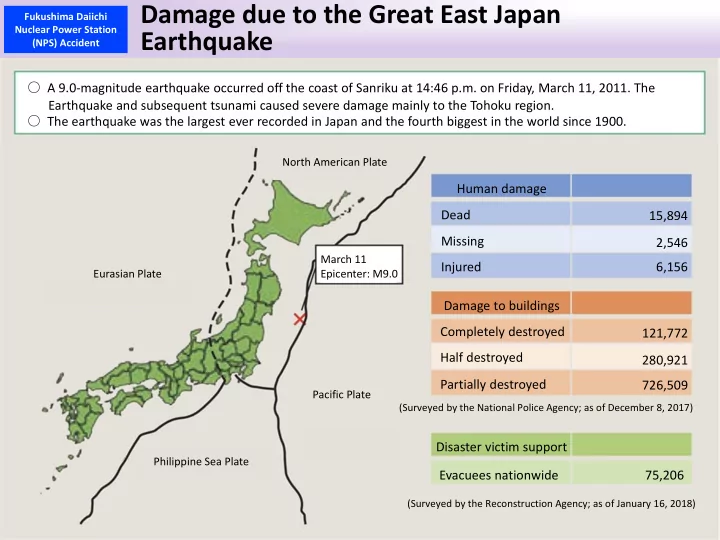

Damage due to the Great East Japan Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Earthquake (NPS) Accident ○ A 9.0‐magnitude earthquake occurred off the coast of Sanriku at 14:46 p.m. on Friday, March 11, 2011. The Earthquake and subsequent tsunami caused severe damage mainly to the Tohoku region. ○ The earthquake was the largest ever recorded in Japan and the fourth biggest in the world since 1900. North American Plate Human damage Dead 15,894 Missing 2,546 March 11 Injured 6,156 Eurasian Plate Epicenter: M9.0 Damage to buildings Completely destroyed 121,772 Half destroyed 280,921 Partially destroyed 726,509 Pacific Plate (Surveyed by the National Police Agency; as of December 8, 2017) Disaster victim support Philippine Sea Plate Evacuees nationwide 75,206 (Surveyed by the Reconstruction Agency; as of January 16, 2018)
Fukushima Daiichi Accident at the Nuclear Power Station Nuclear Power Station (NPS) Accident Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO)'s Fukushima Daiichi NPS Unit 3 (shot from the air) (Shot on March 16, 2011; Provided by TEPCO)
Factors of the Accident: (Estimated) Influence of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station the Earthquake and Tsunami (NPS) Accident Collapse of The transmission Functions to cool line towers emergency Loss of down reactors and power system Failure of external spent fuel pools was activated breakers, etc. power supply were maintained. immediately. Earthquake Automatic shut‐down of reactors Continued on the following page Loss of all Loss of the Tsunami 14:46 p.m. Failure of reactor cooling emergency power AC power on March 11 generators function and coolant injection Failure of cooling 15:27 p.m. to function seawater pumps 15:35 p.m. and switchboards, etc. Reactor Emergency diesel generators Approx. Turbine building 44 m Partially Approx. Tsunami: 14 m to 15 m (flood height ) building 25 m collapsed Height of the premises: Approx. 10 m Sea surface Seawater pump The Secretariat of the Nuclear Regulation Authority
Factors of the Accident: (Estimated) Status within Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station the Reactor (NPS) Accident Events that occurred Loss of functions to cool down reactors Pressure reduction Generation of hydrogen due to water‐ by opening valves Increase in zirconium reaction reactor pressure →Hydrogen explosion due to steam Overheat of core fuel and inject coolant →Core melt the previous page Failed to take these Continued from measures on a timely basis Deterioration of air tightness at the pressure vessel penetrator →Part of the melted fuel flowed down Temperature from the pressure vessel to the Alternative coolant increase due to containment vessel. injection using fuel heating firefighting pumps, Deterioration of the containment without coolant etc. vessel →Outflow of high‐level radioactive‐ contaminated water →Discharge of radioactive materials Structure of nuclear reactor into the air Almost avoided Spent fuel pool Steel containment ◆ Steam explosion vessel ◆ Recriticality Reactor pressure Concrete vessel containment ◆ Fuel damage due to Vessel evaporation of coolant in the spent fuel pool Reactor building Suppression pool The Secretariat of the Nuclear Regulation Authority
Recommend
More recommend