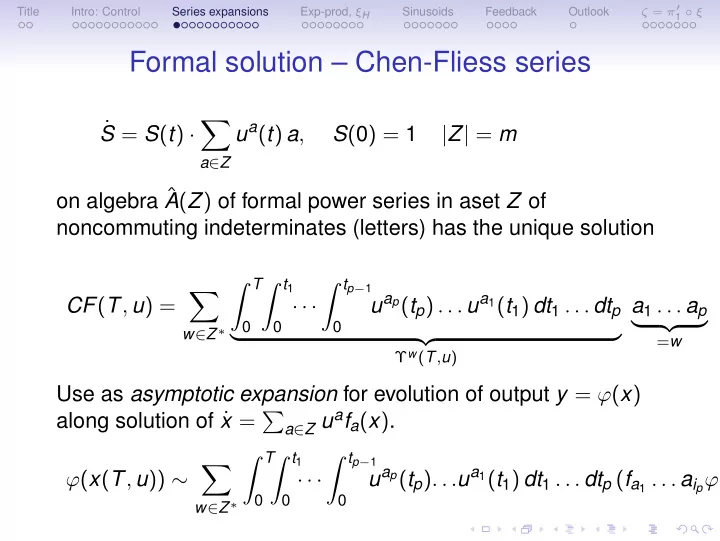

ζ = π ′ Title Intro: Control Series expansions Exp-prod, ξ H Sinusoids Feedback Outlook 1 ◦ ξ Formal solution – Chen-Fliess series � ˙ u a ( t ) a , S = S ( t ) · S ( 0 ) = 1 | Z | = m a ∈ Z on algebra ˆ A ( Z ) of formal power series in aset Z of noncommuting indeterminates (letters) has the unique solution � T � t 1 � t p − 1 � u a p ( t p ) . . . u a 1 ( t 1 ) dt 1 . . . dt p CF ( T , u ) = · · · a 1 . . . a p 0 0 0 � �� � w ∈ Z ∗ � �� � = w Υ w ( T , u ) Use as asymptotic expansion for evolution of output y = ϕ ( x ) x = � a ∈ Z u a f a ( x ) . along solution of ˙ � T � t 1 � t p − 1 � u a p ( t p ) . . . u a 1 ( t 1 ) dt 1 . . . dt p ( f a 1 . . . a i p ϕ )( ϕ ( x ( T , u )) ∼ · · · 0 0 0 w ∈ Z ∗
ζ = π ′ Title Intro: Control Series expansions Exp-prod, ξ H Sinusoids Feedback Outlook 1 ◦ ξ Series solution by iteration φ ( x ( t , u )) = 1 · φ ( x 0 ) � t 0 u a ( s ) ds ( f a φ )( x 0 ) + � t 0 u b ( s ) ds ( f b φ )( x 0 ) + � t � s 1 � s 1 + 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 ( f a f a φ )( x 0 ) 2 0 0 � t � s 1 + 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 ( f a f b φ )( x 0 ) 2 0 � t � s 1 + 1 0 u b ( s 1 ) u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 ( f b f a φ )( x 0 ) 2 0 � t � s 1 + 1 0 u b ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 ( f b f b φ )( x 0 ) 2 0 � t � s 1 � s 2 + 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u a ( s 2 ) u a ( s 3 ) ds 3 ds 2 ds 1 ( f a f a f a φ )( x 0 ) 6 0 0 + . . . Objective: Collect first order differential operators, and minimize number of higher order differential operators involved
ζ = π ′ Title Intro: Control Series expansions Exp-prod, ξ H Sinusoids Feedback Outlook 1 ◦ ξ Integrate by parts: The wrong way to do it � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f a f b + 0 u b ( s 1 ) u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a = 0 0 � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f a f b − 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a = 0 0 � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a + 0 u b ( s 1 ) u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a + 0 0
ζ = π ′ Title Intro: Control Series expansions Exp-prod, ξ H Sinusoids Feedback Outlook 1 ◦ ξ Integrate by parts: The wrong way to do it � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f a f b + 0 u b ( s 1 ) u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a = 0 0 � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f a f b − 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a = 0 0 � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a + 0 u b ( s 1 ) u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a + 0 0
ζ = π ′ Title Intro: Control Series expansions Exp-prod, ξ H Sinusoids Feedback Outlook 1 ◦ ξ Integrate by parts: The wrong way to do it � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f a f b + 0 u b ( s 1 ) u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a = 0 0 � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f a f b − 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a = 0 0 � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a + 0 u b ( s 1 ) u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a + 0 0 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 ( f a f b − f b f a ) = 0 � � � t � s 1 � s 1 u a ( s 1 ) 0 u b ( s 2 ) + u b ( s 1 ) 0 u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 + ds 1 f b f a 0
ζ = π ′ Title Intro: Control Series expansions Exp-prod, ξ H Sinusoids Feedback Outlook 1 ◦ ξ Integrate by parts: The wrong way to do it � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f a f b + 0 u b ( s 1 ) u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a = 0 0 � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f a f b − 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a = 0 0 � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a + 0 u b ( s 1 ) u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a + 0 0 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 ( f a f b − f b f a ) = 0 � � � t � s 1 � s 1 u a ( s 1 ) 0 u b ( s 2 ) + u b ( s 1 ) 0 u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 + ds 1 f b f a 0 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 ( f a f b − f b f a ) = 0 �� t � �� t � 0 u a ( s ) ds 0 u b ( s ) ds + · f b f a
ζ = π ′ Title Intro: Control Series expansions Exp-prod, ξ H Sinusoids Feedback Outlook 1 ◦ ξ Integrate by parts: The wrong way to do it � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f a f b + 0 u b ( s 1 ) u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a = 0 0 � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f a f b − 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a = 0 0 � t � s 1 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a + 0 u b ( s 1 ) u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 f b f a + 0 0 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 ( f a f b − f b f a ) = 0 � � � t � s 1 � s 1 u a ( s 1 ) 0 u b ( s 2 ) + u b ( s 1 ) 0 u a ( s 2 ) ds 2 + ds 1 f b f a 0 � t � s 1 0 u a ( s 1 ) u b ( s 2 ) ds 2 ds 1 ( f a f b − f b f a ) = 0 �� t � �� t � 0 u a ( s ) ds 0 u b ( s ) ds + · f b f a Lie brackets together w/ iterated integrals in right order higher order deriv’s (wrong order) w/ pointwise prod’s of int’s
ζ = π ′ Title Intro: Control Series expansions Exp-prod, ξ H Sinusoids Feedback Outlook 1 ◦ ξ Integrate by parts, smart way Do not manipulate iterated integrals and iterated Lie brackets of vector fields by hand – work on level of “words” (their indices) � I ∈{ a , b } ∗ I ⊗ I = 1 ⊗ 1 = 1 ⊗ 1 + a ⊗ a + a ⊗ a + b ⊗ b + b ⊗ b + 1 + 1 aa ⊗ aa aa ⊗ aa 2 2 + 1 + 1 ab ⊗ ab ab ⊗ ( ab − ba ) 2 2 + 1 + 1 ba ⊗ ba ( ab + ba ) ⊗ ba 2 2 + 1 + 1 bb ⊗ bb bb ⊗ bb 2 2 + 1 + 1 aaa ⊗ aaa aaa ⊗ aaa 6 6 + + . . . . . .
ζ = π ′ Title Intro: Control Series expansions Exp-prod, ξ H Sinusoids Feedback Outlook 1 ◦ ξ Drop everything except the indices - maps • The iterated integral � t � t 1 � t n − 1 Υ a 1 a 2 ... a n = u a 1 ( t 1 ) u a 2 ( t 2 ) · · · u a n ( t n ) dt n dt n − 1 · · · dt 1 · · · 0 0 0 is uniquely identified by the multi-index (“word”) a 1 a 2 . . . a n • The n -th order partial differential operator f a n ◦ f a n − 1 ◦ . . . f a 1 is uniquely identified by the multi-index (“word”) a 1 a 2 . . . a n • The Chen series is identified with the identity map on free associative algebra A ( Z ) over set Z of with | Z | = m � � ∈ ˆ CF ∼ Id A ( Z ) = w ⊗ w A ( Z ) ⊗ A ( Z ) w ∈ Z n n ≥ 0 with shuffle product on left and concatenation on right
ζ = π ′ Title Intro: Control Series expansions Exp-prod, ξ H Sinusoids Feedback Outlook 1 ◦ ξ Homomorphisms I • For fixed smooth vector fields f i F : A ( Z ) �→ partial diff operators on C ∞ ( M ) F : ( a 1 a 2 . . . a n ) �→ f a 1 ◦ f a 2 ◦ . . . f a n associative algebras: concatenation �→ composition • For fixed control u ∈ U Z Υ( u ): A ( Z ) �→ AC ([ 0 , T ] , R ) � T � t 1 � t p − 1 Υ( u ): ( a 1 a 2 . . . a n ) �→ · · · u a p ( t p ) . . . u a 1 ( t 1 ) dt 1 . . . dt p 0 0 0 associative algebras (Ree’s theorem): shuffle of words �→ pointwise multiplication of functions
ζ = π ′ Title Intro: Control Series expansions Exp-prod, ξ H Sinusoids Feedback Outlook 1 ◦ ξ Recall: definition of the shuffle SKIP Combinatorially: for words w , z ∈ Z ∗ and letters a , b ∈ Z ( w a ) X ( z b ) = (( w a ) X z ) b + ( w X ( z b )) a ( ab ) X ( cd ) = a b c d + a c b d + c a b d + Example: a c d b + c a d b + c d a b Algebraically: transpose of the coproduct ∆ < v X w , z > = < v ⊗ w , ∆( z ) > where ∆: A ( Z ) �→ A ( Z ) ⊗ A ( Z ) by ∆( a ) = 1 ⊗ a + a ⊗ 1 for a ∈ Z
ζ = π ′ Title Intro: Control Series expansions Exp-prod, ξ H Sinusoids Feedback Outlook 1 ◦ ξ Shuffles and simplices SKIP On permutations algebras Duchamp and Agrachev consider partially commutative and noncommutative shuffles. Illustration: ✻ ✻ ✻ � � � � � � � � σ 12 � σ 2 σ 1 x 2 � � � = ∪ σ 21 � � � � � ✲ � � ✲ � ✲ σ 1 = ∪ ∪ σ ( 12 ) x 3 = σ 312 ∪ σ 132 ∪ E.g. σ ( 12 ) x 3 = { t : 0 ≤ t 1 ≤ t 2 ≤ 1 , 0 ≤ t 3 ≤ 1 } For multiplicative integrands f ( x , y , z ) = f 1 ( x ) · f 2 ( y ) · f 3 ( z ) �� 1 � � y � 1 � 1 � y � x � 1 � y � z � 1 � z � y ( · ) dx dy · ( · ) dz = ( · ) dz dx dy + ( · ) dx dz dy + ( · ) dx dy dz 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ζ = π ′ Title Intro: Control Series expansions Exp-prod, ξ H Sinusoids Feedback Outlook 1 ◦ ξ Homomorphisms II • Restriction is Lie algebra homomorphism F : L ( Z ) ⊆ A ( Z ) �→ Γ ∞ ( M ) (vector fields) • Do not fix controls: iterated integral functionals Υ: ∈ A ( Z ) �→ IIF ( U Z ) � � T � t 1 � t p − 1 u a p ( t p ) . . . u a 1 ( t 1 ) dt 1 . . . dt Υ: ( a 1 a 2 . . . a n ) �→ u �→ · · · 0 0 0 associative algebras: shuffle of words �→ pointwise multiplication of iterated integral functionals • Much better: Theorem: If U = L 1 ([ 0 , T ] , [ − 1 , 1 ]) then Υ: ( A ( Z ) , ∗ ) �→ IIF ( U Z ) is a Zinbiel algebra isomorphism.
Recommend
More recommend