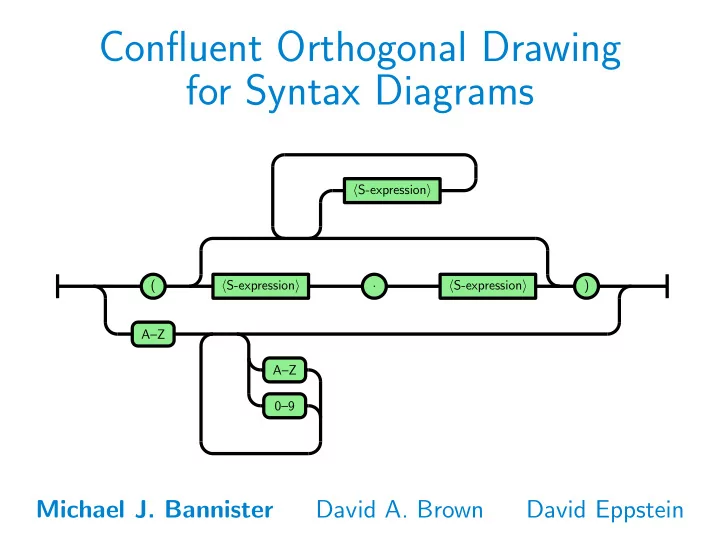

Confluent Orthogonal Drawing for Syntax Diagrams � S-expression � ( � S-expression � � S-expression � ) . A–Z A–Z 0–9 Michael J. Bannister David A. Brown David Eppstein
Context-Free Grammars LISP 1.5 S-expression: ( defun factorial (x) ( if ( zerop x) 1 ( * x (factorial (- x 1))))) Grammar for LISP 1.5: � S-expression � → � atomic symbol � | ( � S-expression � . � S-expression � ) | ( � S-expression list � ) � S-expression list � → ǫ | � S-expression �� S-expression list � � atomic-symbol � → � LETTER �� atom part � � atom part � → ǫ | � LETTER �� atom part � | � number �� atom part � � LETTER � → A | B | C | · · · | Z � number � → 0 | 1 | 2 | · · · | 9
Syntax Diagrams Syntax Diagram from the CANDE Information Manual
Syntax Diagrams Syntax Diagram from the Pascal User Manual and Report
Syntax Diagrams JSON Data Interchange Standard
Extended Backus–Naur Form • More expressive than BNF • More expressive than BNF • Notation for lists: • Notation for lists: natural number = digit { digit } natural number = digit { digit } • Notation for optionals: • Notation for optionals: integer = [ ”-” ] natural number integer = [ ”-” ] natural number • Direct translation to syntax diagrams − − digit
Extended Backus–Naur Form • More expressive than BNF • More expressive than BNF • Notation for lists: • Notation for lists: natural number = digit { digit } natural number = digit { digit } • Notation for optionals: • Notation for optionals: integer = [ ”-” ] natural number integer = [ ”-” ] natural number • Direct translation to syntax diagrams − − digit
Extended Backus–Naur Form • More expressive than BNF • More expressive than BNF • Notation for lists: • Notation for lists: natural number = digit { digit } natural number = digit { digit } • Notation for optionals: • Notation for optionals: integer = [ ”-” ] natural number integer = [ ”-” ] natural number • Direct translation to syntax diagrams − − digit
Hand Optimizations JSON Data Interchange Standard
Software Pipeline BNF Grammar Layered Drawing NFA Conversion Global Optimization Confluent Conversion Local Optimization Syntax Diagram
NFA Representation Grammar for LISP 1.5: � S-expression � → � atomic symbol � | ( � S-expression � . � S-expression � ) | ( � S-expression list � ) � S-expression list � → ǫ | � S-expression �� S-expression list � � atomic-symbol � → � LETTER �� atom part � � atom part � → ǫ | � LETTER �� atom part � | � number �� atom part � � LETTER � → A | B | C | · · · | Z � number � → 0 | 1 | 2 | · · · | 9
NFA Representation � S-expression � → � atomic symbol � | ( � S-expression � . � S-expression � ) | ( � S-expression list � )
NFA Representation � S-expression list � → ǫ | � S-expression �� S-expression list �
NFA Representation
NFA Representation � S-expression � → � atomic symbol � | ( � S-expression � . � S-expression � ) | ( � S-expression list � ) � S-expression list � → ǫ | � S-expression �� S-expression list � � atomic-symbol � → � LETTER �� atom part � � atom part � → ǫ | � LETTER �� atom part � | � number �� atom part � � LETTER � → A | B | C | · · · | Z � number � → 0 | 1 | 2 | · · · | 9
Global Optimization Can modify the entire NFA representation NFA state minimization • Combine graphs to reduce states
Global Optimization Nesting!
Local Optimizations Changes one st -digraph at a time NFA state minimization: • Hard to approximate • Existing heuristic applicable, but complicated and slow • Use fast heuristics, motivated by hand optimizations Crossing minimization: • Add states to reduce crossings
Local Optimizations Loop back!
Local Optimizations Parallel state elimination!
Local Optimizations Confluent pinch!
Optimization Global Optimization Local Optimization
Sugiyama Layering
Sugiyama Layering
Sugiyama Layering
Confluent Conversion
Experimental Results Subset of JSON grammar
Experimental Results Pascal Type Declarations
Conclusion Software pipeline producing syntax diagrams, which optimizes the input grammar and uses standard GD techniques for final drawing. Further directions: • Compare our simple heuristics against existing NFA min heuristics • Reduce bends and crossings in layering • Perform user studies
Conclusion Software pipeline producing syntax diagrams, which optimizes the input grammar and uses standard GD techniques for final drawing. Further directions: • Compare our simple heuristics against existing NFA min heuristics • Reduce bends and crossings in layering • Perform user studies Thank you!
Recommend
More recommend