
13 Jan, 2011 Statistical Literacy: Confounding UTSA Confounding 2011 1 2011 2 Statistical Literacy: Statistical Literacy Confounding Statistical literacy is the ability to read and MILO SCHIELD, interpret summary statistics in everyday life . Augsburg College Statistical Literacy studies Director, W. M. Keck Statistical Literacy Project Vice President, National Numeracy Network (1) the relation between statistical associations US Rep., International Statistical Literacy Project and causation, and (2) the full-range of influences on a statistic January 13, 2011 University of Texas San Antonio (UTSA) or on a statistical association. [Take CARE] Slides at www.StatLit.org/pdf/ 2011-Schield-UTSA-Confounding-Slides.pdf 2011 3 2011 4 Controlling for a confounder Take CARE: Context can DECREASE an association The influence of factors taken into account by MN has 3.8 times as much prison expense as ME • data broken out by subgroups in tables and graphs • averages, ratios and comparisons of averages and ratios State Total # Inmates Per Inmate • epidemiological models (cf., deaths attributed to obesity) MN $184M 4,865 $37,825 • regression models and ME $48M 1,424 $33,711 • the study design (cf., longitudinal vs. cross-sectional; experiment vs. observational study). MN has 3.4 times as many inmates as ME The influence of related factors (confounders) MN has 25% more prison expense per inmate than ME not taken into account in the study and not blocked by the study design. 2011 5 2011 6 Controlling for a confounder Controlling for a confounder can NULLIFY an association can REVERSE an association CA has 50% more prison expense than NY MD has 3 times as much prison expense as KS State Total # Inmates Per Inmate State Total # Inmates Per Inmate MD $481M 21,623 $22,250 CA $2.9B 136K $21,385 KS $159M 7,148 $22,250 NY $1.9B 69K $28,426 CA has almost twice as many inmates as NY MD has three times as many inmates as KS CA has 25% less prison expense per inmate than NY MD has the same prison expense per inmate as KS 2011-Schield-UTSA-Confounding-Slides.pdf 1
13 Jan, 2011 Statistical Literacy: Confounding 2011 7 2011 8 SEASON WINS vs. TOTAL PAYROLL Controlling for a confounder Association vs. Causation US Major League Baseball can INCREASE an association 102 Indians . 92 MN has 27% more prison expense than IA Braves 1995 Season Wins Red Sox Reds State Total # Inmates Per Inmate 82 MN $184M 4,865 $37,825 Yankees Rangers IA $144M 5,929 $24,286 72 Mets Padres Orioles Marlins MN has 18% fewer inmates than IA Expos 62 Tigers Pirates Twins BlueJays MN has 56% more prison expense per inmate than IA 52 10 20 30 40 50 60 Total Payroll ($Millions) 2011 9 2011 10 Adjusting for Land Size: SAT VERBAL SCORES: FLAT Standardize on Average Lot GROUP 1981 2002 CHANGE House Prices (Average Acres = 1.6) $450,000 White 519 (85%) 527 (65%) 8 Black 412 (9%) 431 (11%) 19 $350,000 Asian 474 (3%) 501 (10%) 27 Best-Fit Line $250,000 Mexican 438 (2%) 446 (4%) 8 Puerto Rican 437 (1%) 455 (3%) 18 $150,000 American Indian 471 (0%) 479 (1%) 8 $50,000 ALL Test takers 504 (100%) 504 (100%) ZERO 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Land Size (Acres) 2004AssessMTB 2011 11 2011 12 Multivariate Analysis City Hospital: can be Complex Hospital of Death?? . To simplify, consider cases with Hospital Total Died Death Rate • a binary outcome, City 1,000 55 5.50% • a binary predictor and Rural 1,000 35 3.50% • a binary confounder. Both 2,000 90 4.50% What are the necessary conditions for Condition Total Died Death Rate nullification or a reversal? Good 800 15 1.90% Poor 1,200 75 6.30% See Schield (1999) and Schield and Burnham (2003) 2011-Schield-UTSA-Confounding-Slides.pdf 2
13 Jan, 2011 Statistical Literacy: Confounding 2011 13 2011 14 Can this confounder nullify or Confounder Reverses; reverse this association? City Hospital is Better . . Death Death Rates 6.3% Condition Hospital Total Died Rate Poor City Good City 100 1 1.00% health 5.5% Overall 4.4 Pct. Pts 2 Pct.Pts Rural 700 14 2.00% 4.5% 230% more 60% more Total 800 15 1.90% 3.5% Good Rural health Poor City 900 54 6.00% By Patient 1.9% By Hospital Condition Rural 300 21 7.00% Total 1,200 75 6.30% 2011 15 2011 16 Two-Group Rates Compare Hospital Death Rates with a Binary Confounder Confounder: Patient Condition . . A Confounder can Influence a Difference E: effect 7% AP 6% BP 5% Rc Rd Death Rate 4% 1,0 XP 1,1 XN BQ 3% A: Associated 2% AQ XM Ra Rb 1% 0,0 XQ 0,1 0% B: confounder. 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% Percentage who are in "Poor" Condition 2011 17 2011 18 Standardize on combined Auto Deaths and Airbag Presence Adjusting for Land Size confounder percentage Confounded by Seatbelt Use 125 . Standardizing Can Reverse A Difference Airbag 7% Death Rate per 10,00 98 6% Accidents .. 5% 70 Death Rate Standardized 4% No Airbag 43 3% Airbag 2% 15 1% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% All Percentage who wear Seatbelts None 0% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% Percentage who are in "Poor" Condition 2011-Schield-UTSA-Confounding-Slides.pdf 3
13 Jan, 2011 Statistical Literacy: Confounding 2011 19 2011 20 Subscription Renewal Rates by Month Adjusting for Land Size Confounder: Race 2000n NAEP 4th Grade Math Standardized Scores: LA vs WV Confounded by Change in Subscription Mix 230 230 80% Standardize 226 70% 225 Std. 60% WV Renewal Rate 220 February LA January NAEP Scores 50% 215 40% 210 30% 205 20% 204 203 10% 40% 46% 10% 200 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% Percentage of Renewals which are Agent Percentage who are White 2011 21 2011 22 Income: US Families by Race & Structure Control for Mom’s Age Confounder: Family Structure $65,000 White Families $60,000 $55,000 $50,000 $45,000 Mean Income $40,000 $35,000 $30,000 Population $25,000 Black Families $20,000 $15,000 48% 78% 82% $10,000 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% Percentage who are headed by Married Couple 2011 23 2011 24 Controlling Can Change Conclusion Statistical Significance Statistical educators must show students how confounders can influence associations and change statistical significance. The failure of educators to do this may be seen as “ statistical negligence .” Schield (1999). Simpson's Paradox and Cornfield's Conditions, See www.StatLit.org/pdf/1999SchieldASA.pdf. Schield, Milo (2006). Presenting Confounding and Standardization Graphically. STATS Magazine , ASA. Fall 2006. pp. 14-18. Draft at www.StatLit.org/pdf/2006SchieldSTATS.pdf. Schield, Milo (2009). Confound Those Speculative Statistics. 2009 ASA Proceedings of the Section on Statistical Education. [CD- ROM] 4255-4266. www.StatLit.org/pdf/2009SchieldASA.pdf 2011-Schield-UTSA-Confounding-Slides.pdf 4
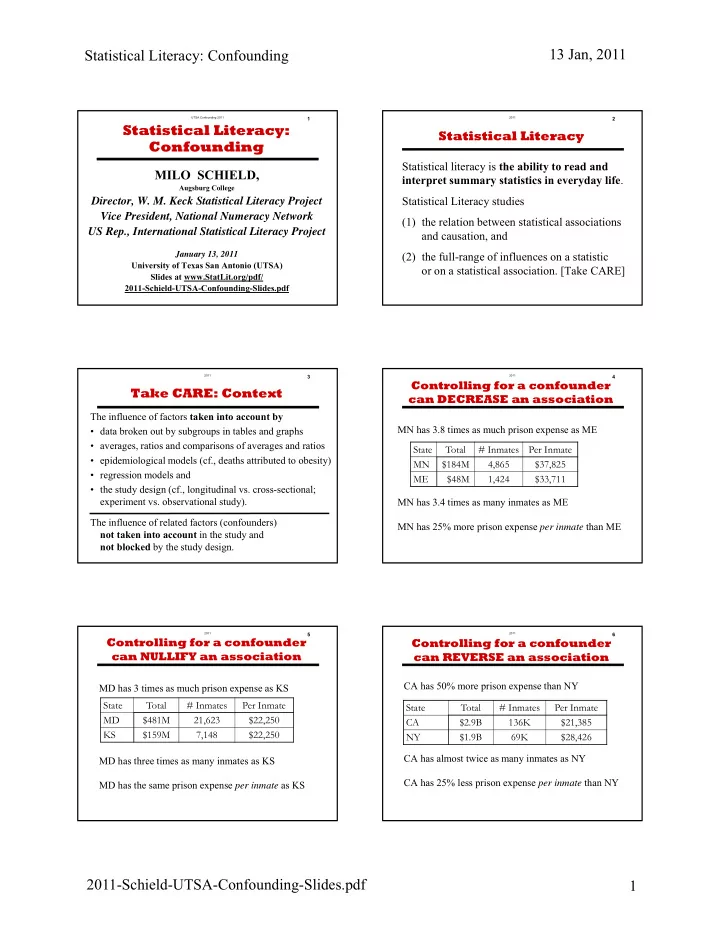
UTSA Confounding 2011 1 Statistical Literacy: Confounding MILO SCHIELD, Augsburg College Director, W. M. Keck Statistical Literacy Project Vice President, National Numeracy Network US Rep., International Statistical Literacy Project January 13, 2011 University of Texas San Antonio (UTSA) Slides at www.StatLit.org/pdf/ 2011-Schield-UTSA-Confounding-Slides.pdf
2011 2 Statistical Literacy Statistical literacy is the ability to read and interpret summary statistics in everyday life . Statistical Literacy studies (1) the relation between statistical associations and causation, and (2) the full-range of influences on a statistic or on a statistical association. [Take CARE]
2011 3 Take CARE: Context The influence of factors taken into account by • data broken out by subgroups in tables and graphs • averages, ratios and comparisons of averages and ratios • epidemiological models (cf., deaths attributed to obesity) • regression models and • the study design (cf., longitudinal vs. cross-sectional; experiment vs. observational study). The influence of related factors (confounders) not taken into account in the study and not blocked by the study design.
2011 4 Controlling for a confounder can DECREASE an association MN has 3.8 times as much prison expense as ME State Total # Inmates Per Inmate MN $184M 4,865 $37,825 ME $48M 1,424 $33,711 MN has 3.4 times as many inmates as ME MN has 25% more prison expense per inmate than ME
2011 5 Controlling for a confounder can NULLIFY an association MD has 3 times as much prison expense as KS State Total # Inmates Per Inmate MD $481M 21,623 $22,250 KS $159M 7,148 $22,250 MD has three times as many inmates as KS MD has the same prison expense per inmate as KS
2011 6 Controlling for a confounder can REVERSE an association CA has 50% more prison expense than NY State Total # Inmates Per Inmate CA $2.9B 136K $21,385 NY $1.9B 69K $28,426 CA has almost twice as many inmates as NY CA has 25% less prison expense per inmate than NY
2011 7 Controlling for a confounder can INCREASE an association MN has 27% more prison expense than IA State Total # Inmates Per Inmate MN $184M 4,865 $37,825 IA $144M 5,929 $24,286 MN has 18% fewer inmates than IA MN has 56% more prison expense per inmate than IA
2011 8 SEASON WINS vs. TOTAL PAYROLL Association vs. Causation US Major League Baseball 102 Indians . 92 Brav es 1995 Season Wins Red Sox Reds 82 Yankees Rangers 72 Mets Padres Orioles Marlins Expos 62 Tigers Pirates Twins BlueJays 52 10 20 30 40 50 60 Total Payroll ($Millions)
Recommend
More recommend