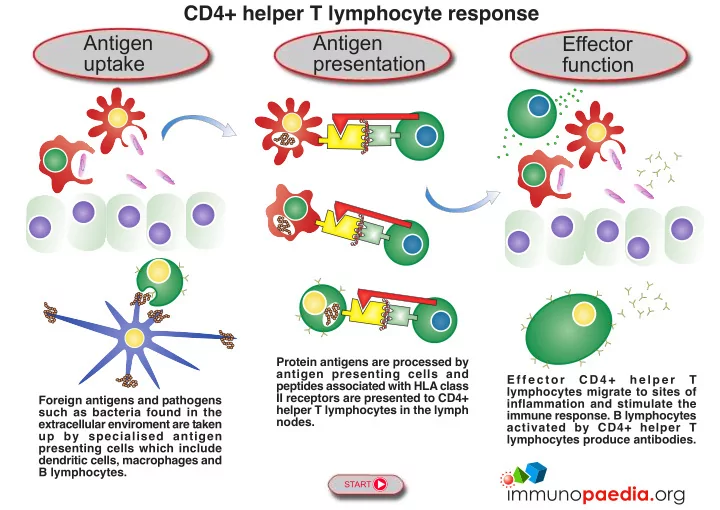

CD4+ helper T lymphocyte response Antigen Antigen Effector uptake presentation function Protein antigens are processed by antigen presenting cells and E f f e c t o r C D 4 + h e l p e r T peptides associated with HLA class lymphocytes migrate to sites of II receptors are presented to CD4+ Foreign antigens and pathogens inflammation and stimulate the helper T lymphocytes in the lymph such as bacteria found in the immune response. B lymphocytes nodes. extracellular enviroment are taken activated by CD4+ helper T up by specialised antigen lymphocytes produce antibodies. presenting cells which include dendritic cells, macrophages and B lymphocytes. START
Antigen Phagocytosis by macrophages and dendritic cells uptake Monocyte Dendritic cell Bone marrow PREVIOUS NEXT Macrophage Secondary T cell Phagocytosis lymphoid zone organ Bacterium Tissue cells Dendritic cells and macrophages are specialised antigen presenting cells derived from monocytes which develop in the bone marrow from long-lived haematopoietic stem cells committed to a myeloid lineage. Dendritic cells and macrophages engulf foreign proteins and micro-organisms in the extracellular environment and process peptide antigens. The activated dendritic cells and macrophages migrate to the T cell zone of secondary lymphoid organs where they present peptide antigens associated with cell surface HLA class II receptors to CD4+ helper T lymphocytes.
Antigen Endocytosis by B lymphocytes uptake B cell T cell zone zone Primed B lymphocyte Naive Bone Secondary B lymphocyte Secondary marrow PREVIOUS NEXT lymphoid lymphoid BCR organ organ Endocytosis Protein antigen Follicular dendritic cell B lymphocytes produce antibodies and are also antigen presenting cells. They develop in the bone marrow from long-lived haematopoietic stem cells committed to a lymphoid lineage. They migrate from he bone marrow to the B cell zone (germinal centre) of secondary lymphoid organs where they contact follicular dendritic cells carrying antigens on their cell surface. Recognition of antigen by the B cell receptor (BCR) initiates endocytosis followed by peptide processing. The B cell is now primed for antibody production and migrates from the B cell zone to the T cell zone for presentation of peptide antigens associated with cell surface HLA class II receptors to CD4+ helper T lymphocytes.
Antigen Generation of naive CD4+ helper T lymphocytes presentation Naive CD4+ helper T lymphocyte Bone TCR PREVIOUS NEXT marrow CD4 Thymus Secondary T cell lymphoid zone organ CD4+ helper T lymphocytes develop in the bone marrow from long-lived haematopoietic stem cells committed to a lymphoid lineage. They migrate to the thymus where through gene rearrangements each T cell expresses a unique T cell receptor (TCR) destined to recognise a single peptide epitope. The T cells also express the CD4 surface molecule. Non-functional and “self”- reactive T cells are deleted by processes of positive and negative selection. Naive CD4+ helper T lymphocytes leave the thymus and circulate to the T cell zone of secondary lymphoid organs for stimulation by dendritic cells presenting peptide antigens associated with cell surface HLA class II receptors.
Activation of CD4+ helper T lymphocytes by dendritic cells Antigen presentation Activated dendritic cell T cell activation signal CD4 HLA II PREVIOUS NEXT TCR How are HLA class II antigens processed? T cell Secondary Click here. zone lymphoid organ CD4+ helper T lymphocyte CD4+ helper T lymphocytes are activated by dendritic cells presenting peptide antigens associated with HLA class II receptors in the T cell zone of secondary lymphoid organs. Activated CD4+ helper T lymphocytes proliferate and migrate to sites of inlammation. Memory CD4+ helper T lymphocytes are also generated for long-term immunity.
Antigen Activation of CD4+ helper T lymphocytes by macrophages presentation Activated macrophage T cell activation signal CD4 PREVIOUS NEXT HLA II TCR How are HLA class II T cell antigens processed? Secondary zone Click here. lymphoid organ CD4+ helper T lymphocyte CD4+ helper T lymphocytes are activated by macrophages presenting peptide antigens associated with HLA class II receptors in the T cell zone of secondary lymphoid organs.
Antigen Activation of B lymphocytes by CD4+ helper T lymphocytes presentation Plasma cell Activated B lymphocyte B cell PREVIOUS NEXT activation signal CD4 T cell HLA II Secondary zone lymphoid TCR organ How are HLA class II antigens processed? Click here. Antibodies CD4+ helper T lymphocyte CD4+ helper T lymphocytes stimulate B lymphocytes presenting peptide antigens associated with HLA class II receptors in the T cell zone of secondary lymphoid organs. The CD4+ helper T lymphocyte provides activation signals to the B lymphocyte to proliferate and differentiate into antibody-secreting cells (plasma cells). Memory B lymphocytes are also generated for long- term immunity.
Effector Immune stimulation by CD4+ helper T lymphocytes function Dendritic Activated CD4+ helper cell T lymphocyte Antibodies PREVIOUS BACK TO Macrophage START Phagocytosis Bacterium Tissue cells Activated CD4+ helper T lymphocytes migrate from the secondary lymphoid organs to sites of inflammation where they stimulate the immune reponse by release of inflammatory cytokines.
Recommend
More recommend