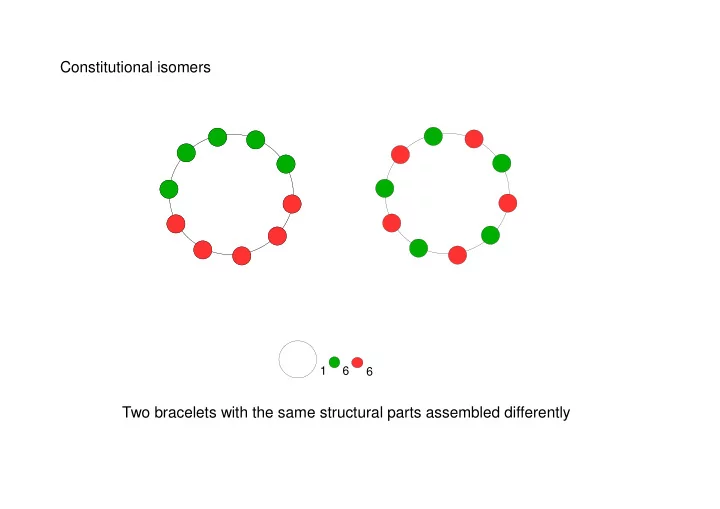

Constitutional isomers 1 6 6 Two bracelets with the same structural parts assembled differently
Constitutional isomers H H H H H H H C H C C H C N H N H H H H C 2 H 7 N Two molecules with the same constituent atoms assembled differently
Rules for writing the Lewis structure of a molecule: 1) MF, constitution, and net charge must be known 2) Draw the dot structures of all the atoms of the MF 3) Determine the total number of valence electrons 4) Connect the atoms by 2 electron covalent bonds 5) Maximize the number of covalent bonds (multiple bonds between atoms are OK) 6) Determine formal and net charge 7) Replace bonded dot pairs with line bonds if desired * * * * * 8) If 2 or more structures (resonance structures) can be drawn, the more representative has a) all octets filled b) minimal formal charge c) has formal charge with the least separation d) has formal charge assigned by relative electronegativities
Bond polarization: a consequence of electronegativity differences Fluorine, F 2 Fluoromethane, CH 3 F Lithium Fluoride, LiF .. - Li + H :F: .. .. .. .. : : F F : .. F C H .. .. not H .. :.. F Li ∆ EN = (4.0 - 4.0) = 0 F-C (4.0 - 2.5) = 1.5 (4.0 - 1.0) = 3.0 nonpolar covalvent polar covalent bond ionic bond bond C-H (2.5 - 2.1) = 0.4 nonpolar covalent bonds
Atomic Orbitals • Quantum mechanics provides a mathematical description of electron energies and locations • It’s called a wave equation • The solution of the wave equation gives a series of wavefunctions, ψ 1 , ψ 2 , ψ 3 . . . • The square of the wavefunction is an atomic orbital
Atomic Orbital Shapes and Phases • 5 classes of orbitals • s , p , d , f , g 2 s orbital see http://www.d.umn.edu/~pkiprof/ChemWebV2/AOs/index.html for orbital diagrams
2 p orbitals 2 p y 2 p x 2 p z
3 d orbitals
Wikipedia’s entry on atomic orbitals describes how the wave-like nature of electrons qualitatively determines the shape of an orbital: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atomic_orbital
. . e - not between - = nuclei if populated = antibonding 1 s 1 s (exclusion) interaction energy σ * 104.2 kcal/mol H H 1 s 1 s σ internuclear distance 0.74 Å . . . . + = or 1 s 1 s (intersection) e - between = bonding interaction nuclei
- = (destructive interference) 1 s 1 s node between nuclei = antibonding interaction + = (constructive inteference) 1 s 1 s electron density between nuclei = bonding interaction
If the idea of LCAO is H 2 σ * H 1s 1 + H 1s 1 = H 2 σ 2 Can this approach be extended to methane, CH 4 ? Yes, but the mathematics is very challenging! C 1s 2 + C 2s 2 + C 2p x 1 + C 2p y 1 + C 2p z + H 1s 1 + H 1s 1 + H 1s 1 + H 1s 1 = ?
So, to model how atomic orbitals overlap to provide valance bonds, we will ● choose to combine only 2 orbitals at a time ● invent hybrid atomic orbitals to reconcile LCAO with VSEPR
Using VSEPR to predict molecular geometries Beryllium hydride, BeH 2 Borane, BH 3 Methane, CH 4 . . . . . Be H . . . . . . B C H H . . H . . H H . . H H . H H:Be:H H H .. .. H:B:H H:C:H .. H H H 180 E 120 E 109.5 E C B H H H H H H Be H linear linear linear linear trigonal planar trigonal planar trigonal planar trigonal planar tetrahedral tetrahedral tetrahedral tetrahedral
. . π * . energy . C 2p C 2p π . . . . or
VSEPR geometries can be distorted is the electrostatic interactions between paris of valence elctrons are not identical: lp - lp interactions > lp - bonded pair interactions > bonded pair - bonded pair interactions H 109.5 E C H H H .. N H Methane H H 107 E .. .. O H Ammonia 105 E H Water distorted tetrahedral distorted tetrahedral distorted tetrahedral distorted tetrahedral
Dipole moments of molecules: net molecular polarity Draw the Lewis structure for nitromethane, CH 3 NO 2 . . . . H O C N . H + . O . . H - . . nitromethane
Dipole moments of molecules: net molecular polarity quantitatively, µ = Q × r visually, dipole moment can be described as a vector with magnitude and direction that is the sum of the bond polarity vectors of a molecule. Usually, it’s OK to ignore the contributions of formally nonpolar covalent bonds that have ∆ EN # 0.4: . . . . H O C N net + H . .. . O H . . -
Accounting for the polarization of every bond with ∆ EN … 0 gives a more accurate µ but rarely changes the gross direction and magnitude: . . . . H O C N net + H . .. . O H . . -
Dipole moments of molecules: net molecular polarity * + * - electrostatic potential maps use color to indicate charge distributions
Recommend
More recommend