
Give Me the Child Until He is Seven … The Early Roots of Human Behavior Donald A. Barr, M.D., Ph.D. Professor (Teaching) of Pediatrics, and of Education (by Courtesy) 1 2 3 4
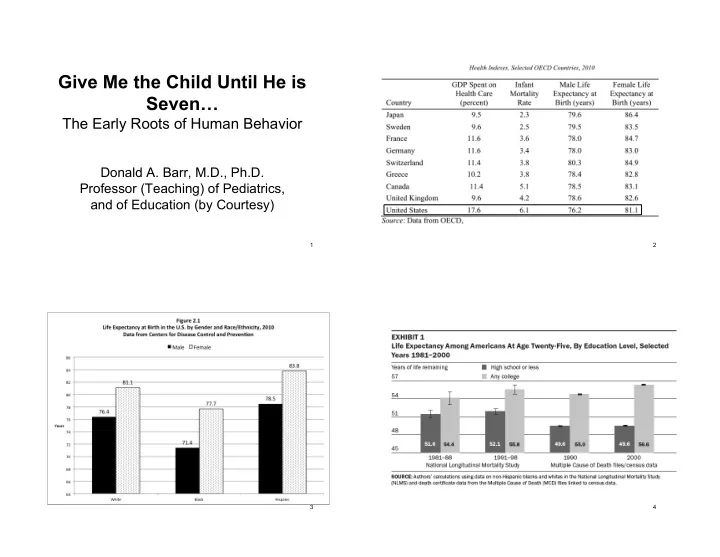
Age-adjusted percentages of selected circulatory diseases, by highest level of educational attainment - U.S., 2009 Less than a high school diploma High school diploma or GED\12 Some college Bachelor's degree or higher 35 Percentage of adults reporting disease 29 30 27.4 26.1 25 20.3 20 15 13.3 12.3 11.7 10.6 9.4 8.7 10 6.6 5.3 3.8 5 2.8 2.8 1.9 0 All types Coronary Artery Hypertension Stroke Disease 5 6 Type of disease Compared to those with lower levels of education, adults with higher levels of education: • Have higher incomes • Have lower rates of high blood pressure • Are less likely to have a stroke • Are less likely to have diabetes or kidney disease And they live longer! 7 8
CONCLUSIONS “A substantial portion of the excess mortality among current smokers between 2000 and 2011 was due to associations with diseases that have not been formally established as caused by smoking.” 9 10 Educational attainment, health risk behaviors, and preventable deaths in the U.S. Health behaviors Reduced life such as Educational expectancy and smoking, diet, Attainment premature death and lack of exercise 11 12
Or is it this way? Time perspective • A psychological construct that describes Health- how one’s perception or weighing of the related past, present, and future influences behaviors current decision making • Thought to represent a subconscious Missing Well-being cognitive response that one uses when third as an adult making decisions about short-term and factor? long-term actions and goals Educational Attainment 13 14 “If you play until I The Marshmallow Study come back, you Done at Bing Pre-School, Stanford can have two of Mischel et al, 1988 these.” 4-year old children – invited into a room of “If you don’t want to toys to play alone wait, ring this bell, and I’ll come right “You can play back. Then you’ll get with these toys, one of these.” and later I’ll give How long will a child you a reward” wait? 15 16
As adolescents, the children who didn’t ring Conclusions : the bell (i.e., they were able to wait 15 minutes for the larger reward) were: • As 4-year olds, these children already had differing time perspectives that offered • More academically and socially them differing levels of rewards. competent • More verbally fluent • More rational, attentive, able to plan • Their time perspective as 4-year olds was ahead associated with their personality characteristics and level of academic • More able to deal with frustration and success as adolescents. stress 17 18 Time perspective – 3 sub-scales Time perspective – 3 sub-scales (From Zimbardo & Boyd, 1999) 1. “Future” 2. “Present – fatalistic” – ‘‘Before making a decision, I weigh the – ‘‘Since whatever will be, it does not really costs against the benefits’’ matter what I do’’ – ‘‘It upsets me to be late for appointments’’ – ‘‘Fate determines much in my life’’ – ‘‘I believe that a person’s day should be – ‘‘You can’t really plan for the future planned ahead each morning.’’ because things change so much.’’ 3. “Present – hedonistic” – ‘‘I take risks to put excitement in my life’’ – ‘‘I try to live my life as fully as possible, one day at a time.’’ 19 20
In college students, how are these scales “If you wait until I associated with personal characteristics and come back, you academic performance? can have two of Zimbardo and Boyd study of several hundred college these.” students in California Academic Future “If you don’t want to Performance wait, ring the bell and I’ll come right back. Then you’ll get one of these.” Present - Aggressive/ Impulsive Fatalistic 21 22 Is Time Perspective Associated With • Eager Socio-Economic Status? • Energetic From Guthrie et al – 2009 (solid line = direct correlation; dashed line = inverse correlation) • Fun-loving • Intelligent Future • Sensible Education • Willing Present - Fatalistic What about the role of personality traits in - study of more than 500 adults recruited from hair salons and barber shops in a suburb of Washington, DC. affecting patterns of behavior? 23 24
Allport, GW, Odbert HS. • Cheerful Psychological Monographs 1936 47(1) • Confident “The list that follows • Hard-working contains all the words • Helpful descriptive of personality or • Likeable personal behavior … • Reliable included in Webster’s New Internat ional Dictionary … Our list contains 17,953 words, or 4 ½ % of the total English vocabulary.” 25 26 Moving to fewer trait clusters in the Summary of personality traits as digital age assessed using the Big Five “These five dimensions represent personality at the broadest level of abstraction, and each dimension summarizes a large number of distinct, The “Big Five” more specific personality characteristics.” I. Extraversion - Oliver John and Sanjay Srivastava, 1999 II. Agreeableness III. Conscientiousness “When factored jointly with personality IV. Emotional stability variables, measures of cognitive ability vs. Neuroticism typically form a distinct sixth factor.” V. Openness - Robert McRae and Oliver John, 1992 27 28
Sarah E. Hampson, Lewis R. Goldberg, et al. Childhood conscientiousness and longevity: Health Psychology , 2006; 25(1) Health behaviors and cause of death Forty Years On: Teachers’ Assessments of Children’s Friedman, H. S., et al. 1995. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 68(4) Personality Traits Predict Self-Reported Health • In the 1920s, Louis Terman began following Behaviors and Outcomes at Midlife more than 1,500 children in California schools • data set gathered between 1959 and 1967 on • As one of their measures, they assessed >2,500 elementary school children in Hawaii children’s conscientiousness • contacted 963 of the individuals in the original • Followed subjects into adulthood study, now 40-50 years old – Many the subjects had died • Children rated higher on conscientiousness • Strong association between – less likely to be smokers as adults conscientiousness as a child and subsequent length of life – more likely to rate their overall health status – Lower rates of smoking explained part of this as better difference 29 30 Adolescence The hippocampus Health- has two main related Childhood functions: behaviors Time Perspective Well-being + 1) Working memory: “combines the temporary as an adult Personality storage and manipulation of information in Traits the service of cognition.” Educational 2) Executive control: “the capacity to focus Attainment attention, to divide attention between two or more tasks, and to control access to long- What is the role of cognitive development in affecting term memory” patterns of behavior and educational attainment? 31 32
Emotionally significant experiences tend to be well remembered, and the amygdala has a pivotal role in this process. But the efficient encoding of emotional memories can become maladaptive — severe stress often turns them into a source of chronic anxiety. 33 34 Stress hormones and stress-activated neurotransmitters enhance the The amygdala, through consolidation of memory for emotionally its projections to other arousing experiences through actions brain regions, also has involving the amygdala. an important modulatory role in regulating stress However, stress and emotional hormone effects on other arousal not only induce strong memory functions, such memories of new information: they as retrieval and working can also impair our remembering memory. through amygdala interactions with other brain regions. 35 36
Stress exposure can induce amygdala activation to create a brain state that on the one hand promotes the long-term storage of memories of emotionally arousing events and thus preserves significant information, but on the other Reduced Long-Term Memory Formation hand impairs memory retrieval and and Retrieval working memory. 37 38 The Harvard study identified three types of stress a child may experience: “The neural circuits for dealing with stress are • Positive stress – e.g., getting an immunization particularly malleable (or ‘plastic’) during the – an important part of the normal developmental fetal and early childhood periods … Toxic stress process, enables a sense of mastery during this early period can affect developing • Tolerable stress – e.g., death of a loved one; brain circuits and hormonal systems in a way a frightening accident – generally occur over limited time periods, in the that leads to poorly controlled stress response context of ongoing, supportive relationships with systems that will be overly reactive or slow to adults shut down when faced with threats throughout • Toxic stress – e.g., child abuse (emotional or physical) the lifespan.’’ – Stressful events that are chronic, uncontrollable, and/or experienced without children having access to support from caring adults 39 40
Recommend
More recommend