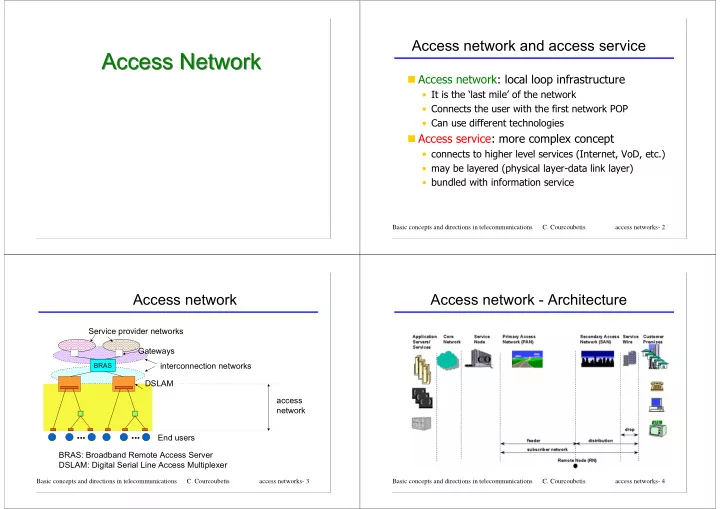

Access network and access service Access Network Access Network � Access network: local loop infrastructure • It is the ‘last mile’ of the network • Connects the user with the first network POP • Can use different technologies � Access service: more complex concept • connects to higher level services (Internet, VoD, etc.) • may be layered (physical layer-data link layer) • bundled with information service Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 2 Access network Access network - Architecture Service provider networks Gateways interconnection networks BRAS DSLAM access network ... ... End users BRAS: Broadband Remote Access Server DSLAM: Digital Serial Line Access Multiplexer Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 3 Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 4
Architecture Access service or Α is a customer of Provider 1 Remote node NIU Provider 1 Provider 2 using access service S1 NIU Remote node Hub ... Customer Α : buys (P1, S1) Ν 2 NIU Remote node Provider P1: builds S1 buying services from Ν 1, Ν 2 Ν 1 S1 Distribution network Feeding network S2 Basic properties: ... ... Feeding network: broadcast - switched A B Distribution network: shared - dedicated Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 5 Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 6 Access networks go to broadband Technology Trends Local networks based on outdated principles are became a “bottleneck”, limiting subscriber’s access to modern services. Key forces: � Data communications exceed telephony � New subscriber’s requirements to providing new services • Wireless/mobile subscribers exceed landline subscribers � New regulations � Development of new services in voice, data and video information in • Broadband on Wireless interactive and broadcasting mode • Emergence of the Next Generation Networks # WWW pages with powerful video information # Multimedia applications, Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB), Video-on-Demand (VoD), interactive TV � Emergence of alternative operators in local networks, who compete with incumbent operators in provisioning a wide set of additional services � Construction of high-speed core networks with a capacity of dozens and hundreds of Gbit/s � Wireless Technologies Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 7 Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 8
Comparison of download duration Service requirements to the access network 1 h video MP3 or high E-mail MPEG 4 in resolution photo Wireless Service Type Downstream Upstream TV-Quality wired Bandwidth Bandwidth Byte 3 k 3 M 300 M Telephony Switched 4kHz 4kHz bit/s ISDN Switched 144kbps 144kbps 2,5 sec 42 min 3 days GSM 9,6 k Broadcast video Broadcast Analog or 6 Mbps 0 Interactive video Switched 6 Mbps Small Live Video Codecs starting with 32 kbit/s 0,4 sec 7 min 12 hours PSTN 56 k Internet access Switched 1-… Mbps Small initally Videoconferencing Switched 6 Mbps 6 Mbps GPRS 115 k 0,2 sec 3,5 min 6 hours Business services Switched 1.5-622 Mbps 1.5-622 Mbps ISDN 128 k UMTS 2 M 0,01 sec 12 sec 20 min ADSL 8 M Cable 30 M 1 ms 1 sec 30 sec WLAN 80 M 3 ms 30 ns 30 µsec Fiber 800 G Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 9 Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 10 Rates vs Distance Basic technologies HDSL SDSL Emerging: ADSL ISDN Powerline, HomePNA 10 Mb/s VDSL VBD MetroEthernet 7.5 Mb/s twisted pair Satellite (copper) 5.5 Mb/s HFC MMDS, LMDS Cellular Coax & wireless 3.5 Mb/s Free space opt transmission fiber SDV 1 Mb/s WiFi (802.11) Increasing loop length WiMax (802.16) 100% SDH PON optical fiber CPE Central MetroEthernet Office DSLAM Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 11 Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 12
Twisted pair: xDSL xDSL downstream Multiplexes many xDSL streams upstream xDSL modem ADSL: asymm. 8Mbps-2Mbps (<1.5km) ADSL lite: 1.5Mbps-0.5Mbps modem ADSL heavy: 8Mbps-1Mbps Splitter ADSL2: asymmetric, 12Mbps-1Mbps DSLAM ADSL2+: asymm. 24Mbps-3.5Mbps User network cooper HDSL: symmetric, 2Mbps (<4km) service network RADSL: rate-adaptive, 12-1 Mbps PSTN (Internet, VoD) Mbps Switch SHDSL: symmetric, 2.3Mbps (<3km) Customer (home) VDSL: 55Mbps-12Mbps (<0.3km) 50 Local switch premises (PSTN) VDSL 40 30 telephony RADSL DSLAM may belong to xDSL data stream 20 ADSL service provider, not to interconnection service 10 ADSL PSTN operator Km 2 6 1 4 30 138 1100 kHz Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 13 Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 14 Access service - Bitstream versions Wireless access to Internet (first steps) satellite � The possibility to differentiate the service offered to the end user (and thus the extent to which value can be downstream added by the new entrant) declines from Option 1 to 4. direct Head Internet receiver end upstream Telephone modem switch Twisted pair • Cellular: voiceband modems, 9.6kbps, CDPD = 19.2kbps • Terrestrial broadcast: – MMDS (wireless cable), 50km, 2GHz, 33 channels, 10(27)Mbps/ch – LMDS: 28GHz, 5km, 2-way • Satellite broadcast (DBS): down link 400kbps - 1Mbps, possibly bidirectional Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 15 Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 16
Comparison of wireless technologies Comparison of wireless technologies MMDS Stands for Multichannel Multipoint � Distribution Services (a.k.a. wireless cable network) Cost Data QoS Security License Require- • Multichannel: multiple spectral bands, Rates Required ments allocated in 6 MHz channels (10-27Mbps of shared capacity per channel) LMDS Medium Very Low Low Yes LoS • Multipoint: available bandwidth is shared among end-users High • Distribution Services: initially used as a Wi-Fi Low High ? Medium No - cableTV substitute Low deployment cost and large area � WiMax Low Very High Medium Yes/No - coverage are important factors for servicing rural areas High Cell splitting increases capacity by � UMTS High High High Medium Yes - reusing spectrum (scalability) High equipment cost (both provider and � Satellite Very Very High High Yes LoS end-user install an antenna) High High Several multiplexing options (FDMA, � TDMA, CDMA, OFDM) Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 17 Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 18 LMDS Wi-Fi (802.11) � Stands for Local Multipoint � An IEEE family of standards for Wireless LANs Distribution Service (a.k.a. wireless (WLANs). Usually used for: fiber-optic network) • Local: Cell range is 1-3 miles • Sharing access to Internet • Multipoint:point-to-multipoint bidirectional connections • Allowing mobility to workers � point-to-point is also feasible � Utilizes air frequencies for transmitting packets • Distribution Services: initially used as a cableTV/satelite substitute • Unlicensed band (2.4GHz) � Spectrum in the 28-GHz and 31- GHz range Internet/ • Licensed band (5.4GHz) Data NW • Higher capacity than MMDS (Up to PSTN • The selected band affects transmission rates and 155Mbps) range • Line-Of-Sight only operation � Ability for cell splitting Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 19 Basic concepts and directions in telecommunications C. Courcoubetis access networks- 20
Recommend
More recommend