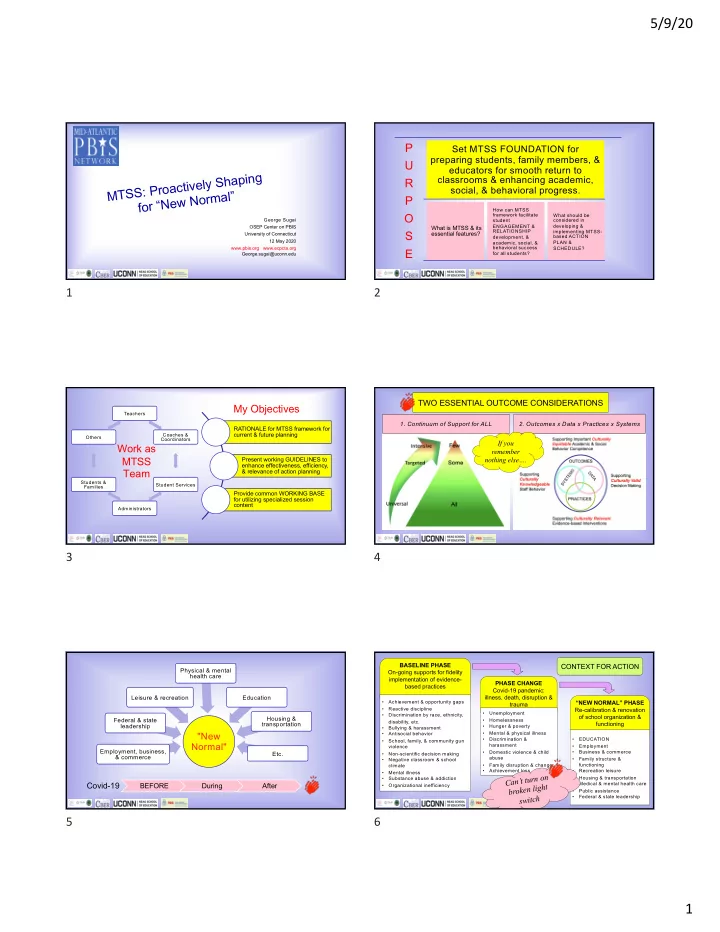

5/9/20 P Set MTSS FOUNDATION for preparing students, family members, & U educators for smooth return to MTSS: Proactively Shaping classrooms & enhancing academic, R social, & behavioral progress. for “New Normal” P How can MTSS O framework facilitate What should be George Sugai considered in student developing & OSEP Center on PBIS What is MTSS & its ENGAGEMENT & RELATIONSHIP implementing MTSS- S essential features? University of Connecticut based ACTION development, & 12 May 2020 PLAN & academic, social, & www.pbis.org www.ecpcta.org behavioral success SCHEDULE? E George.sugai@uconn.edu for all students? 1 2 TWO ESSENTIAL OUTCOME CONSIDERATIONS My Objectives Teachers 1. Continuum of Support for ALL 2. Outcomes x Data x Practices x Systems RATIONALE for MTSS framework for current & future planning Coaches & Others Coordinators If you Work as remember MTSS Present working GUIDELINES to nothing else…. enhance effectiveness, efficiency, Team & relevance of action planning Students & Student Services Families Provide common WORKING BASE for utilizing specialized session content Administrators 3 4 BASELINE PHASE CONTEXT FOR ACTION Physical & mental On-going supports for fidelity health care implementation of evidence- PHASE CHANGE based practices Covid-19 pandemic: Leisure & recreation Education illness, death, disruption & • Achievement & opportunity gaps “NEW NORMAL” PHASE trauma • Reactive discipline Re-calibration & renovation • Unemployment • Discrimination by race, ethnicity, of school organization & Housing & Federal & state • Homelessness disability, etc. transportation functioning leadership • Hunger & poverty • Bullying & harassment • Mental & physical illness "New • Antisocial behavior • Discrimination & • EDUCATION • School, family, & community gun Normal" harassment • Employment violence Employment, business, • Business & commerce • Domestic violence & child Etc. • Non-scientific decision making & commerce abuse • Family structure & • Negative classroom & school functioning climate • Family disruption & change • Achievement loss • Recreation leisure • Mental illness Can’t turn on • Housing & transportation • Substance abuse & addiction Covid-19 • Medical & mental health care BEFORE During After broken light • Organizational inefficiency • Public assistance switch • Federal & state leadership 5 6 1
5/9/20 Trauma-Informed Approach www.pbis.org SPLC Teaching Tolerance Project (Strauss, 26 Mar WashPost) • Establish predictable ROUTINES & clear communications • Actively (RE)ENGAGE to establish RELATIONSHIP & well-being • Maintain sense of SAFETY through positive connections, optimism, ENGAGEMENTS, & RELATIONSHIPS • Consider ALL (students & family & school members) from MTSS perspective www.Tolerance.org • MODEL, prompt, & REINFORCE all above 7 8 Risk & Protective Factors: MTSS & Prevention 2015 9 10 Implementation Consideration EFFECTIVE Implementation Consideration RESPONSE INEFFECTIVE • Trauma-informed RESPONSE decision making Risk Protective • Reactive Risk Risk Protective management Factors Vs Factors • Prevention-based Factors Factors Enhancers Vs behavioral sciences • Exclusion, • Trauma segregation, • Tiered support E systems isolation Academic E Academic Mental illness • Negative Mental illness x competence x competence • Train & hope • Data-based decision- a modelling a making teaming m m • Non-evidence- • Family, school, Disability Healthy habits p Disability Healthy habits p based practices • Continuous coached community l l professional e Interpersonal e • Subjective disruption Interpersonal Substance Use development Substance Use s skills s skills decision making • Discrimination • High fidelity • Low quality Antisocial Self-management Antisocial Self-management implementation implementation behavior skills behavior skills of evidence- • Proactive, based practices competent, informed leadership • 1-time training events MTSS &Trauma-informed 11 12 2
5/9/20 Schools - one of our most structured, predictable, safe, preventive, continuous social support systems Academic success Social, emotional, & Positive adults behavioral MTSS: Working Definition & modeling success Essential Features 12+ yrs., 180 days/yr., 6 hrs./day Neighborhood Caring, availability professional adults Positive Specialized classroom & supports school climate 13 14 MTSS is…. Positive Behavioral Interventions & Supports Empirically • “An evidence-based model of schooling that uses data-based problem-solving to integrate academic and behavioral instruction and intervention” (Batsche, 2015) validated MTSS • “Systemic, continuous-improvement framework in which data-based problem solving and decision- practices Academic “Integration of a number of multiple- making is practiced across all levels of the educational system for supporting students” (CO Dept of Continuum & behavior tiered systems into one coherent, Education, Oct 2016). outcomes strategically combined system meant to • “Practice of providing high-quality instruction and interventions matched to student need, monitoring progress frequently to make decisions about changes in instruction or goals, and applying child address multiple domains or content response data to important educational decisions" (Batsche et al., 2005) areas in education” MTSS • “An integrated, comprehensive framework that focuses on CCSS, core instruction, differentiated learning, student-centered learning, individualized student needs, and the alignment of systems McIntosh & Goodman, 2016, p. 5 All Framework E.g., PBIS necessary for all students’ academic, behavioral, and social success” (CA Dept of Ed., Jul 19, 2017) students • “Blueprint for school improvement that focuses on system structures and supports across the district, school, and classroom to meet the academic and non-academic needs of all students” (MA Exec Office of Ed. 2018). • “An evidence-based model of schooling that uses data-based problem-solving to integrate academic and behavioral instruction and intervention” (FL MTSS, n.d., p.2). 15 16 Integrate Initiatives around Important SHARED OUTCOMES Teach & Arrange Align, Integrate, & Sequence Learning EVIDENCE-based Practices & ENVIRONMENT for Systems w/in CONTINUUM Success o f n s a t i o a r i l l V A e h a r S T S S Develop Local Content M Use DATA to Make n s B c t i o B L S - u n Expertise R B I P T S F S SBH M Big Decisions CSSS MIBLSI PB4L ISF Coordinate R t I PBIS RtI-B SCREEN Regularly, Implementation w/ TEAM R t I - A Early, & Universally S W EBS P B S MTSS-A Continuously Monitor Student PROGRESS & IMPLEMENTATION Fidelity 17 18 3
5/9/20 Tertiary Prevention: Tiered Prevention Specialized Individualized Continuum Logic FEW Supporting Important Culturally Systems for Students Equitable Academic & Social with High-Risk Behavior Behavior Competence Secondary Prevention: OUTCOMES SOME Specialized Group Systems for Students with At-Risk Behavior Supporting Supporting Primary Prevention: Culturally Culturally Valid School-/Classroom- Knowledgeable Decision Making Wide Systems for Staff Behavior All Students, Staff, & Settings PRACTICES PBIS Center, Supporting Culturally Relevant ALL 1996; Vincent, Evidence-based Interventions et al., 2011 19 20 Anger Management Intensive Few Continuum of Support CBT Basic Continuum Logic FBA-BIP Logic for ALL Problem Solving Behavioral FBA-BIP Contracting Targeted Some Blended Continuum Logic Check In Check-In Check-Out Check Out Technology Independent Play Targeted Student Outcome Good Behavior Game Second Steps Peer Social Skills Mentoring Adult Attendance Club District Continuum Small Group Skills Adult-Student Relationship Self Classroom Continuum Practice Lunch-Bunch Family Resource Assessment Continuous Active Center Supervision Continuous Active Frequent Positive Active Universal All Supervision Engagement Frequent Positive Active School-wide Continuum Classroom Teaching Matrix Homework Engagement Contingent & Contingent & Reading Specific Positive Specific Positive Peer Dec 7, 2007 Effective Instruction Comprehension School-wide Teaching Matrix Reinforcement Reinforcement Interactions 21 22 Continuum Logic & Key PBIS Working Elements % of Students V. % of Contributions (Horner, 2011) 10 0% 4.7 Outcomes Data Practices Systems 90 % 11.3 39.7 80 % 16% of 70 % INCREASED students 60 % EFFORT engage in 50 % 79% of 39.3 challenging 84.0 • Intensity 40 % behavior • Frequency 30 % • Duration • Specialization 20 % 39.7 • Differentiation 10 % • Teaming 0% % Stude nts % Effort Responsiveness- 2979 ES 889 MS 390 HS to-Practice 23 24 4
Recommend
More recommend