Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments Fabien Cardinaux cardinau@idiap.ch Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments p.1/33 Outline Problem of Face Recognition in Weakly
Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments Fabien Cardinaux cardinau@idiap.ch Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.1/33
� � � � � Outline Problem of Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments Traditional approaches for Face Recognition Databases and Evaluation Face Verification System based on Generative Models (GMM) Future Plan Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.2/33
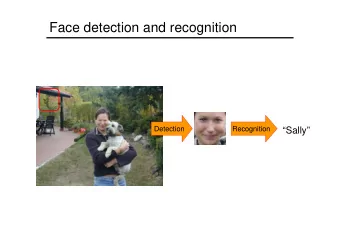
� � Face Verification vs Identification Face Identification (FI): Find the identity of a given person out of a pool of people Face Verification (FV): Authenticate the claimed identity based on the face image Recognition Verification (Who is he?) (Is he Mr X?) Yes/No Mr X Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.3/33
� � � � � � � � � Weakly Constrained Environment Applications: Access control Banking transaction authentication Advanced video surveillance Weakly Constrained Environment: Unrestricted head pose Various in lighting conditions Background change Problems Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.4/33
� � Challenge and Problems Wide variability between face images of the same identity (due to the expression, lighting and head position changes) Limited number of reference images available by identity => can not cover all possible variabilities Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.5/33
� � � � � Outline Problem of Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments Traditional approaches for Face Recognition Databases and Evaluation Face Verification System based on Generative Models (GMM) Future Plan Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.6/33
� � � � Face Recognition system Generally, a full face recognition system can be decomposed into four stages: Face detection : Find the position of the face in the image Normalization : Reduce variabilities in the face images. Illumination normalization and geometric normalization Feature extraction : Extract relevant information in the images Classification : Differs according to the specific task (identification or verification) Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.7/33
✞ ✟ � ✞ ✡ � ✟ ✞ ✝ ✞ ✝ ✠ Feature extraction (1/2) Holistic Representation Principal Component Analysis (PCA) : Projection is based on the directions of largest variance of the face population. Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) : More discriminant features than the PCA subspace. ✄✆☎ �✂✁ ✄✆☎ Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.8/33
� � � Feature extraction (2/2) Local representation Local PCA : Compute principal component of a set of sub-windows of images. The first p principal components were then used to filter the full images 2D Gabor Filters : Face is represented by outputs of Gabor filters at multiple scales, orientations, and spatial locations 2D DCT : Images analysed on a block by block basis. Each block is decomposed in terms of 2D Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) basis functions Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.9/33
� ✄ ✝ ✡ � ✟ � ✁ ✂ ✟ ✟ � ✝ ✝ ☛ ✟ � ✁ ✠ ✞ ✄ ✂ ✟ � ✁ ✂ ✄ ✝ ☞ ✄ ✝ ☎ ✂ � ✁ ☎ ✆ ✁ ✂ Classification Computation of a score corresponding to an opinion on the probe to be the identity . Face identification: (1) Face verification: Given a threshold , the claim is accepted when and rejected when . Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.10/33
� � � � Classification approaches Classification based on distance measures; e.g.: euclidean distance between the feature vector of the probe image and the feature vector of a reference image Elastic Graph Matching Discriminant classifier: MLP or SVM Probabilistic/Generative approach: GMM or HMM Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.11/33
� � � � � Outline Problem of Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments Traditional approaches for Face Recognition Databases and Evaluation Face Verification System based on Generative Models (GMM) Future Plan Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.12/33
� � � � � � � � � � Databases XM2VTS (295 subjects): Multimodal: Face and speech Protocol for face verification: Lausanne Protocol FERET (1199 subjects): Designed for face recognition different camera, lighting, head pose BANCA (52 subjects) : Multimodal database: Face and Speech Protocol for face verification Three different scenarios (controlled, degraded and adverse) Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.13/33
✁ � ✟ ☎ ✞ ✝ ✆ ✄☎ ✡ ✂ ✠ ✎ ✟ ☎ ✞ ✝ ✆ ✄☎ � ✂ ✠ ✏ � ✡ ✁ ✂ ✓ ✒ ✑ ✂ � ☎ ☞ ✡ ✡ ☎ ✎ ✍✎ ✝ ✄ ☎ ✂ ✡ ✁ ✂ ✠ ✟ ☎ ✞ ✝ ✆ ✄☎ ✁ ✁ ✔ � � � ✂ � ✂ � ✕ � ✄ ☎ ✝ ✡ ✡ ☎ ✎ ✍✎ ✞ ✟ ✡ ☎ ✟ ✆✌ ☞ ✠ ✟ ☎ ✞ ✝ ✆ � Evaluation of face verification systems Two types of errors: false acceptances (FA): The system accepts an impostor false rejections (FR): The system rejects a client To measure the performance of the system: ✁☛✡ Half Total Error Rate (HTER): Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.14/33
� � � � � Outline Problem of Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments Traditional approaches for Face Recognition Databases and Evaluation Face Verification System based on Generative Models (GMM) Future Plan Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.15/33
✁ ✝ ✂ ✁ ✆ ✄ ✂ ✁ � ✞ ☎ ✁ ✂ ✄ � ☎ ✆ ✝ ✞ ✄ FV based on Generative Models 1. Face image decomposed into a sequence of overlaping windows 2. To reduce the dimensions of the observation vectors and to reduce noise, we perform a feature extraction (such as 2D-DCT) 3. We train a GMM using a large set of face images from different identities Universal Background Model (UBM). Trained by EM algorithm 4. Client models are trained by adapting the UBM using MAP adaptation 5. Opinion on the claim: Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.16/33
� � ✄ ✁ ✄ � � � Feature extraction Face extraction DCT-mod2 Components Analyze on block by block Feature Vectors Face extracted from image using location of the eyes (manually or automatically located) Face image analysed on a block by block basis. Each block is ( ) and overlaps neighbouring blocks by 50% �✂✁ Each block is decomposed in terms of DCT-mod2 (extension of 2D DCT) one face is represented by a set of feature vectors Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.17/33
✁ ✝ ✄ ✆ � ✟ ✞ ✁ ✔ ✁ ✆ � GMM training The UBM is trained by Expectation Maximization (EM) algorithm using training data from all identities GMM parameters for each client model are found by adapting the UBM using a maximum a posteriori (MAP) adaptation (In practice we adapt only the means) : �✂✁☎✄ ✁☎✄ This approach deals with the problem of lack of training data for each identity. Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.18/33
✟ ✂ ✂ ✝ ✞ ✂ ✄ ☎ ✆ ✁ ✝ ✆ ✞ ✁ ✄ � ✝ ✝ ☛ ✄ � ✁ ✄ ✂ ✞ � ✁ ✂ ✄ ☎ ✆ ✁ ✂ ✝ ✟ ☞ ✄ ✆ ✁ ✂ ✝ ✞ ✟ ✄ ✝ ✁ Verification decision An opinion on the claim is found using: (2) Since the UBM is a good representation of many clients, it is also used to find the likelihood of the claimant being an impostor, i.e.: (3) UBM The verification decision is reached as follows: given a threshold , the claim is accepted when and rejected when . Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.19/33
� � � � � � � � � � � � � � Results on the XM2VTS db (LP1) Manually located faces: Approach FAR FRR HTER GMM (IDIAP) 1.69 2.25 1.97 MLP (IDIAP) 3.22 3.50 3.36 NC (U. Surrey) 3.5 2.8 3.15 Automatically located faces: Approach FAR FRR HTER GMM (IDIAP) 2.15 2.75 2.45 MLP (IDIAP) 7.98 9.75 8.86 NC (U. Surrey) 7.6 6.8 7.2 EGM (U. Thessaloniki) 8.2 6.0 7.1 Results from Face Recognition Contest ICPR2000 Accepted for publication in AVPBA03 conference Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.20/33
� � � � � Outline Problem of Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments Traditional approaches for Face Recognition Databases and Evaluation Face Verification System based on Generative Models (GMM) Future Plan Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.21/33
� � � Future Plan Face Recognition using HMM classifiers Application in a Weakly Controlled Environment (Meeting Room) Face Recognition with unrestricted Head Pose Automatic Face Recognition in Weakly Constrained Environments – p.22/33
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.