Prediction Markets Thomas Steinke & David Rezza Baqaee October - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion Prediction Markets Thomas Steinke & David Rezza Baqaee October 17, 2010 Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion Contents Introduction
Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion Prediction Markets Thomas Steinke & David Rezza Baqaee October 17, 2010
Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion Contents Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion
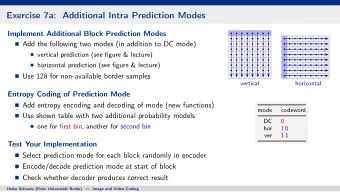
Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion What is a Prediction Market? • Payoffs are tied to the outcomes of precisely-defined easily-observable events. • Three main types of contract: • Winner take all—costs $ p , pays off $1 iff correct (probability of event). • Index contract—amount paid varies continuously (expectation of function). • Spread betting—prices are fixed but cutoff varies (quantile function).
Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion Questions Question Is risk-neutrality a valid assumption if the stakes are so high? Question Is expected utility a valid assumption, given ambiguity?
Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion Examples • Iowa Electronic Market (up to $500), TradeSports (Intrade), Hollywood Stock Exchange (HSX). • Small-scale virtual currency to large-scale financial markets turning over hundereds of millions. • Economic forecasting, retail sales, business confidence, inflation futures, elections, sports, current events.
Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion Bayesian vs. Classical • Prediction markets can give implied uncertainty about statistics. • Statistical agencies also give uncertainties. • These are different—comparing apples to oranges.
Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion Accuracy • Prediction markets outperform alternatives. • Prediction markets will subsume alternative prediction methods (EMH). • A study was done on 7,000 NFL, 20,000 MLB, and 100 Movies. • Empirically, only 3% better in RMSE. Question Are NFL, MLB, and movies meaningful examples? Is RMSE a good metric?
Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion Challenger Disaster
Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion Challenger Continued
Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion Market Manipulation • There appear to be few possibilities for arbitrage. • Prediction markets show behavioral biases. • Favorite/long shot bias (Allais Paradox?) • Preferences contaminating beliefs. • Potential for bubbles.
Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion Market Design • Real money or virtual money? • Servan-Schreiber et al find comparable performance. • “wealth” is only accumulated through a history of accurate prediction. • More flexible and allow for more experimentation. • Rules out arbitrage, possibly poor incetivization. • Motivating participation can be difficult.
Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion Applications • Contingent markets that explicitly tie events. • Rather than working out implied beliefs about Saddam and the price of oil, the payoffs could be denominated in oil (no regression). • Could use prediction markets to make decisions for you (correlation/causation, moral hazard). • Hedging risks (most prediction markets are too small, moral hazard).
Introduction Efficacy Market Manipulation Market Design Conclusion Conclusions • Prediction markets seem to weakly dominate all alternatives (but can be costly). • They have positive externalities. So we may need to subsidize them. • We’re currently regulating and outlawing them. The Science article discusses the need to reduce regulation.
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.