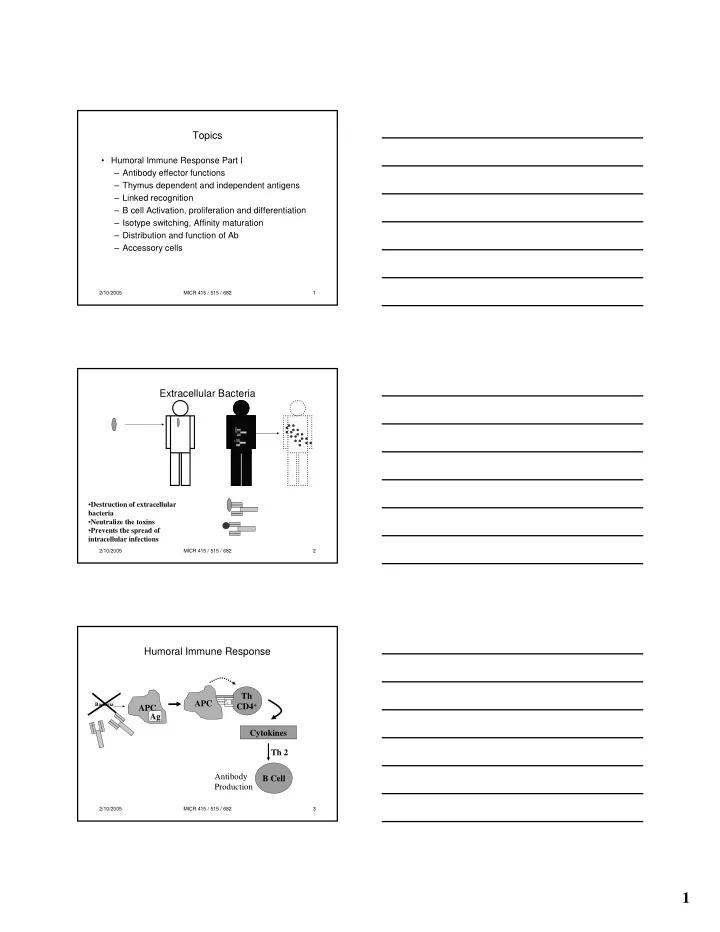

Topics • Humoral Immune Response Part I – Antibody effector functions – Thymus dependent and independent antigens – Linked recognition – B cell Activation, proliferation and differentiation – Isotype switching, Affinity maturation – Distribution and function of Ab – Accessory cells 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 1 Extracellular Bacteria • Destruction of extracellular bacteria • Neutralize the toxins • Prevents the spread of intracellular infections 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 2 Humoral Immune Response Th APC Bacteria CD4 + APC Ag Cytokines Th 2 Antibody B Cell Production 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 3 1
Humoral Immune Response Bacteria Th2 B Cell Bacteria CD4 + B Cell Ag Cytokines – Epitope recognition B Cell – Internalization of Ag – Processing and presentation B Cell B Cell – Stimulation by armed Th2 cell Plasma Cell – B cell proliferation B Cell B Cell – Differentiation – Production of Ab 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 4 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 5 Antibody effector functions 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 6 2
Thymus dependent antigens –Proteins –Require T cell help 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 7 Thymus independent antigens –Bacterial Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) –Do not require T cell 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 8 Linked recognition Fig 9.3 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 9 3
2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 10 • Adhesion molecules interaction • Stimulation via TCR • CD40 /CD40 ligand stimulation (Accessory signal) 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 11 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 12 4
– Secretion of cytokines (IL4) by the Th2 cell 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 13 B cell proliferation and differentiation –IL4, CD40 lead to B cell proliferation –IL5 and IL6 lead to B cell differentiation into plasma cells 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 14 Isotype switching • A variable region can be associated with the constant region of any • IgM isotype • IgD • mRNA splicing • IgA • IgG – IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG3 • IgE 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 15 5
2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 16 Cytokines determine Isotype 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 17 –B cell is activated –Migrate to primary follicles of spleen and lymph nodes –Proliferates and forms germinal center (follicular dendritic cells) –Proliferating B cells are called centroblasts (random somatic Hypermutation of V region) –Produce centrocytes (positive selection by FDC) –Differentiation into memory cells and Ab producing plasma cells (Th cells) 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 18 6
2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 19 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 20 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 21 7
Affinity maturation Caused by: –somatic hypermutation –Selection cells with high affinity receptors 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 22 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 23 Centrocyte selection at the germinal center Take up foreign Ag from FDC? Yes Interaction No with T cells Apoptosis Differentiation 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 24 8
2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 25 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 26 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 27 9
Distribution and function of Ab – Pathogens are can grow in all the body – Ab need to be available in all the body • Route of entry of pathogens: • Epithelial barries: – Mucosa of the respiratory, digestive, urogenital tract, damaged skin • Directly to the blood – Insects, wounds, needles 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 28 IgM –First to be produced –Low affinity –Forms pentameres (high avidity) –Large, confined to the blood –Activates complement 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 29 • IgG Monomeric • IgA forms dimers • IgG is the most • IgA is most important in important in the blood secretions (epithelium • IgG Opsonization, of intestine and Complement activation, respiratory tract) neutralization • Neutralizing antibodies • Transported through • Present in mother’s milk placenta 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 30 10
IgA 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 31 IgE • Monomeric • Binds receptor in mast cells beneath skin and mucosa • Acts as a receptor • Binding causes degranulation of mast cells 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 32 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 33 11
Distribution of Igs –IgG, IgM: Plasma –IgG, IgA (monomeric): Extracellular fluid –IgG Fetus – IgA (dimeric): Secretions, cross epithelia –IgE Mast cells beneath epithelia 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 34 2/10/2005 MICR 415 / 515 / 682 35 12
Recommend
More recommend