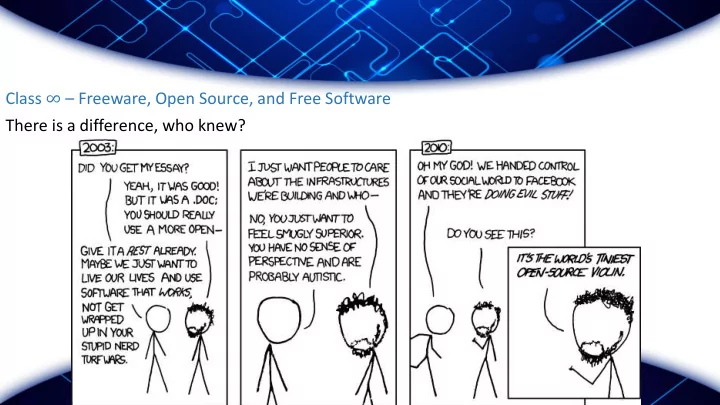

Class ∞ – Freeware, Open Source, and Free Software There is a difference, who knew?
Not otes • Homework graded • I’m SORRY • Homework 4&5: no homework this week • Midterms • How was it? Honestly… • Random, mostly unrelated note on free textbooks.
Troja ojan Hor orses Appear to be useful software, but like in the myth, conceal malware to your system. Unlike previous viruses, does not necessarily self replicate • Used to create “botnets” or “zombie armies”, with which criminals can: • Send their own spam or scams • Malware such as Key Logging • Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
(D (Dis istr tributed) Den enia ial of of Ser ervic ice e Attack acks ([D ([D]DoS) ) an attempt to make an online service unavailable by overwhelming it with traffic (from multiple sources) http://blog.lifars.com/2015/08/20/ddos-attacks- are-stronger-more-in-number-than-ever/
Man an in in the the Mid iddle
Soc ocia ial l En Engin ineering An attack that relies heavily on human interaction and often involves tricking people into breaking normal security procedures. • Baiting : Offering the user something, such as a free download, while hiding malware or obtaining login information • 2006 Steve Stasiukonis, VP and founder of Secure Network Technologies, dropped USBs in a client’s parking lot that were infected with a Trojan Horse key logger, and was able to obtain a number of employee credentials. • Informal Survey: Employees will give away their password for a cheap pen (granted, took place in 2003)
Phi hishin ing (S (Socia ial l En Engin ineerin ing) • Phishing • “Fishing” for personal information • Misdirects users • http://www.it.cornell.edu/security/phishbowl.cfm
Phi hishin ing (S (Socia ial l En Engin ineerin ing)
Top opic ic Swit itch!
Moving on… Question • What does it mean to be Open Source?
Moving on… Question What does it mean to be Open Source? • OPEN SOURCE • The term "open source" refers to something that can be modified because its design is publicly accessible. https://opensource.com/resources/what-open-source • OPEN SOURCE INITIATIVE • As a global non-profit, The Open Source Initiative (OSI) protects and promotes Open Source, championing Open Source in society through education, collaboration, and infrastructure, stewarding the Open Source Definition (OSD), and preventing abuse of the Open Source concept. • http://opensource.org/definition
Next xt Que uestio ion What does it mean to be “Free Software”? • Free Software • Software that respects users' freedom and community. Roughly, it means that the users have the freedom to run, copy, distribute, study, change and improve the software . • Thus , “free software” is a matter of liberty, not price • https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.en.html
Las ast Que uestio ion So what then is freeware ?
Som ome His istory ry UNIX : fancy OS • Created by AT&T / Bell Labs early 1970s after attempting Multics ("Multiplexed Information and Computing Service") • Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, M. D. McIlroy, and J. F. Ossanna decided to continue on “text editor program”, instead they created “UNICS (UNiplexed Information and Computing Service) ” • “Revolutionary” because, OS was coded in C • Meaning it can outlive the hardware it was built on
Som ome His istory ry UNIX : fancy OS – Explodes in 70s-80s • 1949 - AT&T involved in an antitrust action with Department of Justice • Price-fixing • Monopoly on telephones • Settled quietly. Important to us, there was a provision that Bell Systems patents be licensed to competitors on request (note, not give away for free, but allow others access to pay for a license of the code)
Som ome His istory ry GNU Operating System : G NU’s N ot U nix • 1983 – Richard Stallman (rms) created GNU OS, built on the principle that software should be “free” (free as in free speech, not free as in free beer). • Four Freedoms: 1. Run the program however you want 2. Freedom to understand how the program works (need access to source code) 3. Freedom to redistribute copies 4. Freedom to make improvements and share improvements.
Som ome His istory ry Linux : • 1991 – Linus Torvalds • Wanted to call it Freax = " free” + "freak” + " x" (as an allusion to Unix)
(d (dis istro fl flavor for or thi this cl class) TAIL ILS • Comes with default most secure settings • Uses ToR and I2P • Encryptions wherever possible • Boots from usb/cd, does not alter host computer OS in any way, leaves no trace on machine
Fr Free ee Soft oftware vs s Ope pen Sou ource Open source is a development methodology; free software is a social movement ~Richard Stallman
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ag1AKIl_2GM
Reference to o Amaz azon and and 1984 • Amazon remotely removed 1984 and Animal Farm from kindle devices from users who had legitimately purchased books • These books were added to Amazon by a company that did not have the rights to the books • http://www.nytimes.com/2009/07/18/technology/companies/18amazon.htm l?_r=0 • The issue: “I never imagined that Amazon actually had the right, the authority or even the ability to delete something that I had already purchased .” - Charles Slater
Disc iscussio ion Poi oint • If you bought a bootleg paper copy of 1984, Amazon could not break into your house to take it back. Is this different? Is it ok because it was not legitimately purchased? • Who is responsible for these infringements? The customer? Amazon? The Seller?
Disc iscussio ion Poi oint How much right do you have to know about the programs that are running on your computer? How much details about the programs? https://www.pidder.de/blog/2010/03/online- privacy-comic/?lang=en
Recommend
More recommend