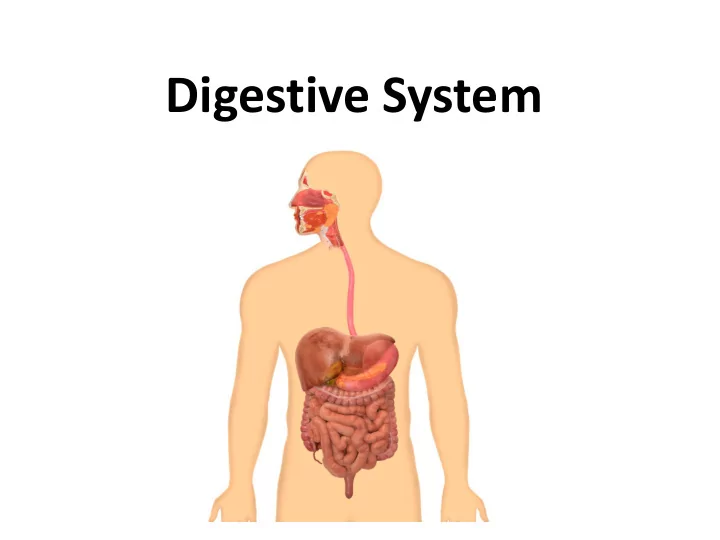

Digestive System
What is the function of the digestive system? • The physical and chemical breakdown of large food molecules into smaller molecules that can be used by cells
Diagram the pathway of food through the digestive system (gastrointestinal tract) (we will complete this part together in class on Friday, November 15 th )
Mechanical and Chemical Digestion • Physical breakdown of • Chemical digestion of large pieces of food into polymers of food into small pieces monomers with the action of enzymes • Occurs in the mouth, • Occurs in the mouth stomach and small and stomach intestine
Mouth and Salivary Glands
Mouth • Mechanically digests food with the teeth when chewing • Salivary glands produce salivary amylase to chemically digest polysaccharides into disaccharides (carbohydrates) • Food is mixed with saliva to form a bolus
Pharynx • Back of the throat • Common passageway for food and air • Leads to a muscular tube called the esophagus
Esophagus
Esophagus • Flap of cartilage called the epiglottis covers the top of the trachea (airway) when food is swallowed • Produces mucus to lubricate food • Lined with involuntary smooth muscle • Pushes food to the stomach with wave-like muscle contractions called peristalsis
Stomach
Stomach • Three layers of smooth muscle, protected by mucus • Mechanically digests food by churning and mixing food with gastric juices ( HCl and pepsinogen ) • Pepsin chemically digests proteins into peptides in the stomach • Mixture of gastric juices and food is called chyme
Hydrochloric Acid • Produced by the stomach • Provides the proper pH (2.0) for the enzyme pepsin to function • Converts inactive pepsinogen into active pepsin
Small Intestine
Small Intestine • Three sections: duodenum, jejunum, ileum • Lined with two layers of smooth muscle and finger-like projections called villi • Villi absorb nutrients from digested food into the bloodstream • Chemical digestion of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates
Small Intestine Enzymes • Produces sucrase , maltase , and lactase – chemical digestion of disaccharides into monosaccharides • Produces peptidase – chemical digestion of peptides into amino acids
Villi of Small Intestine
Large Intestine
Large Intestine • Also known as the colon • No further mechanical or chemical digestion takes place • Absorbs excess water from undigested wastes • Absorbs vitamins, minerals, and other ions
Rectum
Rectum • Last 20 cm of the large intestine • Solid waste (feces) is stored here until it exits the body through the anus
Accessory Organs for Digestion • Liver , pancreas and gall bladder all produce enzymes and/or fluids that assist in the digestion of food • FOOD DOES NOT PASS THROUGH THESE ORGANS
Liver, Gall Bladder and Pancreas
Liver and Gall Bladder • Liver produces bile to emulsify fats (break up large pieces of fat into smaller pieces) • Emulsification is mechanical digestion • Gall bladder is a storage pouch for bile • Bile is secreted into the small intestine through the bile duct
Pancreas • Produces pancreatic juice – consists of sodium bicarbonate and enzymes • Sodium bicarbonate neutralizes the acidic material from the stomach • Enzymes are secreted into the small intestine from the pancreas to assist in digestion
Pancreas Enzymes • Lipase – chemical digestion of lipids into fatty acids and glycerol • Trypsin – chemical digestion of peptides into amino acids • Pancreatic amylase – chemical digestion of disaccharides into monosaccharides
Bozeman Science - Digestion
Recommend
More recommend