron G i G s ATP cAMP 7
DOPAMINERGIC SYNAPSE 1a Antipsychotic Tyrosine Increase of synthesis Can produce ( L -DOPA) Tyrosine psychotic symptoms 1b Inhibition of synthesis ( α -methyltyrosine) DOPA 2 Interference with vesicular storage (reserpine, Dopamine 6 tetrabenazine) Inhibition of breakdown (pargyline) 3 Stimulation of release of DA at nerve terminal (amphetamine, tyramide) MAO Autoreceptor D 3 Vesicular monoamine transporter Dopamine 4 transporter 5 Blocking of DA receptors Inhibition of reuptake and autoreceptors (cocaine, amphetamine, (antipsychotics: benztropine) perphenazine, haloperidol) COMT D 2 D 2 MESOCORTICOLIMBIC DOPAMINERGIC SYSTEM A Midsagittal section B Coronal section Mesocortical system: Neocortex ? involved in the Nucleus negative symptoms accumbens of schizophrenia (ventral striatum) Limbic forebrain Frontal cortex Hippocampal formation Mesolimbic and Ventral mesocortical tegmental system Mesolimbic Midbrain area system: ? involved in the positive symptoms Hippocampal Ventral of schizophrenia formation tegmental area SEROTONERGIC SYSTEM A Pathways B Targets Neocortex Caudate nucleus To and putamen Thalamus Cingulum hippocampus Striatum Cingulate gyrus Neocortex Globus pallidus Nucleus accumbens Thalamus (ventral striatum) Limbic forebrain Hypothalamus Hypothalamus Olfactory and entorhinal Medial cortices forebrain Deep Midbrain bundle Amygdala cerebellar nuclei Hippocampus Pons Cerebellar Rostral cortex raphe nuclei Caudal To spinal raphe cord nuclei Raphe nuclei 8
Depressant Antidepressant A Serotonergic neurons 1 Inhibition of synthesis Tryptophan (p-chlorophenylalanine, p-propyldopacetamide) 5-OH-Tryptophan 5-HIAA 5-HT 2 Interference with vesicular storage 5-HT (reserpine, 5 tetrabenazine) 5-HT Inhibition of enzyme that oxidizes 5-HT MAO inhibitors (iproniazid, clorgyline) 3a Stimulation of MAO autoreceptor agonist 8-Hydroxy-diproplamino- tetraline (8-OH-DPAT) 4 Inhibition of reuptake Tricyclics and (imipramine, 3b selective serotonin Stimulation of 5-HT 5-HT amitryptyline, fluoxetine, reuptake inhibitors sertraline) receptors as partial agonist (lysergic acid diethylamide) 5-HT receptor B Noradrenergic neurons Tyrosine 1a hydroxylase Inhibition of synthesis Deaminated ( α -methyltyrosine) products 1b DOPA Inhibition of synthesis (FLA 63) Dopamine 2 Interference with vesicular storage NE 7 (reserpine, Inhibition of enzyme tetrabenazine) that oxidizes NE MAO inhibitors (pargyline) NE 3 Stimulation of release of MAO NE at nerve terminals (amphetamine) 6 Inhibition of reuptake (desipramine) Tricyclics Receptor NM 4a 5 Stimulation of receptors Inhibition of enzyme (clonidine) that inactivates NE Inactivation inhibitor COMT (tropolone) 4b Blocking of receptors (phenoxybenzamine and phentolamine) ASCENDING AROUSAL SYSTEM 9
Recommend
More recommend