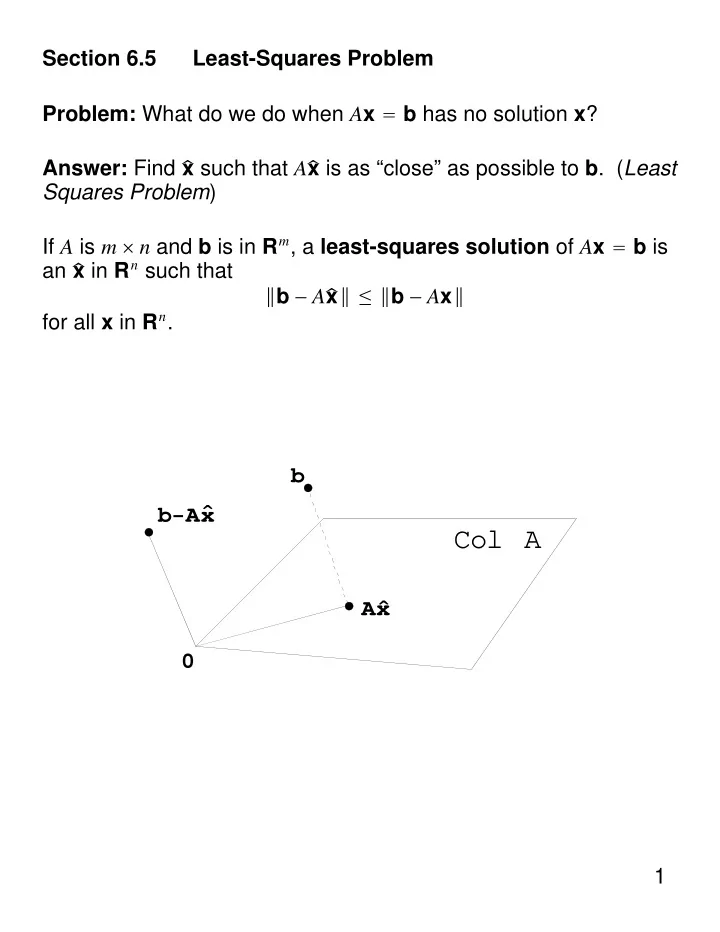

Section 6.5 Least-Squares Problem Problem: What do we do when A x = b has no solution x ? Answer: Find x such that A x is as “close” as possible to b . ( Least Squares Problem ) If A is m × n and b is in R m , a least-squares solution of A x = b is x in R n such that an ‖ b − A x ‖ ≤ ‖ b − A x ‖ for all x in R n . b ˆ b − Ax Col A Ax ˆ 0 1
Let W = Col A where A is m × n and A = . a 1 a 2 ⋯ a n Suppose b is in R m and b = proj W b . b z W ˆ b 0 b is the point in W = Col A closest to b 2
b b − Ax ˆ Col A Ax ˆ 0 x is a vector in R n such that b = A Since b is in Col A , then x . 3
By the Orthogonal Projection Theorem, z is in W where z = b − A x . Then b − A x is orthogonal to every column of A . Meaning that T b − A T b − A T b − A a 1 x = 0 a 2 x = 0 a n x = 0 ⋯ T a 1 0 T a 2 0 b − A x = ⋮ ⋮ a n T 0 A T b − A x = 0 A T b − A T A x = 0 A T A x = A T b (normal equations for x ) THEOREM 13 The set of least squares solutions of A x = b is the set of all solutions of the normal equations A T A x = A T b . 4
EXAMPLE: Find a least squares solution to the inconsistent system A x = b where 2 0 1 and b = . A = 0 1 2 2 2 3 Solution: Solve A T A x = A T b after first finding A T A and A T b . 2 0 2 0 2 8 2 A T A = 0 1 = 0 1 2 4 3 2 1 1 2 0 2 8 A T b = 2 = = 0 1 2 8 3 So solve the following: 8 2 x 1 8 = 4 3 x 2 8 1 1 1 0 8 2 8 2 2 x = ∼ 4 3 8 0 1 2 2 5
When A T A is invertible, A T A x = A T b A T A − 1 A T A x = A T A − 1 A T b x = A T A − 1 A T b So in the last example, − 1 3 − 1 8 2 A T A − 1 = 16 8 = − 1 1 4 3 4 2 and 3 − 1 1 8 x = A T A − 1 A T b = 16 8 2 = − 1 1 8 2 4 2 6
THEOREM 14 The matrix A T A is invertible if and only if the columns of A are linearly independent. In this case, the equation A x = b has only one least-squares solution x , and it is given by x = A T A − 1 A T b . least-squares error = ‖ b − A x ‖ From the last example, 1 2 0 1 1 and A 2 b = x = 2 0 1 2 = 2 3 2 2 5 1 1 least-squares error = ‖ b − A x ‖ = = 2 2 2 − 3 5 7
b b − Ax ˆ Col A Ax ˆ 0 For another way to compute x , see Theorem 15 (page 414) and Example 5, page 415. 8
Recommend
More recommend