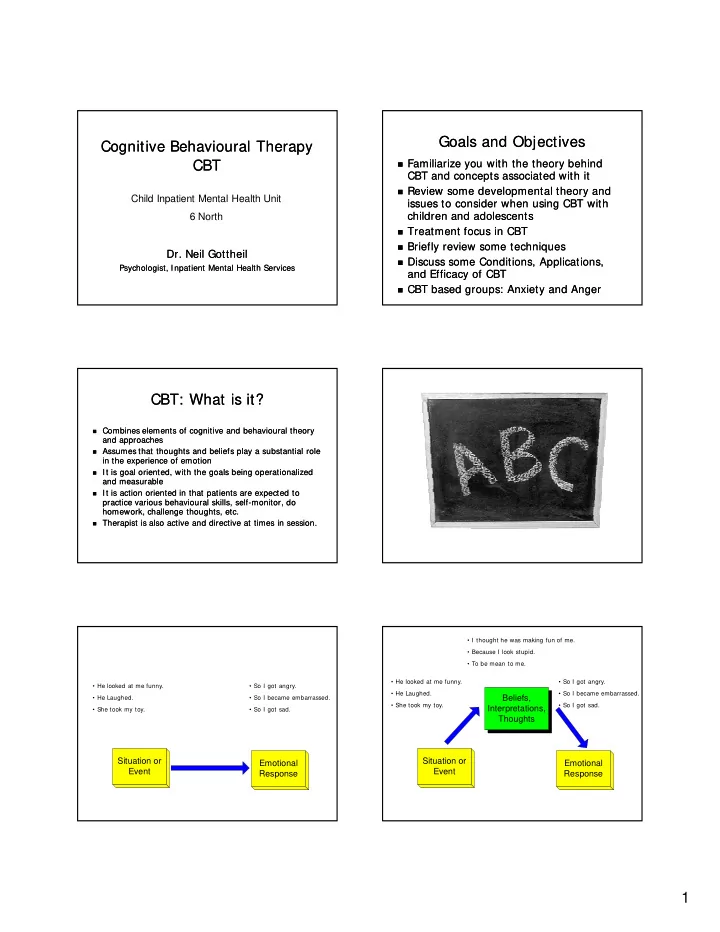

Goals and Objectives Goals and Objectives Cognitive Behavioural Therapy Cognitive Behavioural Therapy CBT CBT Familiarize you with the theory behind Familiarize you with the theory behind CBT and concepts associated with it CBT and concepts associated with it Review some developmental theory and Review some developmental theory and Child Inpatient Mental Health Unit issues to consider when using CBT with issues to consider when using CBT with children and adolescents children and adolescents 6 North Treatment focus in CBT Treatment focus in CBT Briefly review some techniques Briefly review some techniques Dr. Neil Gottheil Dr. Neil Gottheil Discuss some Conditions, Applications, Discuss some Conditions, Applications, Psychologist, Inpatient Mental Health Services Psychologist, Inpatient Mental Health Services and Efficacy of CBT and Efficacy of CBT CBT based groups: Anxiety and Anger CBT based groups: Anxiety and Anger CBT: What is it? CBT: What is it? Combines elements of cognitive and behavioural theory Combines elements of cognitive and behavioural theory and approaches and approaches Assumes that thoughts and beliefs play a substantial role Assumes that thoughts and beliefs play a substantial role in the experience of emotion in the experience of emotion It is goal oriented, with the goals being operationalized It is goal oriented, with the goals being operationalized and measurable and measurable It is action oriented in that patients are expected to It is action oriented in that patients are expected to practice various behavioural skills, self practice various behavioural skills, self-monitor, do monitor, do homework, challenge thoughts, etc. homework, challenge thoughts, etc. Therapist is also active and directive at times in session. Therapist is also active and directive at times in session. • I thought he was making fun of me. • Because I look stupid. • To be mean to me. • He looked at me funny. • So I got angry. • He looked at me funny. • So I got angry. • He Laughed. • So I became embarrassed. • He Laughed. • So I became embarrassed. Beliefs, • She took my toy. • So I got sad. Interpretations, • She took my toy. • So I got sad. Thoughts Situation or Situation or Emotional Emotional Event Event Response Response 1
1. Antecedents 2. Behaviours Other CBT Concepts Other CBT Concepts 3. Consequences Automatic thoughts Automatic thoughts Current beliefs and thoughts that are easily triggered Current beliefs and thoughts that are easily triggered Applied without proper evidence or scrutiny Applied without proper evidence or scrutiny Beliefs, Often happen so fast that people aren’t even aware they are there Often happen so fast that people aren’t even aware they are there Interpretations, Cognitive Distortions Cognitive Distortions Thoughts From making predictions about the future and how people will behave, From making predictions about the future and how people will behave, without sufficient evidence without sufficient evidence Selectively focusing on information consistent with beliefs and ignoring Selectively focusing on information consistent with beliefs and ignoring or devaluing contradictory information or devaluing contradictory information Taking too much responsibility for negative events and not considering Taking too much responsibility for negative events and not considering contributions made by others or the situation contributions made by others or the situation Situation or Emotional Failure to recognize partial successes Failure to recognize partial successes Event Response Beck’s Cognitive Triad Beck’s Cognitive Triad – – thoughts about Self, World, and Future thoughts about Self, World, and Future Other CBT Concepts cont’d Other CBT Concepts cont’d Behaviourism Behaviourism Learning is a result of connections established between stimuli and Learning is a result of connections established between stimuli and Irrational thoughts Irrational thoughts behavioural responses, and between behaviour and consequences behavioural responses, and between behaviour and consequences Catastrophic Catastrophic – If fail my exam I will never get into college or get If fail my exam I will never get into college or get It is a continuous process It is a continuous process a job a job All All-or or-none none – Either I succeed at this or I am a total failure Either I succeed at this or I am a total failure Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning Shoulds and Musts Shoulds and Musts – I should be loved by everyone. If he I should be loved by everyone. If he Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning dislikes me then I must be a bad person dislikes me then I must be a bad person Extinction Extinction Generalization Generalization It is easier to avoid than to face life’s difficulties and It is easier to avoid than to face life’s difficulties and Reinforcement Reinforcement – Positive versus Negative Positive versus Negative responsibilities responsibilities Punishment Punishment Happiness is externally caused Happiness is externally caused Schedules – Fixed versus Variable Schedules Fixed versus Variable Modeling Modeling A person’s worth is based solely on the opinions of others A person’s worth is based solely on the opinions of others What makes children different from What makes children different from Development Development adolescents? adolescents? Nature versus Nurture Nature versus Nurture Stage versus Continuous Development Stage versus Continuous Development 2
Recommend
More recommend