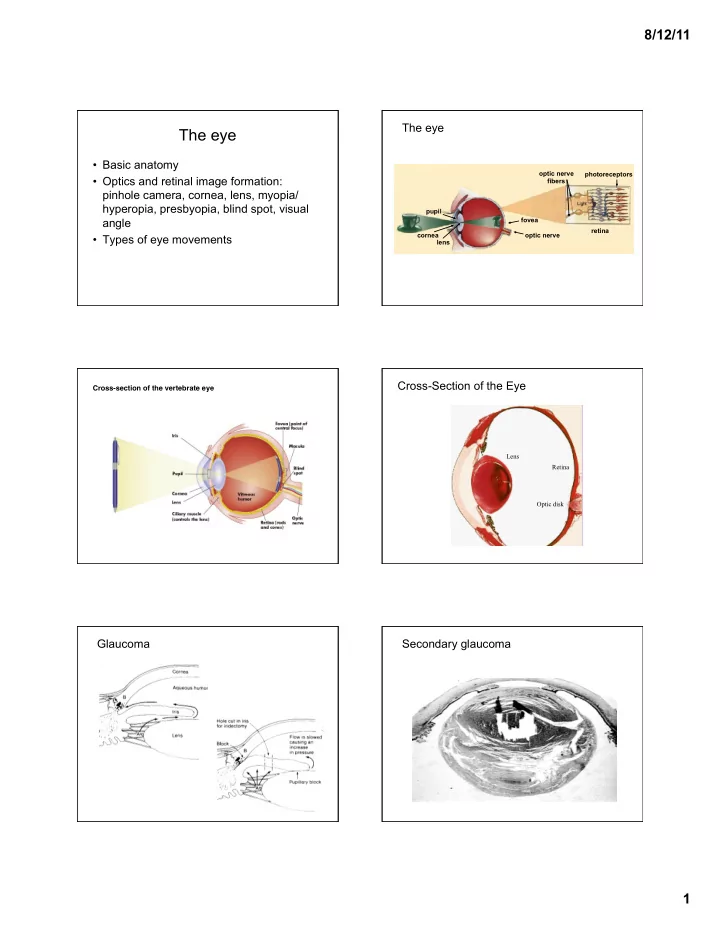

8/12/11 The eye The eye • Basic anatomy optic nerve photoreceptors • Optics and retinal image formation: fibers pinhole camera, cornea, lens, myopia/ hyperopia, presbyopia, blind spot, visual pupil fovea angle retina cornea optic nerve • Types of eye movements lens Cross-Section of the Eye Cross-section of the vertebrate eye � Cornea Lens Retina Optic disk Glaucoma Secondary glaucoma 1
8/12/11 Schiotz tonometer Detached retina Non-contact tonometer Ouch! Measures the time from the generation of the air puff until the cornea is flattened. It takes less time for the puff to flatten a soft eye than it does a hard eye. S.B. Some properties of light • Light bounces off of surfaces ( reflection ) • Light bends when the index of refraction changes air ( refraction ) water or glass • The amount of refraction depends on wavelength (the prism ’ s rainbow, dispersion ) air water or glass • Light bends when passing by an edge or through a small aperture ( diffraction ) Mike May 2
8/12/11 Retinal projection depends on size and Image formation distance Visual angle Visual angle Pinhole optics Pinhole size Aperture 3
8/12/11 Normal eye Focused for far Focused for near (e.g. 60 D) (e.g. 70 D) Object in world far away Good Object in world near Good Hyperopic (farsighted) eye Myopic (nearsighted) eye (shown here with hyperopia caused by shortened eyeball) Focused for far Focused for near (e.g. 60 D) (e.g. 70 D) Focused for far Focused for near (e.g. 60 D) (e.g. 70 D) Object in Object in world far world far away away Good Object in Object in world near world near Good The Eye ’ s Optics • Gathering and focusing light vs. image formation • Focal power is measured in diopters: Focal power is 1/focal length (diopters are in units of 1/m). • The eye has a focusing power of 60+ Diopters (D) – 60 D when focused far, more when focused near – What is the focal length of the eye? 1/x = 60 D... – Cornea: 43 D, Lens: 17+ D – Young children can accommodate 20 D; teenagers 10 D, 60-year- olds typically only 0.5 D at best. – Bionic lenses? – Myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia, and emmetropia 4
8/12/11 Right eye in bony orbit Eye movements • Why torsion? (Listing ’ s Law) • Basic types of eye movements – Saccades – Smooth pursuit – Nystagmus (including optokinetic) – Vestibulo-ocular reflex – Vergence – Tremor, microsaccades 5
Recommend
More recommend