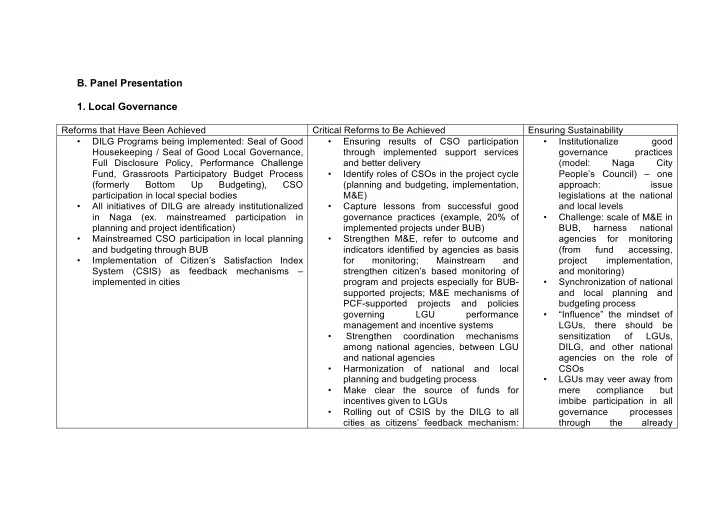

B. Panel Presentation 1. Local Governance Reforms that Have Been Achieved Critical Reforms to Be Achieved Ensuring Sustainability • DILG Programs being implemented: Seal of Good • Ensuring results of CSO participation • Institutionalize good Housekeeping / Seal of Good Local Governance, through implemented support services governance practices Full Disclosure Policy, Performance Challenge and better delivery (model: Naga City Fund, Grassroots Participatory Budget Process • Identify roles of CSOs in the project cycle People’s Council) – one (formerly Bottom Up Budgeting), CSO (planning and budgeting, implementation, approach: issue participation in local special bodies M&E) legislations at the national • All initiatives of DILG are already institutionalized • Capture lessons from successful good and local levels in Naga (ex. mainstreamed participation in governance practices (example, 20% of • Challenge: scale of M&E in planning and project identification) implemented projects under BUB) BUB, harness national • Mainstreamed CSO participation in local planning • Strengthen M&E, refer to outcome and agencies for monitoring and budgeting through BUB indicators identified by agencies as basis (from fund accessing, • Implementation of Citizen’s Satisfaction Index for monitoring; Mainstream and project implementation, System (CSIS) as feedback mechanisms – strengthen citizen’s based monitoring of and monitoring) implemented in cities program and projects especially for BUB- • Synchronization of national supported projects; M&E mechanisms of and local planning and PCF-supported projects and policies budgeting process governing LGU performance • “Influence” the mindset of management and incentive systems LGUs, there should be • Strengthen coordination mechanisms sensitization of LGUs, among national agencies, between LGU DILG, and other national and national agencies agencies on the role of • Harmonization of national and local CSOs planning and budgeting process • LGUs may veer away from • Make clear the source of funds for mere compliance but incentives given to LGUs imbibe participation in all • Rolling out of CSIS by the DILG to all governance processes cities as citizens’ feedback mechanism: through the already
Issues of sustainability and existing bodies complementation with other citizen’s • Continuous joint capacity based feedback initiatives building among CSOs, • Enforcement of existing mandates and LGUs, and national legal issuances that institutionalize government agencies (on expanded CSO participation in local focused areas: planning and budgeting, and M&E sensitization, partnership • Formalize and institutionalize citizen’s building) role in enhanced LGU Performance • Leverage technology in Assessment/Measurement Systems (ex. monitoring LGU project SGLG) implementation (ex. geo- tagging, e-Gov project of DOST and DBM, knowledge sharing using teleconferences)
2. Justice, Peace and Human Rights Reforms that Have Been Achieved Critical Reforms to Be Achieved Ensuring Sustainability A. Justice A. Justice For the Bangsamoro: - Appointment of reform-oriented personalities to prepare/capacitate the ensure sustainability of the reforms in the judiciary On the witness protection program (WPP): bureaucracy, the MILF and their – Maria Lourdes Sereno as Supreme Court Chief – Review of the WPP and increase its allies to govern/lead the new entity Justice and Marvic Leonen as Associate budgetary allocation Justice – Passage of the Whistle Blower Maximize the openness of the – Leila de Lima as Justice Secretary Protection Program government to engage the – Conchita Carpio-Morales as Ombudsmad broadest range of stakeholders – Amparo Cabotaje-Tang as Sandiganbayan On improving jail security: Presiding Justice – still to be allocated with larger budget – Promoting speedy resolution of cases and in order to effectively address security providing easier access to the courts and judicial concerns processes – SC issuance of an order for the guidelines on On providing support to the DOJ the use of judicial affidavits in court; Increase of (Cybercrime Office) salary of Public Attorneys; better perception – still to be allocated with larger budget towards Public Attorneys (relative to Public to effectively enforce the law and take Prosecutors) on its extensive responsibility – Improving the Witness Protection Program – Increase in the budget allocation for the On access to legal services: program - the government to also provide legal services (Php 175M in 2012) not just for the usual criminal cases; strengthening the PAO • Improving the jail security, upgrade the living conditions and intensifying development programs of the inmates B. Peace and Security – Allotment of Php 4.9B for the implementation Complete the FAB before the expiration of the Jail Management and Penology of the Aquino administration (BBL by 2014), Program of the Bureau of Jail Management and address challenges to inclusivity
and Penology • The process to be also subjected to the limits of the Constitution and other legal • Providing support to the DOJ limitations – Allotment of Php 9.7B for the passing of final • Contingency legislative support from resolutions on various cases under its the Congress to expedite the process jurisdiction to be fast-tracked of transformation – Setting –up of the National Justice Information System Convergence (tripartite review completion • a knowledge-based and knowledge –driven + ARMM governance reform + Bangsamoro) database portal that will solve information gaps and address collaboration issues in the criminal justice system Resume the peace talks between the – Creation of a cybercrime office with provision CPP-NPA-NDF and GPH that is time bound and of Php 5M as its budget agenda-based – Allotment of funds for salary differential of justices, signing a MoA restoring the Special On dealing with security issues involving foreign Allowances of the Judiciary and raised their states: salaries as per the Salary Standardization Law – Provide clear foreign policies; and III – Provide clear/standard approach – Php 2B has also been set aside under the in resolving issues involving MISCELLANEOUS PERSONNEL BENEFITS foreign states FUND to fill in vacant positions in the judiciary Realization of the reform agenda on the regulation of small arms and the existence of 2. Peace and Security private armed groups in the regions, specifically Winning the Peace in Mindanao. Review/revisit the amnesty program – pursuing a negotiated political settlement of all internal armed conflicts C. Human Rights – actions towards completion and implementation of the Comprehensive Peace Improvement of the performance in Agreement with the MILF leading to the combating extra judicial killings (politically enactment of the Bangsamoro Basic Law motivated killings of activists and journalists)
– resumption of the talks with the CPP-NPA- and enforced disappearances NDF that is time bound and agenda-based – steps towards the final completion of the Strengthen the Commission on Human Tripartite Implementation Review Process and Rights through the provision of its ensuring the inclusion of the MNLF legislative charter/enabling statutory basis agenda into the Bangsamoro Basic Law – signed final closure agreements with CPLA An interagency effort for general human and RPM-P/RPA/ABB now being completed rights (including normalization) Empowerment of the Presidential Human Community resilience against armed violence now being Rights Committee built – PAMANA implementation (9.85B for 408 Establish the Human Rights Compensation municipalities; 2010-2013) Board to start the process of giving – Transition Investment Support Program – compensation to the ML victims; pass the IRR of ARMM (8.5B) the compensation law Governance reforms in ARMM Strengthening the security sector: • Enacted the Modernization of AFP • Acquiring of naval ships and patrol fleet to increase the presence of the government in territorial seas The use of diplomatic means in resolving territorial claims / defending the country’s sovereignty. c. Human Rights Signing of the Anti-Enforced Disappearance act in 2012 Human rights engenderment trainings for the military and
the police as arranged by the Commission on Human Rights Passage of the compensation law for the victims of human rights violations during Martial Law AO 5 creating a high-level interagency committee tasked to assist in the speedy resolution of cases involving EJKs, EDs and torture Joint Operational Guidelines between the DOK and PNP on the investigation and case build-up of EJKs Monitoring, Reporting and Response System (MRRS) to protect children from different child rights violations in situations of armed conflict –EO 138, s.2013 AFP Guidelines on the Conduct of Activities inside or within the Premises of Schools and Hospitals ARMM Regional Human Rights Commission established
Recommend
More recommend