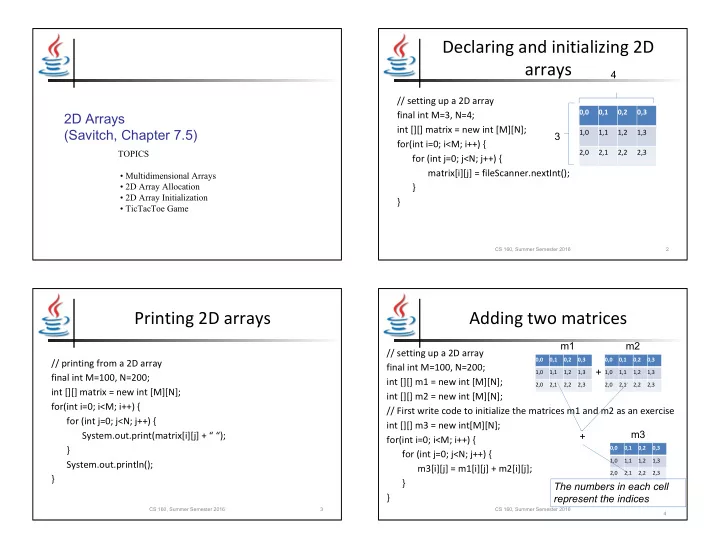

Declaring and initializing 2D arrays 4 // setting up a 2D array 0,0 0,1 0,2 0,3 2D Arrays final int M=3, N=4; int [][] matrix = new int [M][N]; (Savitch, Chapter 7.5) 1,0 1,1 1,2 1,3 3 for(int i=0; i<M; i++) { TOPICS 2,0 2,1 2,2 2,3 for (int j=0; j<N; j++) { matrix[i][j] = fileScanner.nextInt(); • Multidimensional Arrays • 2D Array Allocation } • 2D Array Initialization } • TicTacToe Game CS 160, Summer Semester 2016 2 Printing 2D arrays Adding two matrices m1 m2 // setting up a 2D array 0,0 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,0 0,1 0,2 0,3 // printing from a 2D array final int M=100, N=200; + 1,0 1,1 1,2 1,3 1,0 1,1 1,2 1,3 final int M=100, N=200; int [][] m1 = new int [M][N]; 2,0 2,1 2,2 2,3 2,0 2,1 2,2 2,3 int [][] matrix = new int [M][N]; int [][] m2 = new int [M][N]; for(int i=0; i<M; i++) { // First write code to initialize the matrices m1 and m2 as an exercise for (int j=0; j<N; j++) { int [][] m3 = new int[M][N]; m3 System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + “ “); + for(int i=0; i<M; i++) { } 0,0 0,1 0,2 0,3 for (int j=0; j<N; j++) { 1,0 1,1 1,2 1,3 System.out.println(); m3[i][j] = m1[i][j] + m2[i][j]; 2,0 2,1 2,2 2,3 } } The numbers in each cell } represent the indices CS 160, Summer Semester 2016 3 CS 160, Summer Semester 2016 4
More on 2D arrays Review (Java) • int[][] matrix = new int[3][4]; • Assignments & expressions • What is matrix.length? It is 3 • Sequential control: if & switch • What is matrix[0].length? It is 4 – So is matrix[1].length, matrix[2].length, and matrix[3].length • Looping control: while, for, do • You can access a particular row using matrix[i] where i refers • Organization: classes & methods to the row number between 0 and 2 • Each row is a one-dimensional array • Tools: Eclipse & debugging • You cannot access a column like that ☹ • Exercises: Why? So you can program… – Write code that subtracts one matrix from another – Write code that transposes the given matrix CS 160, Summer Semester 2016 5 CS 160, Summer Semester 2016 6 Programming Challenge Problem • … but programming isn’t about syntax • So here is a problem to be worked through – You can program in many languages together: • Programming is about problem solving – Write a person versus computer TicTacToe game. – Player goes first, plays ‘X’, select with mouse. – Problem definition/refinement – Machine selects random, legal moves – Problem decomposition – Update the board after every move – Managing complexity – Program detects when game is over – Ability to show user the current state of the board. CS 160, Summer Semester 2016 7 CS 160, Summer Semester 2016 8
Decomposition Code • Game board • Focusing on the game: – Board state needed by multiple subtasks – State, Initialization – Good candidate for an class variable • Making moves – Obvious mapping to 2D array (3 rows, 3 columns) – User: inputs integers for row and column • Initialize the board : method – Computer: selects random, legal moves • Player moves: method • Game status • Computer moves: method • Detect game over : method(s) – Tie Game, Player or Computer Wins, In Progress • Print the board: method CS 160, Summer Semester 2016 9 CS 160, Summer Semester 2016 10 Constructors Eclipse Demo • The syntax for constructors is unique • Write the program for TicTacToe – Constructors can take parameters, but they never • Will be posted on the progress page return a value – The constructor name is always the same as the class name – The default constructor has no parameters, but we can add them – The constructor is generally used to initialize class instance variables CS 160, Summer Semester 2016 11 CS 160, Summer Semester 2016 12
Recommend
More recommend