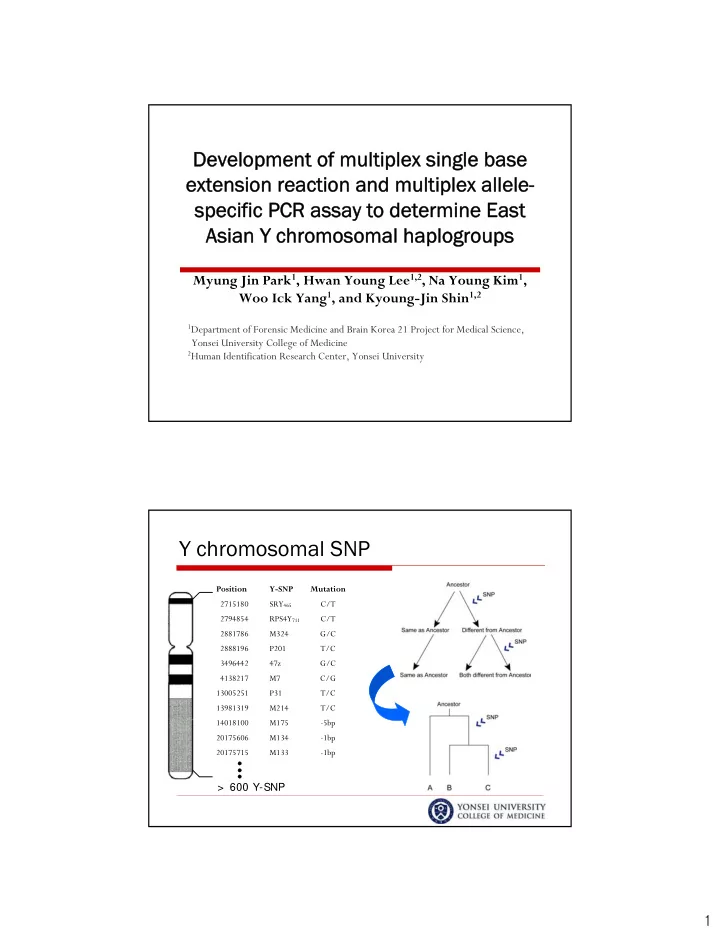

Developmen Development of multiplex single base t of multiplex single base extension reaction and multiplex allele- extension reaction and multiplex allele- specific PCR assay to determine East specific PCR assay to determine East Asian Y chromosomal haplogroups Asian Y chromosomal haplogroups Myung Jin Park 1 , Hwan Young Lee 1,2 , Na Young Kim 1 , Woo Ick Yang 1 , and Kyoung-Jin Shin 1,2 1 Department of Forensic Medicine and Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine 2 Human Identification Research Center, Yonsei University Y chromosomal SNP Position Y-SNP Mutation 2715180 SRY 465 C/T 2794854 RPS4Y 711 C/T 2881786 M324 G/C 2888196 P201 T/C 3496442 47z G/C 4138217 M7 C/G 13005251 P31 T/C 13981319 M214 T/C 14018100 M175 -5bp 20175606 M134 -1bp 20175715 M133 -1bp > 600 Y-SNP 1
Y chromosome phylogenetic tree Haplogroup O Y chromosome consortium F A G H B L1 retroposon insertion D I (LINE 1) polymorphisms was removed from this tree J Contradictory results E with N7, P201, JST002611 L M N C K O Q Define O3 P R S T Genome Res. 2008;18:830-38 Y haplogroup tying in forensics Forensic utility of Y-SNPs Human identification purposes (criminal, paternity, evolutionary, population studies) Haplogroups are non-randomly distributed among populations therefore Requiring a sensitive and efficient method for potential exists for predicting population of origin the Y chromosomal haplogroup determination The short PCR amplicons required for typing SNPs may result in success in East Asians with degraded samples and possibly higher sensitivity Increasing of need for ethnicity prediction Globalization of crime suspects and victims Increase of movement from East-southern population Increase of excavation of Korean War victims and ancient remains. Individual identification in mass disaster such as airplane crashes, tsunamis or terrorist attacks where people from various geographical areas are involved 2
Objects Development of multiplex systems for determination of East Asian Y haplogroups Single base extension (SBE) method with SNaPshot™ Multiplex kit Amplicon size < 100 bp to be suitable for the analysis of highly degraded forensic samples Allele specific PCR (AS-PCR) assay with fluorescent dyes Convenient method similar to STR typing for reference samples Validation of the multiplex systems Sensitivity test and efficiency test Concordance test between multiplex SBE reaction and multiplex AS-PCR assay Strategy for SNP typing SBE reaction G A GA AS-PCR A G G 5’ 3’ G allele C 3’ 5’ G G A A A 3’ 5’ A allele T 3’ 5’ G A 3
Materials and Methods Multiplex PCR conditions DNA samples Detection Systems 300 DNA samples obtained from the National Biobank of Korea. ABI prism 310 genetic analyzer, GeneScan software 3.7, and Genemapper Multiplex SBE reactions 3.2 software (Applied Biosystems) Total 25 l PCR reaction: 1 ng of DNA, 2.5 l of Gole STR buffer, 2.0 U of Serially diluted DNA samples (1 ng, 500 pg, 250 pg, 125 pg, 62 pg and 31 AmpliTaq Gold polymerase and PCR primer mix pg) of 9948 standard DNA (Promega, Madison, MA, USA) PCR cycling condition: 95 ° C 11 min; 94 ° C 20 sec, 60 ° C 1 min, 72 ° C 7 min X Artificially degraded DNA prepared by digesting 1.2 g of human genomic 33; 72 ° C 7 min DNA with 0.02 U of DNase I (NEB, Ipswich, MA, USA) for 40 min Total 10 l SBE reactions: 1 l of purified multiplex PCR product, SBE 10 DNA samples extracted from 60-year-old skeletal remains primer mix and a SNaPshot ™ Multiplex kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) SBE cycling condition: 96 ° C 10 sec, 50 ° C 5 sec, 60 ° C 30 sec X 25 Multiplex AS-PCR assay Total 10 l PCR reaction: 1 ng of DNA, 1.0 l of Gole STR buffer, 2.5 U of AmpliTaq Gold polymerase and AS-PCR primer mix AS-PCR cycling condition: 95 ° C 11 min; 94 ° C 20 sec, 60 ° C 1 min, 72 ° C 7 min X 30; 60 ° C 45 min Selection of Y-SNP for Multiplex SBE reactions A, B M145 DE DE RPS4Y 711 C C F Multiplex I M89 F K M9 K NO NO M214 * O* M175 O * O1* 1 M119 a O1a * O2* P31 M95 a 2 Multiplex II O2a * SRY 465 O2b* b 47z 1 O2b1 * O3* M122 3 O3a M324 a O3a3* P201 M159 a 3 O3a3a Multiplex III M7 b O3a3b O3a3c M134 c M133 1 O3a3c1 4
Schematic of multiplex SBE reactions 20 bp 30 bp 40 bp 50 bp 60 bp 70 bp Multiplex I M145 RPS4Y 711 M89 M9 M214 M175 (PCR 93 bp) (PCR 86 bp) (PCR 93 bp) (PCR 85 bp) (PCR 99 bp) (PCR 96 bp) 22 bp 31 bp 39 bp 48 bp 55 bp 63 bp Multiplex II M119 P31 M95 SRY 465 47z M122 (PCR 94 bp) (PCR 88 bp) (PCR 79 bp) (PCR 83 bp) (PCR 87 bp) (PCR 88 bp) 25 bp 33 bp 42 bp 50 bp 58 bp 66 bp Multiplex III M324 P201 M159 M7 M134 M133 (PCR 70 bp) (PCR 97 bp) (PCR 99 bp) (PCR 100 bp) (PCR 72 bp) (PCR 98 bp) 23 bp 30 bp 39 bp 47 bp 55 bp 67 bp All amplicon size ≤ 100 bp Y haplogroup determinations using multiplex SBE reactions Multiplex I Multiplex II Multiplex III DE O1a O3a C O3a3 O2 K O3a3b O2b O3a3c NO O2b1 O3a3c1 O3 O 5
Sensitivity test Multiplex I Multiplex II Multiplex III 1 ng 1 ng 1 ng 500 pg 500 pg 500 pg 250 pg 250 pg 250 pg 125 pg 125 pg 125 pg 62 pg 62 pg 62 pg 31 pg 31 pg 31 pg Repetition by 5 times All Y-SNPs were successfully called at as low concentration as 62 pg of DNA Efficiency test DNA from old skeletal remains Artificially degraded DNA Success rate (%) Concentration No. Y haplogroup (pg/ l) RPS4Y 711 M9G M214C STR Y-SNP C M145G M89T M175T 1 114.8 ± 10.20 93.3 100.0 NO 2 205.7 ± 2.75 100.0 100.0 O2 3 55.9 ± 5.94 66.7 100.0 O2b M122T P31T 106.5 ± 3.56 4 100.0 100.0 O2b M119A SRY 465 C M95C 47zG 5 766.1 ± 39.03 100.0 100.0 O3a3 Treated with 6 149.8 ± 11.30 80.0 100.0 O3a3c DNase I 27.8 ± 0.13 7 33.3 100.0 O1a M7C M134G M324G P201T 8 169.9 ± 10.96 100.0 100.0 O2b M159A M133T 9 84.9 ± 14.71 100.0 100.0 O3a3 275.2 ± 57.04 10 100.0 100.0 O2b Some skeletal remain samples had been typed only at some STR The fully correct Y-SNP profiles were obtained using artificially loci, Y-haplogroup could be successfully determined based on degraded DNA with the fragment size of around 100 bp. the amplified Y-SNP scoring results. 6
Selection of Y-SNP for AS-PCR assay A, B M145 DE DE M174 D RPS4Y 711 C C F F K M9 K NO M214 M231 NO N N * O* M175 O * O1* 1 M119 a O1a * O2* Multiplex P31 M95 a 2 O2a AS-PCR SRY 465 * O2b* b 47z 1 O2b1 * O3* M122 3 O3a M324 a O3a3* P201 a M159 3 O3a3a M7 b O3a3b O3a3c M134 c M117 M133 1 O3a3c1 4 002611 O3a4 Schematic of multiplex AS-PCR 70 bp 90 bp 110 bp 130 bp 150 bp FAM C ‐ RPS4Y 711 K ‐ M9 N ‐ M231 D ‐ M174 102 105 127 130 153 156 78 81 C wild wild T G wild A wild VIC O ‐ M175 O1a ‐ M119 O3 ‐ M122 O3a4 ‐ 002611 75 80 105 109 128 131 156 159 ‐ 5bp wild A wild C wild T wild NED O2 ‐ P31 O2a ‐ M95 O2b ‐ SRY 465 O2b1 ‐ 47z 78 81 102 105 129 132 156 159 C wild T wild T wild C wild PET O3a3 ‐ P201 O3a3c ‐ M134 O3a3c1 ‐ M117 O3a3b ‐ M7 79 82 126 130 152 156 103 106 C wild ‐ 1bp wild ‐ 4bp wild wild G 7
Haplotyping using multiplex AS-PCR assay Ladder N O1a O3a3c1 Future study for multiplex AS-PCR assay Concordant test A total of 300 Korean males will be tested by this assay and the results will be compared with those from the multiplex SBE reactions Validation test Sensitivity of the multiplex AS-PCR assay Efficiency of the multiplex AS-PCR assay 8
Conclusion Two different multiplex PCR sets, three multiplex SBE reactions and a multiplex AS-PCR assay, were developed for the identification of Y- haplogroups frequent in East Asians for analyzing forensic samples and reference samples, respectively. Using the multiplex SBE reactions, reliable genotypes were obtained from the amount as 62 pg of DNA and highly degraded DNA from old skeletal remains. The multiplex SBE reactions are very sensitive and optimized for analyzing old degraded forensic casework samples. The multiplex allele-specific PCR assay was developed for simple, rapid and reliable scoring of alleles in large number of samples and will be tested concordance with the results of the multiplex SBE reactions. This study would suggest that selective use of these multiplex sets for specific purpose is useful to obtain genotypes rapidly and effectively in forensic casework and reference samples. Thank you for your attention http://forensic.yousei.ac.kr 9
Recommend
More recommend