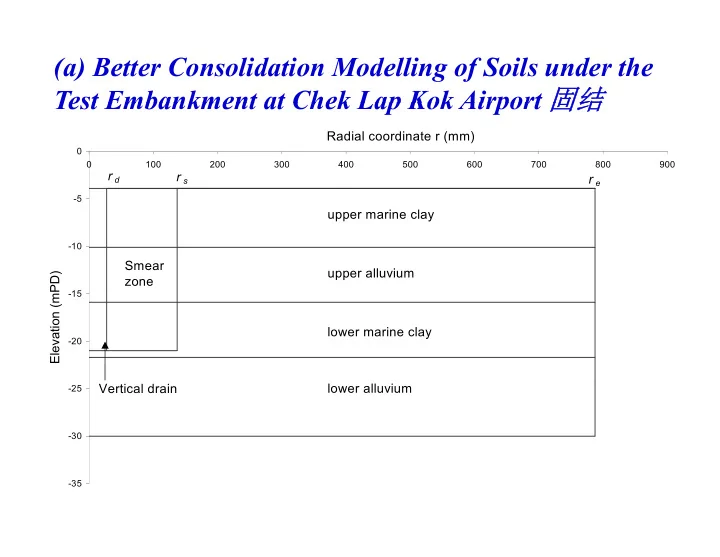

(a) Better Consolidation Modelling of Soils under the Test Embankment at Chek Lap Kok Airport !" Test Embankment at Chek Lap Kok Airport !" !" !" Radial coordinate r (mm) 0 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 r d r s r e -5 upper marine clay -10 10 Smear upper alluvium n (mPD) zone -15 Elevation lower marine clay -20 Vertical drain lower alluvium -25 -30 -35
(a) Better Consolidation Modelling of Soils under the Test Embankment at Chek Lap Kok Airport !" Test Embankment at Chek Lap Kok Airport !" !" !" 3 2.5 Sondex (a) anchor 2 2 1 1 ement (m) 2 3 1.5 4 4 Settle 1 1 2 3 4 0.5 0 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 Contract Days
(b) Application of Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) - satellite based radar remote sensing technology Radar (InSAR) - satellite based radar remote sensing technology
Settlement of the Chek Lap Kok Airport #$%& #$%& over 315 Days: (29 12 98 - 09 11 99) over 315 Days: (29.12.98 - 09.11.99) 820500 9500 819 818500 17500 81 808500 809500 810500 811500 812500 (mm) -5 -15 -25 -30 0 -10 -40 -50
5. Reclamation Methods for a Third 5. Reclamation Methods for a Third Runway at HK International Airport Runway at HK International Airport (a) (a) Undredged Undredged mud with vertical drains mud with vertical drains (b) (b)Deep cement mixing (DCM) Deep cement mixing (DCM)
(a) (a) Undredged Undredged mud with vertical drains mud with vertical drains Wick Drains (Prefabricated (Prefabricated Vertical Drains) Purpose: speed up consolidation, reduce post-construction settlement reduce post-construction settlement Limitation: no good for loose sand Applications: clayey soils, below or above water table, very A li ti l il b l b bl efficient and economy, easy to install …
Band drains ( '() '() )
Geo-textile Drainage channels
2 2 2 ! ! ! ! u u 1 u u # " " e e e e c ( ) c h v ! ! ! ! 2 ! ! 2 ! ! 2 t t r r r r r r z z $ # $ $ % # $ $ $ ( 1 U ) ( 1 U )( 1 U ) U 1 ( 1 U )( 1 U ) v r v r c t c t # # # # v h U f f ( ( T ); ); T ; ; U f f ( ( T ); ); T v v v v v v r r r r r r 2 2 2 2 d 4 R
'()*+,- '()*+,- %&.%/012 %&.%/012
Pre-loading – removed afterward removed afterward
Purpose of Vertical Drains and Preloading (a) Vertical Drains '() • Speed up escaping/dissipation of excess porewater/ pressure due to preloading (b) Preloading *+ • Making the soil over-consolidated and reducing both “primary” and creep consolidation More accurately speaking, reducing instant compression and creep
Soil pressure/stress Soil pressure/stress before construction after construction Log(Pressure) (or Stress) Settlem ent/strain - large Large creep settlem ent/strain Settlem ent/strain - sm all Settlem ent/strain - sm all Sm all creep settlem ent Pre-loading to here Illustration of settlement/strain reduction using pre-loading technique -reduction in primary consolidation (instant) settlement/strain reduction in “primary” consolidation (instant) settlement/strain -reduction in “secondary” consolidation (creep) settlement/strain
(b) Deep cement mixing (DCM) (b) Deep cement mixing (DCM)
Deep cement mixing Deep cement mixing (DCM) at marine site (DCM) at marine site (DCM) at marine site (DCM) at marine site
Unconfined compression strength q peak (kPa) vs. A w and w i from UC tests (after Yin and Lai 1998) f UC t t ( ft Yi d L i 1998) 2000 1500 q peak (kPa) w i =100% 1000 w i =80% 500 500 w i =60% 0 0 0 5 5 10 10 15 15 20 20 C em ent/S oil R atio A w %
(c) Sand compaction pile (sand drains) (c) Sand compaction pile (sand drains)
6. Conclusions and Recommendations 6. Conclusions and Recommendations 6.1 6.1 Conclusions Conclusions (1) (1) Reclamations were done in the past and also are needed in Reclamations were done in the past and also are needed in the future. the future. (2) (2) Confinements and improvement of mud in place are Confinements and improvement of mud in place are required and can be done using various methods. required and can be done using various methods. required and can be done using various methods. required and can be done using various methods. (3) The two methods of (a) (3) The two methods of (a) undredged undredged mud with vertical mud with vertical drains (plus preloading) and (b) deep cement mixing drains (plus preloading) and (b) deep cement mixing ( l ( l (plus preloading) at site are technically possible to confine, (plus preloading) at site are technically possible to confine, l l di di ) t it ) t it t t h i h i ll ll ibl t ibl t fi fi improve mud in place and to reduce the post improve mud in place and to reduce the post- -construction construction settlement. settlement. (4) (4) Other methods such as sand drains (sand compaction pile) Other methods such as sand drains (sand compaction pile) and a combination of the methods could be used and even and a combination of the methods could be used and even better better better. better.
6. Conclusions and Recommendations 6. Conclusions and Recommendations (5) (5) Previous study and cases have indicated large settlements Previous study and cases have indicated large settlements of marine reclamations (also large post of marine reclamations (also large post-construction of marine reclamations (also large post of marine reclamations (also large post construction construction construction settlement such as Japan Kansai Airport. settlement such as Japan Kansai Airport. (6) (6) Care must be paid to the creep of the marine soils with Care must be paid to the creep of the marine soils with d drains (and DCM) and the calculation methods (it is drains (and DCM) and the calculation methods d i i ( ( d DCM) d DCM) d h d h l l l l i i h d h d (i i (i i (it is recommend to use Hypothesis B method and Yin’s recommend to use Hypothesis B method and Yin’s simplified method; also consolidation solutions by Yin simplified method; also consolidation solutions by Yin p p ; ; y y and Zhu) and Zhu). . (7) (7) No mater which method to be used, the reclamation with No mater which method to be used, the reclamation with pre pre- -loading shall start as earlier as possible and shall last l loading shall start as earlier as possible and shall last l di di h ll t h ll t t t li li ibl ibl d h ll l d h ll l t t for a longer duration for a longer duration in order to reduce the post in order to reduce the post- - construction settlement) construction settlement). ) .
6. Conclusions and Recommendations 6. Conclusions and Recommendations 6.2 6.2 Recommendations Recommendations (1) (1) Study is needed on the proposed two methods of (a) Study is needed on the proposed two methods of (a) undredged mud with vertical drains (plus preloading) and undredged d d d d d d mud with vertical drains (plus preloading) and d d i h i h i i l d l d i i ( l ( l l l di di ) ) d d (b) deep cement (b) deep cement mixing ( mixing (plus preloading) at site. plus preloading) at site. ( ) ( ) (2) Study is also needed on other methods such as sand drains (2) Study is also needed on other methods such as sand drains y (sand compaction pile) and a combination of the methods. (sand compaction pile) and a combination of the methods. (3) (3) Large Large- -scale lab model tests are recommended to simulate scale lab model tests are recommended to simulate these methods individually or a combination of them. th these methods individually or a combination of them. th th d i di id th d i di id ll ll bi bi ti ti f th f th (4) (4) Field trial study is also recommended on these methods. Field trial study is also recommended on these methods. (5) (5) Calculation methods shall be used to predict the Calculation methods shall be used to predict the p settlements of reclamations in lab models and in the field settlements of reclamations in lab models and in the field trial and pore water pressure dissipation inside the trial and pore water pressure dissipation inside the marine soils and are verified by comparing with measured marine soils and are verified by comparing with measured marine soils and are verified by comparing with measured marine soils and are verified by comparing with measured data. data.
Thank You Thank You 3345 3345 3345 3345 Tel: 2766 6065, Mobile: 9716 5375 Email: cejhyin@polyu.edu.hk Webpage: www cse polyu edu hk/ cejhyin Webpage: www.cse.polyu.edu.hk/~cejhyin 94
Recommend
More recommend