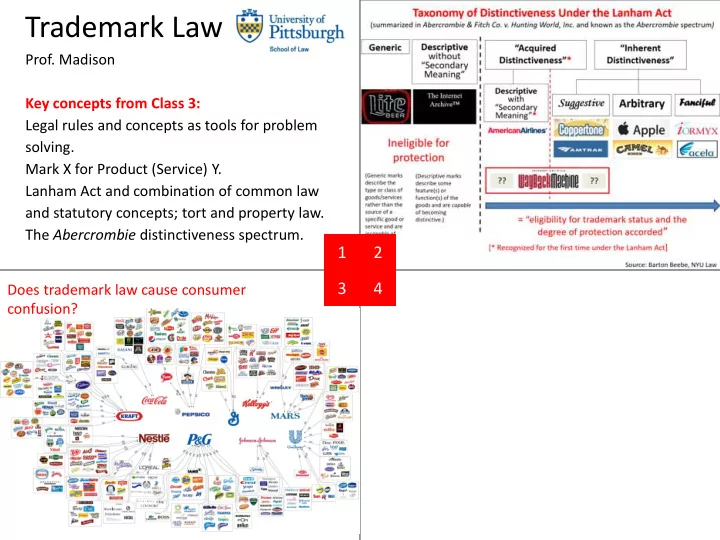

Trademark Law Prof. Madison Key concepts from Class 3: Legal rules and concepts as tools for problem solving. Mark X for Product (Service) Y. Lanham Act and combination of common law and statutory concepts; tort and property law. The Abercrombie distinctiveness spectrum. 1 2 3 4 Does trademark law cause consumer confusion?
The line between descriptive marks (not valid or Result of the “choose a mark” exercise: protected unless secondary meaning / acquired distinctiveness is shown; consumer goodwill must be built) and suggestive marks (automatically valid because inherently distinctive; consumer goodwill is assumed): 1.Dictionary definition 2.Imagination test In the language of trademark law, is this mark 3.Competitive need distinctive (i.e., valid)? If not – yet – how can 4.Third-party uses the owner ensure that trademark rights attach to the mark? 1 2 The line between descriptive marks that lack 3 4 secondary meaning (not valid or protected) and descriptive marks that have developed secondary meaning (valid and protected because they have acquired distinctiveness ). Frosty Treats Inc. v. Sony Computer Entertainment America (8th Cir. 2005)
Factors and Problems evidence: • Producer (An illustration: does it matter who caused the distinctiveness to investment (time, arise?) “ Red for staplers ”: $$, sales success)? created as film prop (1999), • Consumer/comp- produced by fans (1999-2002), etitor reliance/ manufactured by Swingline in opportunity? 2002. What is the first date of Swingline’s trademark? Board of Supervisors for Generic marks : Ask “what do Louisiana State consumers believe the product / University Agricultural service is? Is the mark source & Mechanical College v. indicating to them? ” Smack Apparel Co. (Note in this case: Right outcome, (5 th Cir. 2008) 1 2 wrong reasoning.) 3 4
Recommend
More recommend