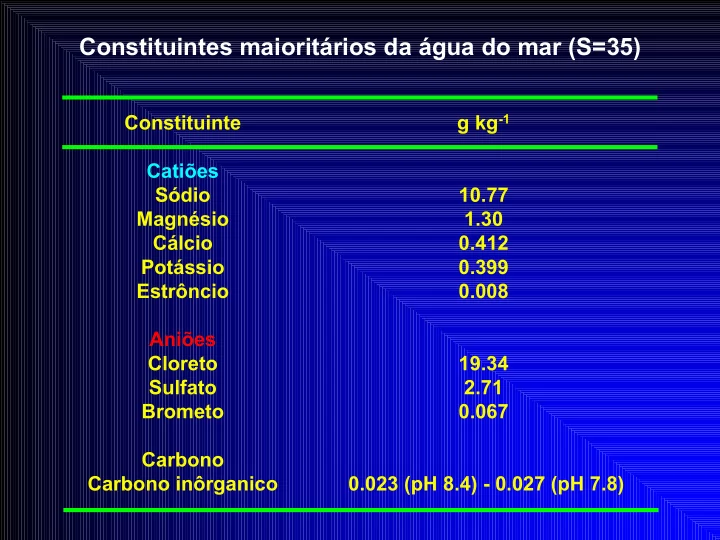

Constituintes maioritários da água do mar (S=35) Constituinte g kg -1 Catiões Sódio 10.77 Magnésio 1.30 Cálcio 0.412 Potássio 0.399 Estrôncio 0.008 Aniões Cloreto 19.34 Sulfato 2.71 Brometo 0.067 Carbono Carbono inôrganico 0.023 (pH 8.4) - 0.027 (pH 7.8)
World ocean bathymetry - - NOAA NOAA World ocean bathymetry
Batimetria do Oceano Atlântico Plataforma larga Crista média atlântica Plataforma estreita
North Atlantic Ridge North Atlantic Ridge Bathymetry profile obtained by the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory at Columbia University http://imager.ldeo.columbia.edu/ridgembs/
Características gerais do oceano Província nerítica Província oceânica Termoclina Camada quente z < 250m Camada fria Pelagos Plataforma continental z ~4000m Declive continental Bentos T ~ 4 o C S ~ 35 Planície abissal
Major wind systems Major wind systems N Polar easterlies of the world of the world 60 o N Westerlies 30 o N Subtropical highs Northeast trades Intertropical convergence zone 0 o Southeast trades Subtropical highs 30 o S Westerlies 60 o S Polar easterlies S
General sub- -surface circulation of the World surface circulation of the World General sub Ocean Ocean 80 o S 60 o N 40 o N 0 o 20 o S 60 o S 20 o N 40 o S 0 SA Central NA Central i n t Permanent Water L t h e e r m Water o a c l r i n e m b r e a 1000 d d ( i o S a r Antartic intermediate water t m e i n w ) a (Smin) t e r N 2000 o r w Weddell Sea e Depth (m) g i a n 3000 S e North Atlantic Deep Water a overflow (Smax, Omax) 4000 Norwegian Sea ) m i n T e r ( W a t m o o t t c B a r t i n t A 5000 6000 American Antartic Iceland Demerara Rio Grande Ridge Faeroe Rise Sohm Abyssal Plateau Brazil Weddell Abyssal Argentine Plain Basin Abyssal Plain Plain Basin Adapted from Dietrich et al., 1980 - - General Oceanography: An General Oceanography: An Adapted from Dietrich et al., 1980 Introduction Introduction
Coriolis effect effect Coriolis • Coriolis parameter = 2 Ω sin φ Where: Ω = rate of angular rotation of the earth φ = latitude • Coriolis acceleration = 2 Ω v sin φ Where: v = velocity F=ma therefore: • Coriolis force = 2 Ω mv sin φ Where: m = mass
Ocean circulation - - 160 million years ago 160 million years ago Ocean circulation Currents http://earth.usc.edu/~stott/Catalina/Oceans.html * Upwelling areas Continental drift
Ocean circulation - - 100 million years ago 100 million years ago Ocean circulation Currents http://earth.usc.edu/~stott/Catalina/Oceans.html Continental drift
Ocean circulation - - 30 million years ago 30 million years ago Ocean circulation Currents http://earth.usc.edu/~stott/Catalina/Oceans.html Continental drift
Global ocean - - surface gyres surface gyres Global ocean and temperatures and temperatures
Surface currents in the global ocean Surface currents in the global ocean Warm current Cold current Warm current Cold current
Sea surface temperature - - NOAA NOAA Sea surface temperature Data in oC - COADS monthly climatology dataset (1946-1989)
Global ocean surface temperature Global ocean surface temperature December temperature (oC) - - Data from NOAA Data from NOAA December temperature (oC)
Global ocean surface temperature Global ocean surface temperature July temperature (oC) - - Data from NOAA Data from NOAA July temperature (oC)
North Atlantic gyre North Atlantic gyre 6 m 3 s Flows in Sverdrup (1 Sv = 10 6 m 3 s - ) Flows in Sverdrup (1 Sv = 10 -1 1 )
Gulf stream Gulf stream current current U.S.A. U.S.A. Temperature profile (oC) Temperature profile (oC)
Gulf stream current, showing ring formation Gulf stream current, showing ring formation
Circulação geral do Mar do Mar Mediterrâneo Mediterrâneo Circulação geral 1000m 2000m 3000m 4000m 35 o E 30 o E 25 o E 20 o E 15 o E 10 o E 5 o E 45 o N 0 o W 28 o C 20 o C 12 o C 4 o C 40 o N 5 o W
Wind- -driven surface currents driven surface currents Wind y y y Water drag Water drag Water drag Wind drag Wind drag Wind drag Forces x x x Coriolis Coriolis Coriolis y y y Water x x x velocity v v 45 o v
Eckman spiral spiral - - schematic representation schematic representation Eckman y z = D E Wind x 45 o z = 0 Horizontal projection of currents at 11 equally- Horizontal projection of currents at 11 equally -spaced levels from the spaced levels from the surface to bottom of the Eckman layer (D E ) surface to bottom of the Eckman layer (D E )
Eckman spiral spiral - - schematic representation schematic representation Eckman Wind Surface water Wind force Wind force Direction of motion Friction Direction of motion 45 o Average flow
Geostrophic balance balance Geostrophic Continental mass N Wind Balanced N-S wind stress stress and S-N coriolis force Coriolis force Water current E Equator Upwelling areas at western continental margin S
Coastal upwelling upwelling - - vertical section vertical section Coastal Front H H 0 ρ 1 ρ 2 R i D H - Depth of water R i - Rossby radius D - Distance to shore ρ 1 - Density of upper water z ρ 2 - Density of lower water z - Depth Mann & Lazier - Dynamics of Marine Ecosystems, Blackwell, 1991
Coastal upwelling upwelling - - plan view plan view Coastal y (west) Front Coast x (south) Mann & Lazier - Dynamics of Marine Ecosystems, Blackwell, 1991
Azores Front Azores Front 55 o N 2000m 4000m 50 o 45 o 4000m 40 o 2000m 35 o 30 o 4000m 2000m 25 o 20 o 70 o W 60 o 50 o 40 o 30 o 20 o 10 o 5 o Data from Macedo et al, 1999
Azores Front depth Azores Front depth contours contours 37.0 36.5 Depth (m) 36.0 350 35.5 Latitude (º N) 300 35.0 250 34.5 200 34.0 150 33.5 100 33.0 50 32.5 32.0 32.0 31.5 31.0 30.5 30.0 29.5 29.0 Longitude (º W) Data from Macedo et al, 1999
Temperature profile - - Azores Azores Temperature profile Front Front North South Temperature (ºC) 25 50 24 23 100 22 21 m) 150 20 Depth( 19 200 18 17 16 250 15 14 300 13 12 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 Distance (km) Data from Macedo et al, 1999
Salinity profile - - Azores Azores Salinity profile Front Front North South Salinity 36.8 50 36.7 36.6 100 36.5 ) Depth(m 150 36.4 36.3 200 36.2 36.1 250 36.0 35.9 300 35.8 35.7 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 Distance (km) Data from Macedo et al, 1999
Density profile - - Azores Azores Density profile Front Front North South Density 27.0 50 26.8 26.6 26.4 100 26.2 ) 26.0 m 150 pth( 25.8 25.6 De 200 25.4 25.2 250 25.0 24.8 24.6 300 24.4 24.2 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 Distance (km) Data from Macedo et al, 1999
Chlorophyll a a profile profile - - Azores Azores Chlorophyll Front Front South North Chl a (mg m-3) 0.26 50 0.24 0.22 100 0.20 0.18 Depth(m) 0.16 150 0.14 0.12 200 0.10 0.08 250 0.06 0.04 300 0.02 0.00 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 Distance (km) Data from Macedo et al, 1999
Vertical profiles for temperature, chlorophyll a Vertical profiles for temperature, chlorophyll a and nitrate - - Azores Front Azores Front and nitrate 0 Temperature (ºC) 25 0 Temperature (ºC) 25 0 0.42 0 0.42 Chlorophyll a (mg m -3 ) Chlorophyll a (mg m -3 ) Nitrate (mmol m -3 ) Nitrate (mmol m -3 ) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 0 0 12 12 T NO 3 - 24 24 T 36 36 48 48 60 60 72 72 84 84 Depth (m) 96 96 108 108 120 120 132 132 Chl a 144 144 156 156 168 168 NO 3 - 180 180 192 192 204 204 Chl a 216 216 228 228 240 240 252 252 Data from Macedo et al, 1999 South North
Tides and tide generating forces Tides and tide generating forces North pole Quadrature Sun To Sun Syzygy • Mass of the earth = 80X moon • Mass of sun = 27 X 10 6 moon • Sun-earth = 400X moon-earth
Tides and tide generating forces Tides and tide generating forces Model for a daily tide Model for a daily tide 24h Tidal bulge Earth Moon F = GMm r 2
Tides and tide generating forces Tides and tide generating forces Model for a semi semi- -diurnal diurnal tide tide Model for a 29.5 days Earth Moon Centre of rotation Is 1600km inside the earth (1/4 radius), and is the point about which the forces are balanced
Tides and tide generating forces Tides and tide generating forces Model for tidal delay tidal delay Model for Lunar orbit: 29.5 days 24h Earth Moon Every day the moon moves approximately 360/30 degrees, i.e. 12 o . The time on earth equivalent to 1 degree is 24 * 60 / 360 = 4 minutes, therefore the time lag is 12 * 4 = 48 minutes
Early tide gauges and prediction equipment Early tide gauges and prediction equipment Tide gauge at Anchorage, Alaska Mechanical tide prediction machine NOAA website
Mechanical tide prediction equipment Mechanical tide prediction equipment NOAA website
Recommend
More recommend