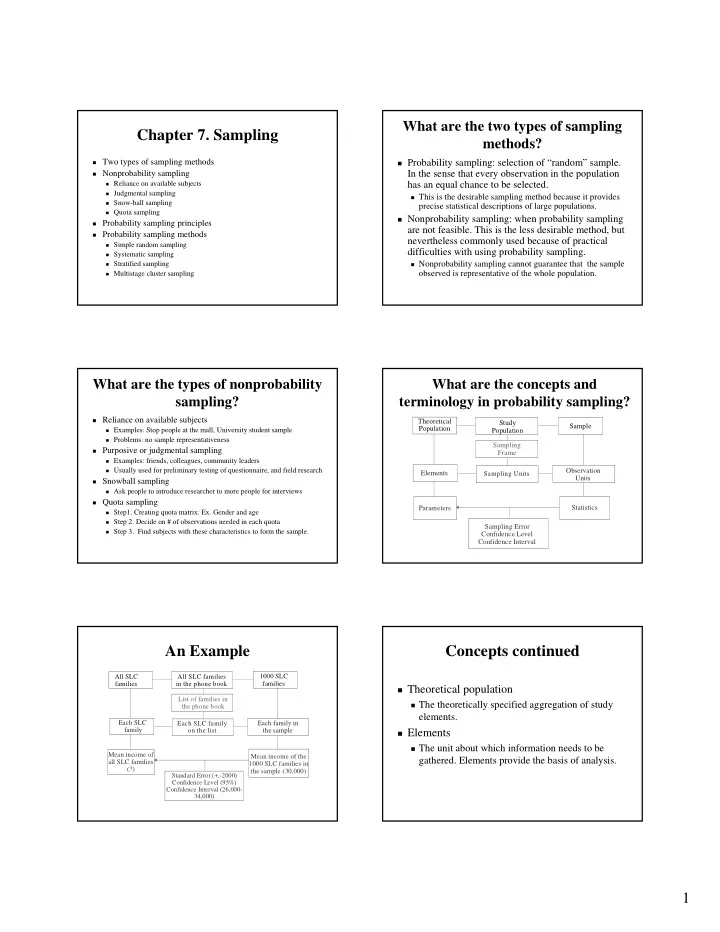

What are the two types of sampling What are the two types of sampling Chapter 7. Sampling Chapter 7. Sampling methods? methods? � Two types of sampling methods Two types of sampling methods � Probability sampling: selection of “random” sample. Probability sampling: selection of “random” sample. � � � Nonprobability sampling Nonprobability sampling In the sense that every observation in the population In the sense that every observation in the population � � Reliance on available subjects Reliance on available subjects has an equal chance to be selected. � has an equal chance to be selected. � Judgmental sampling Judgmental sampling � � This is the desirable sampling method because it provides This is the desirable sampling method because it provides � � Snow Snow- -ball sampling ball sampling � precise statistical descriptions of large populations. precise statistical descriptions of large populations. � Quota sampling Quota sampling � � Nonprobability sampling: when probability sampling Nonprobability sampling: when probability sampling � � Probability sampling principles Probability sampling principles � are not feasible. This is the less desirable method, but are not feasible. This is the less desirable method, but � Probability sampling methods Probability sampling methods � nevertheless commonly used because of practical nevertheless commonly used because of practical � Simple random sampling Simple random sampling � difficulties with using probability sampling. difficulties with using probability sampling. � Systematic sampling Systematic sampling � � Stratified sampling Stratified sampling � Nonprobability sampling cannot guarantee that the sample Nonprobability sampling cannot guarantee that the sample � � observed is representative of the whole population. observed is representative of the whole population. � Multistage cluster sampling Multistage cluster sampling � What are the types of nonprobability What are the concepts and What are the types of nonprobability What are the concepts and sampling? terminology in probability sampling? sampling? terminology in probability sampling? � Reliance on available subjects Reliance on available subjects � Theoretical Study Sample Population � Examples: Stop people at the mall, University student sample Examples: Stop people at the mall, University student sample Population � � Problems: no sample representativeness Problems: no sample representativeness � Sampling � Purposive or judgmental sampling Purposive or judgmental sampling � Frame � Examples: friends, colleagues, community leaders Examples: friends, colleagues, community leaders � � Usually used for preliminary testing of questionnaire, and field Usually used for preliminary testing of questionnaire, and field research research Each SLC family Observation � Elements Sampling Units on the list Units � Snowball sampling Snowball sampling � � Ask people to introduce researcher to more people for interviews Ask people to introduce researcher to more people for interviews � � Quota sampling Quota sampling � Parameters Statistics � Step1. Creating quota matrix: Ex. Gender and age Step1. Creating quota matrix: Ex. Gender and age � � Step 2. Decide on # of observations needed in each quota Step 2. Decide on # of observations needed in each quota � Sampling Error � Step 3. Find subjects with these characteristics to form the sa Step 3. Find subjects with these characteristics to form the sample. mple. � Confidence Level Confidence Interval An Example An Example Concepts continued Concepts continued All SLC All SLC families 1000 SLC families families in the phone book � Theoretical population Theoretical population � List of families in � The theoretically specified aggregation of study The theoretically specified aggregation of study � the phone book elements. elements. Each SLC Each SLC family Each family in Each SLC family family on the list the sample on the list � Elements Elements � � The unit about which information needs to be The unit about which information needs to be � Mean income of Mean income of the gathered. Elements provide the basis of analysis. gathered. Elements provide the basis of analysis. all SLC families 1000 SLC families in (?) the sample (30,000) Standard Error (+,-2000) Confidence Level (95%) Confidence Interval (26,000- 34,000) 1
Concepts continued Concepts continued Concepts continued Concepts continued � Study population Study population - - the aggregation of elements the aggregation of elements � Sample Sample � � from which the sample is actually selected. from which the sample is actually selected. � A selected group of elements of the study A selected group of elements of the study � population about which information is gathered. population about which information is gathered. � Sampling frame Sampling frame - - the actual list of sampling the actual list of sampling � units from which the sample is selected. � Sampling unit Sampling unit units from which the sample is selected. � � The element considered for selection of sampling The element considered for selection of sampling � � Observation unit Observation unit � � An element from which information is collected An element from which information is collected � Probability Sampling Theory Probability Sampling Theory Concepts continued Concepts continued and Sampling Distribution and Sampling Distribution � Parameter Parameter � The ultimate purpose of sampling is The ultimate purpose of sampling is � � � A summary description of a given variable in a population A summary description of a given variable in a population � � To select a set of elements from a population in To select a set of elements from a population in � � Statistic Statistic � such a way that descriptions of those elements such a way that descriptions of those elements � A summary description of a given variable in a sample A summary description of a given variable in a sample accurately portray the parameters of the total accurately portray the parameters of the total � population from which the sample is selected. population from which the sample is selected. � Sampling error Sampling error � � When using statistics to estimate parameters, the estimation When using statistics to estimate parameters, the estimation � Probability sampling Probability sampling � � is seldom exact. The error margin is called sampling error. is seldom exact. The error margin is called sampling error. � Can improve our chance to achieve this goal. Can improve our chance to achieve this goal. � (If you are familiar with the concept of standard err (If you are familiar with the concept of standard err � Is a very well developed sampling method backed Is a very well developed sampling method backed � up by probability theory. up by probability theory. Probability Sampling Theory Probability Sampling Theory Basic Rules of Sampling Basic Rules of Sampling � Random selection Random selection � The larger the sample size, the better chance The larger the sample size, the better chance � � we have to get an accurate estimate of the we have to get an accurate estimate of the � Each element has an equal chance of being Each element has an equal chance of being � selected. population parameter. population parameter. selected. � Reasons of random selection Reasons of random selection � The more homogeneous the population, the The more homogeneous the population, the � � smaller the sampling error. smaller the sampling error. � Avoid conscious or unconscious bias by the Avoid conscious or unconscious bias by the � researcher. researcher. � Offer access to probability theory, which provides Offer access to probability theory, which provides � the basis for estimation of parameter and the basis for estimation of parameter and estimation error. estimation error. 2
Recommend
More recommend