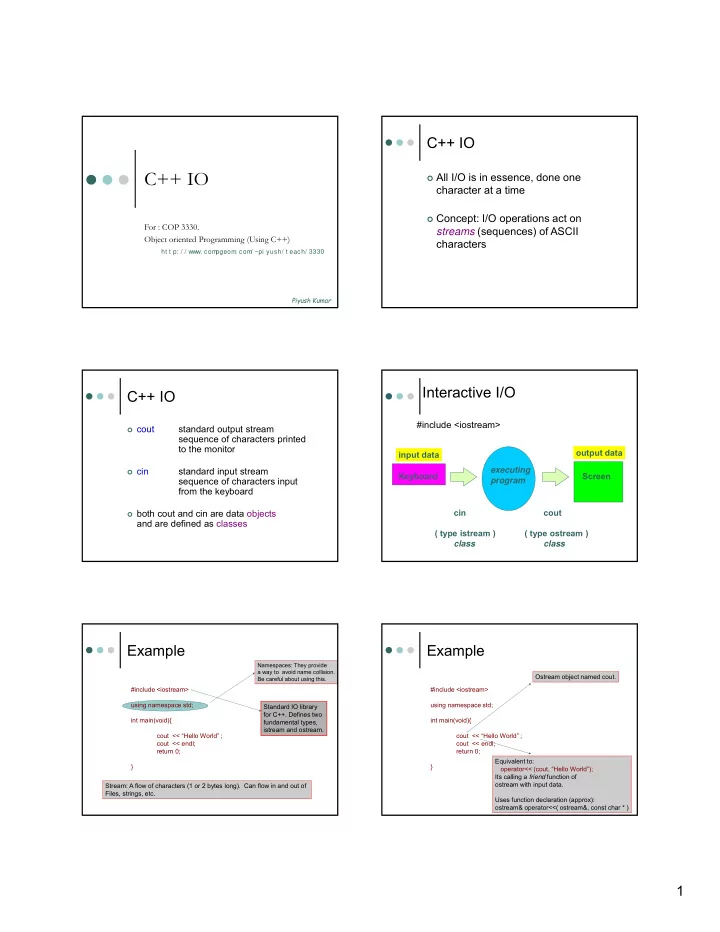

C++ IO C++ IO All I/O is in essence, done one character at a time Concept: I/O operations act on For : COP 3330. streams (sequences) of ASCII Object oriented Programming (Using C++) characters ht t p: / / www. com pgeom . com / ~pi yush/ t each/ 3330 Piyush Kumar Interactive I/O C++ IO #include <iostream> cout standard output stream sequence of characters printed to the monitor output data input data cin standard input stream executing Keyboard Screen sequence of characters input program from the keyboard cin cout both cout and cin are data objects and are defined as classes ( type istream ) ( type ostream ) class class Example Example Namespaces: They provide a way to avoid name collision. Ostream object named cout. Be careful about using this. #include <iostream> #include <iostream> using namespace std; using namespace std; Standard IO library for C++. Defines two int main(void){ int main(void){ fundamental types, istream and ostream. cout << “Hello World” ; cout << “Hello World” ; cout << endl; cout << endl; return 0; return 0; Equivalent to: } } operator<< (cout, “Hello World”); Its calling a friend function of ostream with input data. Stream: A flow of characters (1 or 2 bytes long). Can flow in and out of Files, strings, etc. Uses function declaration (approx): ostream& operator<<( ostream&, const char * ) 1
Example Special Output Characters invokes a manipulator function called endl. endl looks something like this: ostream& endl( ostream& os) { os << '\n'; \n new line #include <iostream> os.flush(); \t tab return os; using namespace std; } \b backspace int main(void){ \r carriage return cout << endl; return 0; Equivalent Compiler statement: \ ʹ single quote std::cout.operator<<( } std::endl(std::cout) \ ʺ double quote ); \\ backslash Scope Operator for namespaces. Stream IO headers A Stream iostream -- contains basic information A flow of characters. required for all stream I/O operations Buffers: IO to streams goes thru a iomanip – used for performing formatted I/O buffer. C++ allows you change the with stream manipulators default behavior of associated buffers. fstream – used for performing file I/O State: Each stream is associated with operations a state indicating various things like if stringtream -- used for performing in- an error has occurred or not… memory I/O operations (i.e., into or from strings in memory) C++ IO Class hierarchy C++ IO Class hierarchy ios ios istream ostream streambuf istream ostream streambuf cin cout ifstream istringstream ostringstream ofstream ifstream istringstream ostringstream ofstream stringbuf stringbuf filebuf filebuf 2
C++ IO Hierarchy Other Predefined Streams The ios hierarchy defines the cerr - the standard destination for interface of the IO system. error messages (often the terminal window). Output through this stream The streambuf hierarchy defines the is unit-buffered, which means that implementation of the IO system, characters are flushed after each mostly provides the facilities of block of characters is sent. buffering and byte-level I/O clog - like cerr, but its output is buffered. Formatting with predefined Stream IO streams. Inside ios << (left-shift operator) Remember: Due to inheritance, anything you learn about formatting IO Overloaded as stream insertion operator with predefined streams (cin, cout, clog, cerr) also applies to file IO and >> (right-shift operator) string IO. Overloaded as stream extraction operator Anything available or defined in the Both operators used with cin , cout , ios class is available everywhere in cerr , clog , and with user-defined the IO subsystem. stream objects Example << operator cin >> cin >> Variabl able; << is overloaded to work on built-in cout << cout << Varia riable; le; types of C++. clog << clog << Variab riable; le; Can also be used to output user- Buffere Buffered defined types. cerr << cerr << Varia riable; le; Other interesting examples: Unbuffered, Unbuffered, pr prints V ints Variable able cout << ‘\n’; // newline. imme immediately diately. cout << “1+2=” << (1+2) << endl; Note: Note: Variable ty able types pes a are e availa ailable to ble to cout << endl; // newline. cout << flush; // flush the buffer. the compiler. the compile 3
<< operator Stream insertion: One char. Associates from left to right, and returns a reference to put member function its left-operand object (i.e. cout ). This enables Outputs one character to specified stream cascading. cout.put(‘C'); Outputs “char *” type as a string. Returns a reference to the object that called If you want to print the address, typecast it to (void *). it, so may be cascaded Example: char name[] = “cop3330”; cout.put( ‘C' ).put( '\n' ); cout << name << static_cast<void *>( name ) << endl; May be called with an ASCII-valued static_cast<void *>( name ) equivalent to ((void *) expression name) in C except that it happens at compile time. cout.put( 65 ); • Outputs A Input Stream Input Stream : Looping >> (stream-extraction) while (cin >> fname) Used to perform stream input Normally ignores whitespaces (spaces, tabs, newlines) Returns zero ( false ) when EOF is encountered, “>>” returns 0 ( false ) when EOF otherwise returns reference to the object from which it was invoked (i.e. cin ) encountered and loop terminates. • This enables cascaded input cin >> x >> y; >> controls the state bits of the stream failbit set if wrong type of data input badbit set if the operation fails Example Program Output #include <iostream> using std::cout; $ ./a.exe using std::cin; Enter the heights: (enter end of file to end): 72 using std::endl; 89 54 int main(void) { 33 int height = 0, maxheight = 0; 68 66 cout << "Enter the heights: (enter end of file to end): "; Tallest person's height = 89 while(cin >> height) if( height > maxheight) maxheight = height; cout << "Tallest person's height = " << maxheight << endl; return 0; } 4
istream member function: get istream member function: get get (array_name, max_size) ; char fname[256] char ch = cin.get(); cin.get ( fname, 256 ); Inputs a character from stream (even white spaces) and returns it. Read in up to 255 characters and inserts a null at the end of the string “fname". If cin.get( c ); a delimiter is found, the read terminates. Inputs a character from stream and The array acts like a buffer. The stores it in c delimiter is not stored in the array, but is left in the stream. istream member function: istream member functions: getline (array_name, max_size) ignore() char fname[256] cin.ignore ( ) ; cin.getline ( fname, 256 ); Discards one character from the input stream. cin.ignore (10) ; Same as get, except that getline Discards 10 characters. discards the delimiter from the stream. cin.ignore(256,’\n’); Discards 256 characters or newline, whichever comes first. istream member functions: FILE IO Example. peek(), putback() Copy File “first.txt” into “second.txt”. char ch = cin.peek ( ) ; #include <iostream> #include <fstream> Peeks into the stream’s next character. using namespace std; cin.putback (‘A’) ; int main(void) { Puts ‘A’ back in the stream. ifstream source("first.txt"); ofstream destin("second.txt"); char ch; while (source.get(ch)) destin<<ch; return 0; } 5
Slightly modified More IO functions #include <iostream> #include <fstream> read() using namespace std; cin.read(fname, 255); • Reads 255 characters from the input int main(void) { stream. Does not append ‘\0’. ifstream source("first.txt"); cout.write(fname,255); ofstream destin("second.txt"); • Writes 255 characters. char ch; gcount: returns the total number of while (source.peek() != EOF){ source.get(ch); characters read in the last input destin.put(ch); operation. } return 0; } C++ IO Class Hierarchy Another example Revisited #include <iostream> #include <sstream> ios What if I replace this #include <string> with istringstream? istream ostream using namespace std; cin cout int main() { ifstream ofstream int i; string line; while(getline(cin,line)){ stringstream sfstream(line); istringstream ostringstream iostream while (sfstream >> i){ cout << i << endl; } } return 0; } stringstream fstream stringstream operations #include <iomanip> Stream stringstream strm; Manipulators stringstream strm(mystring); Initializes strm with a copy of mystring. strm.str(); Returns the content of strm in string format. strm.str(s); Copies the string s into strm. Returns void. 6
Recommend
More recommend