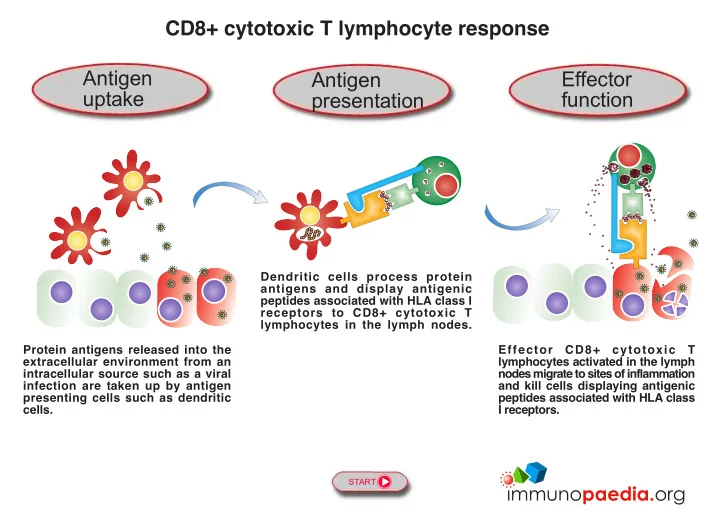

CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte response Antigen Effector Antigen uptake function presentation Dendritic cells process protein antigens and display antigenic peptides associated with HLA class I receptors to CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the lymph nodes. Protein antigens released into the Effector CD8+ cytotoxic T extracellular environment from an lymphocytes activated in the lymph intracellular source such as a viral nodes migrate to sites of inflammation infection are taken up by antigen and kill cells displaying antigenic presenting cells such as dendritic peptides associated with HLA class cells. I receptors. START
Antigen Phagocytosis by dendritic cells uptake Dendritic Monocyte cell Bone marrow PREVIOUS NEXT Phagocytosis T cell Secondary zone lymphoid organ Virus Tissue cells Dendritic cells are specialised antigen presenting cells derived from monocytes which develop in the bone marrow from long- lived haematopoietic stem cells committed to a myeloid lineage. Dendritic cells engulf foreign antigens and micro-organisms in the extracellular environment and process peptide for antigen presentation. The activated dendritic cells migrate to the T cell zone of secondary lymphoid organs where they present peptide antigens associated with cell surface HLA class I and II receptors to T lymphocytes.
Antigen Generation of naive T lymphocytes presentation Naive CD4+ helper T lymphocyte TCR CD4 Bone PREVIOUS NEXT marrow Thymus T cell Secondary zone CD8 lymphoid TCR organ Naive CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte T lymphocytes develop in the bone marrow from long-lived haematopoietic stem cells committed to a lymphoid lineage. They migrate to the thymus where through gene rearrangements each T cell expresses a unique T cell receptor (TCR) destined to recognise a single peptide epitope. T cells also express either the CD4 or CD8 surface molecules. Non-functional and “self”- reactive T cells are deleted in the thymus by positive and negative selection processes. Naive T lymphocytes leave the thymus and circulate to the T cell zone of secondary lymphoid organs where they can be stimulated by dendritic cells presenting peptide antigens associated with cell surface HLA class I and II receptors.
Antigen Priming of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes presentation Activated dendritic cell T cell priming signal CD8 PREVIOUS NEXT HLA I TCR T cell Secondary zone lymphoid organ Naive CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte Activated dendritic cells present peptide antigens associated with cell surface HLA class I receptors to CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the T cell zone of secondary lymphoid organs. They are able to prime naive CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes expressing cell surface T cell receptors (TCR) that recognise the peptide antigens displayed. Once primed, CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes require activation signals from activated CD4+ helper T lymphocytes are in order to develop into killing cells.
Activation of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes Antigen presentation Activated CD4+ helper T lymphocyte TCR CD4 T cell activation signal PREVIOUS NEXT T cell Secondary zone CD8 lymphoid organ TCR Primed CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte Primed CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes acquire activation signals from activated CD4+ helper T lymphocytes. Following activation, CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes proliferate and differentiate into effector cells capable of killing infected cells. Effector cells migrate to sites of inflammation. Memory CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes cells also develop to establish long-term immunity.
Effector HLA class I antigen presentation by infected cells function Activated CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte TCR Virus Kill PREVIOUS NEXT HLA I How are HLA class I antigens processed? Click here. CD8 Tissue cells Viral protein “Self” protein Cells infected by viruses or intracellular bacteria and also certain types of tumour cells are detected and destroyed by CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes. CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes are activated in the secondary lymphoid organs and migrate to sites of inflammation where they scan cell surfaces with their T cell receptors (TCR) for recognition of foreign peptide antigens displayed on cell surface HLA class I receptors. HLA class I receptors are constitutively expressed on the surface of all cells except erythrocytes. CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes destroy target cells by releasing perforin and cell degrading molecules.
Effector HLA class I antigen presentation by healthy cells function Activated CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte No TCR Recognition “Self” peptide PREVIOUS BACK TO START HLA I How are HLA class I antigens processed? CD8 Click here. Tissue cells “Self” protein Effector CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes that are activated in the secondary lymphoid organs migrate to sites of inflammation where they scan cell surfaces with their T cell receptors for recognition of foreign peptide antigens associated with HLA class I receptors. HLA class I receptors are constitutively expressed on the surface all cells except erythrocytes. “Self”-peptides are not normally recognised due to prior deletion of auto-reactive T lymphocytes in the thymus.
Recommend
More recommend