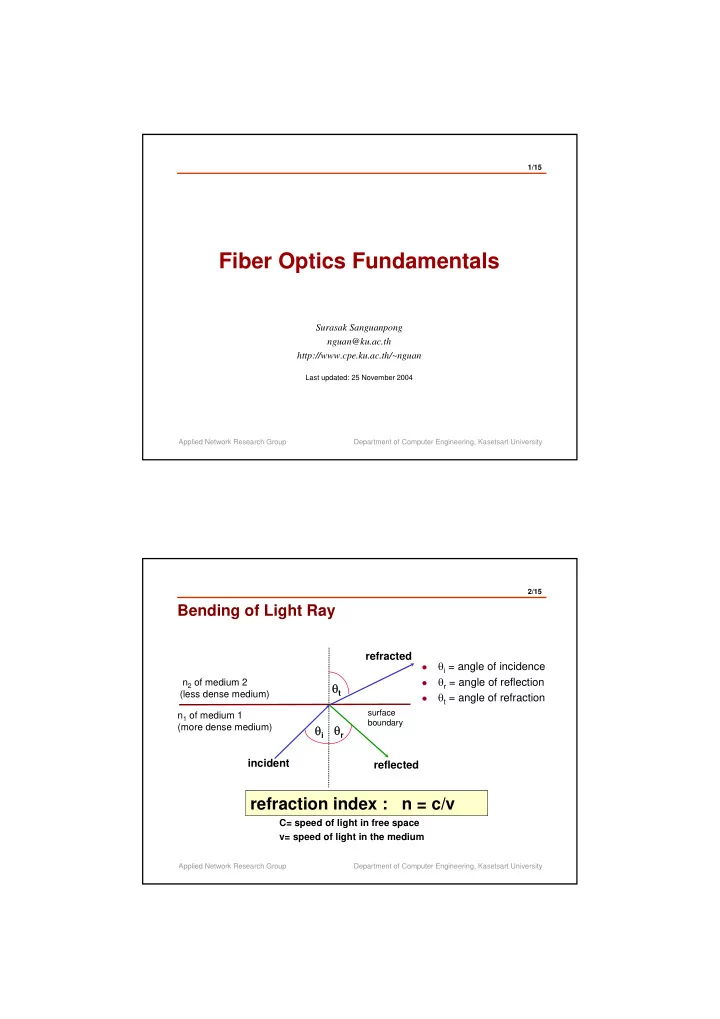

1/15 Fiber Optics Fundamentals Surasak Sanguanpong nguan@ku.ac.th http://www.cpe.ku.ac.th/~nguan Last updated: 25 November 2004 Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 2/15 Bending of Light Ray refracted θ i = angle of incidence � θ r = angle of reflection n 2 of medium 2 � θ t (less dense medium) θ t = angle of refraction � surface n 1 of medium 1 boundary (more dense medium) θ i θ r incident reflected refraction index : n = c/v C= speed of light in free space v= speed of light in the medium Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
3/15 Snell ’ s Law critical angle θ t n 1 > n 2 1 2 n 2 θ i 3 n 1 n 1 sin θ i = n 2 sin θ t 4 4 θ i = sin -1 n 2 /n 1 3 2 = θ c θ c = critical angle 1 Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 4/15 How it works cladding Total reflection Loss n 2 n 1 core Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
5/15 Propagation Modes • Finite number of angles at which the rays reflect and propagate • Each angle defines a path or a mode M = the number of modes π d 2 d = core diameter (m) ( n 1 ) 2 -( n 2 ) 2 λ λ = wavelength (m) M = n 1 = refraction index of core 2 n 2 = refraction index of cladding Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 6/15 Fiber classification Single Mode Single Mode Fiber Optics Fiber Optics Multimode Multimode Step-Index Step-Index Graded-Index Graded-Index Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
7/15 Multimode step-index input signal output signal n 1 Step-change n 2 • refraction index is uniformly throughout the core core/cladding characteristics Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 8/15 Multimode graded-index input signal output signal n 1 Gradually change n 2 • Light begins to bend back toward the center, eventually reflecting back • Because the material also less dense, the light travels faster core/cladding characteristics Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
9/15 Single Mode input signal output signal n 1 n 2 • Reducing the core diameter to that of a single wavelength (3-10 micrometer) will let the light propagates along a one mode only core/cladding characteristics Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 10/15 Typical Fiber Cable Single core • Materials for cladding and core: core cladding Jacket � glass cladding/glass core � plastic cladding/glass core � plastic cladding/plastic core Multicore Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
11/15 Cable Structures Examples Strength Outer Jacket Elements Color Coded Jacket Central Strength fiber Elements cladding core Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 12/15 Optical Fiber Comparison Multimode Single mode Light source LED/ILD ILD Bandwidth >1 GHz/km up to 1000 GHz/km Wavelength 850, 1300 1300,1550 core/cladding 62.5/125 * 8/125 Applications LAN, backbone Long distance, Telcom lines * options with 50/125, 100/140 core core cladding cladding 62.5/125 micron 8/125 micron Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
13/15 Loss in Glass Fibers 2.0 0.85 μ band 1.30 μ band 1.55 μ band 1.8 1.6 Attenuation (dB/km) 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Wavelength (microns) Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 14/15 Light Source power ILD LED LED Injection Laser Diode wavelength Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
15/15 Fiber in use • Plenums or non-plenums • plenum cable has a fire-resistant jacket, which will not burn, smoke or • give off toxic fumes when expose to heat • Riser cables • cable that runs vertically; e.g. between floors in a building • Indoor or Outdoor • Indoor cable used in building. Outdoor cable used in underground, • directed buries, and aerial applications between building. Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
Recommend
More recommend