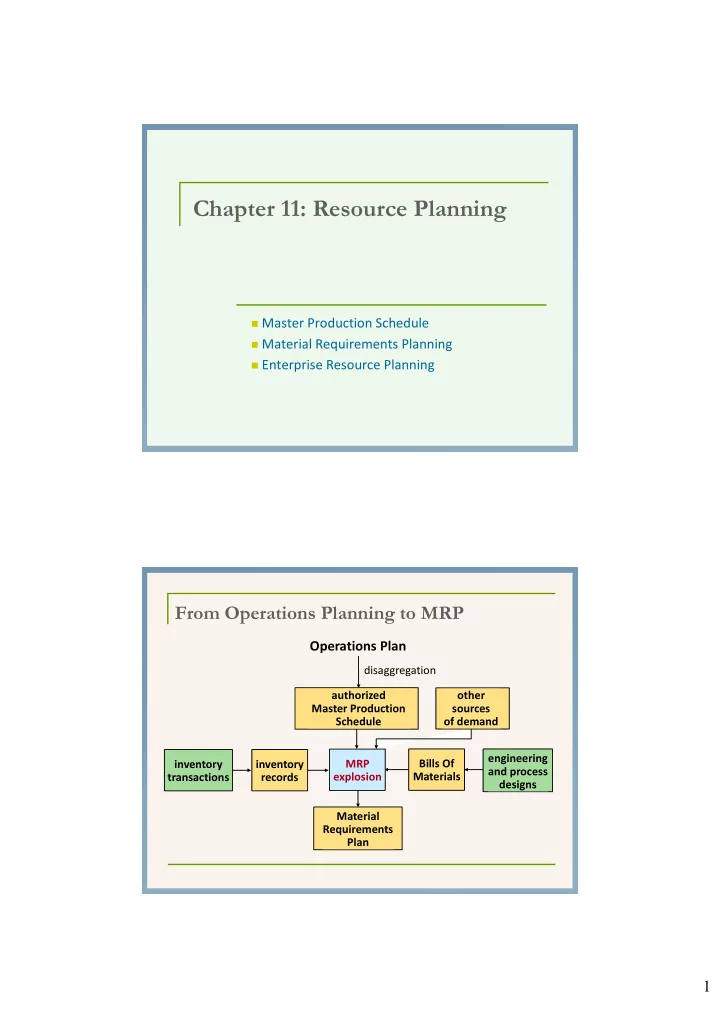

Chapter 11: Resource Planning Master Production Schedule Material Requirements Planning Enterprise Resource Planning From Operations Planning to MRP Operations Plan disaggregation authorized other Master Production sources Schedule of demand engineering MRP Bills Of inventory inventory and process explosion Materials transactions records designs Material Requirements Plan 1
Master Production Scheduling A part of the production plan that details how many end items will be produced within specified periods of time ( 通常以週為單位 ) 六七月預定 五月 六月 七月 八月 product 產量根據接 11000 8800 9800 11000 生產目標 單比例計算 family 6500 3600 2800 1200 A 型已接訂單 4500 3600 2100 1000 B 型已接訂單 八月預定產 五月接單額滿, 6500 4400 5600 6600 A 型預定產量 量根據歷史 預定產量取決於 B 型預定產量 4500 4400 4200 4400 銷售比例約 實際訂單 為6:4計算 MPS 五月 六月 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 A 型產量 2400 0 2400 1700 1100 1100 1100 1100 0 2400 0 2100 1100 1100 1100 1100 B 型產量 Rough‐Cut Capacity Planning level scheduling 3 Developing a Master Production Schedule 1/4 Step 1: Calculate projected on‐hand inventories 期初庫存 本期產出量 預估需求 Projected on-hand On-hand MPS quantity Projected = + – inventory at end inventory at due at start requirements of this week end of last week of this week this week where: Projected requirements = Max(Forecast, Customer Orders Booked) 2
Developing a Master Production Schedule 2/4 Item: Ladder-back chair April Quantity Forecast is less than booked on Hand: 55 1 2 orders in week 1; projected on‐ hand inventory balance Forecast 30 30 = 55 + 0 – 38 = 17. Customer orders 38 27 (booked) Forecast exceeds booked orders in Projected week 2; projected on‐hand on-hand 17 –13 inventory = 17 + 0 – 30 = –13. The inventory shortage signals a need to schedule an MPS quantity in week 2. MPS quantity 0 MPS start Developing a Master Production Schedule 3/4 Step 2: Determine the timing and size of MPS quantities • The goal is to maintain a nonnegative projected on‐hand inventory balance at the end of each period. • As shortages in inventory are detected, MPS quantities should be scheduled to cover them. ( 如果產能許可 ) • At the end of week 2: 17 chairs in + MPS quantity Forecast of Projected inventory at the – = of 150 chairs 30 chairs Inventory end of week 1 = 137 chairs 3
Developing a Master Production Schedule 4/4 Item: Ladder-back chair Order Policy: 150 units Lead Time: 1 week April May Quantity on Hand: 55 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Forecast 30 30 30 30 35 35 35 35 Customer 38 27 24 8 0 0 0 0 orders booked Projected on-hand 17 137 107 77 42 7 122 87 inventory MPS quantity 0 150 0 0 0 0 150 0 MPS start 150 0 0 0 0 150 0 0 The time needed to assemble 150 chairs The MPS quantity is needed to avoid a is 1 week. The assembly department must shortage of 17 – 30 = ‐13 chairs in week start assembling chairs in week 1 to have 2. On‐hand inventory balance = 17 + them ready by week 2. 150 – 30 = 137. MPS and Available-to-Promise Available‐to‐Promise ( ATP ) Quantities The quantity of end items that marketing can promise to deliver on specific dates 可允諾訂購量 ATP =Initial Inventory ‐ customer orders until 1st production. ATP = MPS quantity – customer orders until next production. ATP projected on‐hand inventory. Freezing the MPS Disallow changes to the near‐term portion of the MPS Reconciling the MPS with Sales and Operations Plans Capacity is limited and forecasts may change. 4
Available-to-Promise Item: Ladder-back chair Order Policy: 150 units Lead Time: 1 week April May Quantity 55 on Hand: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Forecast 30 30 30 30 35 35 35 35 Customer 38 27 24 8 0 0 0 0 orders booked Projected on-hand 17 137 107 77 42 7 122 87 inventory MPS quantity 0 150 0 0 0 0 150 0 MPS start 150 0 0 0 0 150 0 0 ATP 17 91 ATP=55+0‐38=17 ATP=150‐(27+24+8+0)=91 Materials Requirements Planning A computerized information system developed to help manage dependent demand inventory and schedule replenishment orders. Dependent demand : The demand for an item that occurs because the quantity required varies with the production plans for other items. Parent : An product that is manufactured from one or more components Component : An item that is transformed into part of one or more parents MRP Explosion : A process that converts the requirements of final products into a time plan that specifies the replenishment schedules of all the subassemblies, components, and raw materials needed to produce final products 5
MRP Inputs: Bill of Materials A record of all the components of a final product, the parent‐ component relationships, and the usage quantities. A Level 0 Ladder‐back chair Back Level 1 slats Back Seat B (1) C (1) D (2) E (4) legs cushion Ladder‐back Seat Front Leg subassembly subassembly legs supports Front legs F (2) G (4) H (1) I (1) Level 2 Back legs Back slats Seat frame Seat cushion Leg Seat‐frame supports boards J (4) Seat‐frame Level 3 boards MRP Input: Inventory Records A record that shows an item’s lot‐size policy, lead time, and various time‐phased data. 6
MRP Explosion A Ladder‐back chair B (1) C (1) D (2) E (4) Ladder‐back Seat Front Leg subassembly subassembly legs supports MPS lot size = 25 chairs F (2) G (4) H (1) I (1) Inventory on hand Back legs Back slats Seat frame Seat cushion 20D, 20F, 10H J (4) Seat‐frame 30F, 100G 50F, 100G 25B boards 15H, 25I 60J, 25I 25H, 25I 25C 30D 50D 100E MRP Terminology Gross requirements: total demand of an item from all parents. Scheduled receipts: order that has been placed but not yet received or completed. 先前已發出的訂單或工單,期初將收到的數量 Projected on‐hand inventory (期末庫存) Gross Projected on-hand Inventory on Scheduled or – inventory balance requirements = hand at end of + planned receipts at end of week t in week t week t –1 in week t Planned receipts: order that should be received from the shop or the supplier. 需要在該期期初進貨或完工的數量 Planned order releases: order for a specified quantity of an item is to be issued to the shop or the supplier . 需要在該期下單或開工的數量 7
April May Explosion 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Ladder‐back chair 150 150 part commonality 120 120 Kitchen chair Lot Size: 230 units Item: C (Seat subassembly) Lead Time: 2 weeks Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 150 120 150 120 Gross requirements 0 0 0 0 230 Scheduled receipts 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 37 117 Projected 117 117 –3 –3 –153 –273 –273 on‐hand inventory Planned receipts Planned order releases 37 + 230 – 150 = 117 units. MRP Explosion Lot‐sizing rule: Fixed Order Quantity Lot Size: 230 units Item: C (Seat subassembly) Lead Time: 2 weeks Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 120 120 Gross requirements 150 0 0 0 150 0 230 0 Scheduled receipts 0 0 0 0 0 0 37 117 227 187 Projected 227 77 187 117 117 on‐hand inventory 230 230 Planned receipts 230 230 Planned order releases 117+230–120=227 77+230–120=187 8
Lot-sizing Rule: Lot-for-Lot (L4L) Explosion of Seat Subassembly Item C : Seat subassembly Lot size: 230 Week Lead time: 2 weeks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Gross requirements 150 0 0 120 0 150 120 0 Planned 230 230 receipts Planned 230 230 order releases Usage quantity: 1 Usage quantity: 1 Item H : Seat frames Item I : Seat cushion Lot size: 300 Lot size: L4L Week Week Lead time: Lead time: 2 weeks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Gross Gross 230 230 230 230 requirements requirements Scheduled Scheduled 300 receipts receipts Projected Projected 40 40 110 110 110 180 180 180 180 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 inventory inventory Planned Planned 300 230 230 receipts receipts Planned order Planned order 230 300 230 releases releases 9
Explosion of Seat Frames Item H : Seat Frames Lot size: 300 Week Lead time: 1 week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Gross 230 230 requirements Planned 300 receipts 300 Planned order releases Usage quantity: 4 Item J : Seat frames board Lot size: 1500 Week Lead time: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 week Gross 1200 requirements Scheduled receipts Projected 200 200 200 500 500 500 500 500 500 inventory Planned 1500 receipts Planned order 1500 releases Outputs from MRP MRP Explosion Routings and time standards 10
Recommend
More recommend