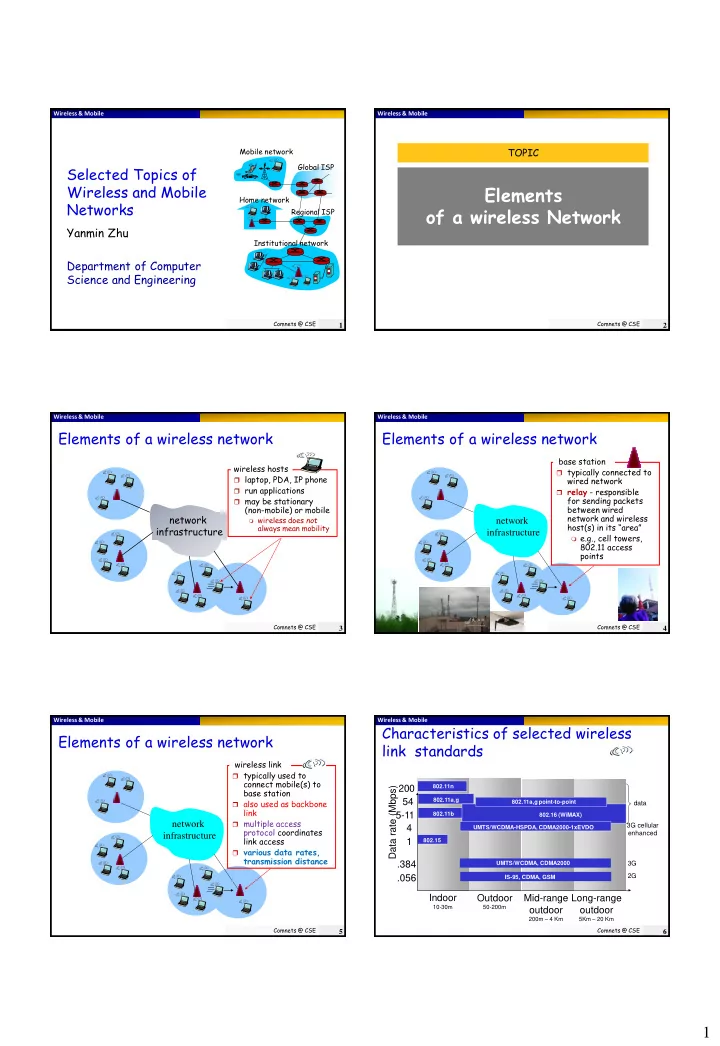

Wireless & Mobile Wireless & Mobile Mobile network TOPIC Global ISP Selected Topics of Wireless and Mobile Elements Home network Networks of a wireless Network Regional ISP Yanmin Zhu Institutional network Department of Computer Science and Engineering Comnets @ CSE Comnets @ CSE 1 2 Wireless & Mobile Wireless & Mobile Elements of a wireless network Elements of a wireless network base station wireless hosts typically connected to laptop, PDA, IP phone wired network run applications relay - responsible for sending packets may be stationary (non-mobile) or mobile between wired network and wireless network wireless does not network host(s) in its “area” always mean mobility infrastructure infrastructure e.g., cell towers, 802.11 access points Comnets @ CSE Comnets @ CSE 3 4 Wireless & Mobile Wireless & Mobile Characteristics of selected wireless Elements of a wireless network link standards wireless link typically used to connect mobile(s) to 802.11n Data rate (Mbps) 200 base station 54 802.11a,g also used as backbone 802.11a,g point-to-point data link 5-11 802.11b 802.16 (WiMAX) multiple access network 3G cellular 4 UMTS/WCDMA-HSPDA, CDMA2000-1xEVDO protocol coordinates enhanced infrastructure link access 1 802.15 various data rates, transmission distance .384 UMTS/WCDMA, CDMA2000 3G .056 2G IS-95, CDMA, GSM Indoor Outdoor Mid-range Long-range 10-30m 50-200m outdoor outdoor 200m – 4 Km 5Km – 20 Km Comnets @ CSE Comnets @ CSE 5 6 1
Wireless & Mobile Wireless & Mobile Modes of wireless network TOPIC infrastructure mode base station connects mobiles into wired network Two Modes handoff: mobile changes base station of Wireless Network providing connection network into wired network infrastructure Comnets @ CSE Comnets @ CSE 7 8 Wireless & Mobile Wireless & Mobile Wireless network taxonomy Modes of wireless network ad hoc mode single hop multiple hops no base stations nodes can only host may have to host connects to transmit to other infrastructure relay through several base station (WiFi, nodes within link (e.g., APs) wireless nodes to WiMAX, cellular) coverage connect to larger which connects to nodes organize Internet: mesh net larger Internet themselves into a network: route among no base station, no themselves connection to larger no no base station, no Internet. May have to infrastructure connection to larger relay to reach other Internet (Bluetooth, a given wireless node ad hoc nets) MANET, VANET Comnets @ CSE Comnets @ CSE 9 10 Wireless & Mobile Wireless & Mobile Wireless network characteristics TOPIC Multiple wireless senders and receivers create additional problems (beyond multiple access): Two Problems Signal attenuation: B, A hear each other in Wireless Networks B, C hear each other A B C A, C can not hear each other interfering at B C’s signal A’s signal strength strength space Comnets @ CSE Comnets @ CSE 11 12 2
Wireless & Mobile Wireless & Mobile Hidden Terminal Problem Exposed Terminal Problem Even if CSMA is used, it is not enough. C Hidden terminal problem! Hidden terminal problem B A B, A hear each other B, C hear each other A, C can not hear each other B D C A means A, C unaware of their interference at B When collision ETP reduces the throughput of the whole happens, A does network B A C not know Collision happens at the receiver side! Comnets @ CSE Comnets @ CSE 13 14 Wireless & Mobile Wireless & Mobile Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) TOPIC One of Multiple Access Methods TDMA, FDMA CDMA: Code Division Used in several wireless broadcast channels (cellular, satellite, etc) standards Multiple Access unique “code” assigned to each user; i.e., code set partitioning all users share same frequency, but each user has own “chipping” sequence (i.e., code) to encode data Comnets @ CSE Comnets @ CSE 15 16 Wireless & Mobile Wireless & Mobile Code Division Multiple Access CDMA (CDMA) encoded signal = (original data) X (chipping sequence) decoding: inner-product of encoded signal and chipping sequence allows multiple users to “ coexist ” and transmit simultaneously with minimal interference (if codes are “orthogonal”) Comnets @ CSE Comnets @ CSE 17 18 3
Wireless & Mobile Wireless & Mobile CDMA CDMA Encode/Decode channel output Z i,m A Z i,m = d i . c m B data d 0 = 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 E 1 1 d 1 = -1 bits sender - 1 1 - 1 - - 1 1 - - 1 - 1 - 1 C slot 0 slot 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 code D channel channel - 1 - - 1 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 output output slot 1 slot 0 SCENARIO 1 M D i = S Z i,m . c m m=1 M SCENARIO 2 received 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 d 0 = 1 input - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 1 - - 1 - 1 - 1 d 1 = -1 slot 1 slot 0 code 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 channel channel - 1 - 1 - 1 1 - - - - - 1 1 1 1 receiver output output slot 1 slot 0 SCENARIO 3 Comnets @ CSE Comnets @ CSE 19 20 Wireless & Mobile Wireless & Mobile FDMA, TDMA,CDMA CDMA: two-sender interference 0 1 A B 1 1 1 0 Reception from A Comnets @ CSE Comnets @ CSE Code of A 21 22 4
Recommend
More recommend