Paper Tips Overview Introduction Writing technical papers is not - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
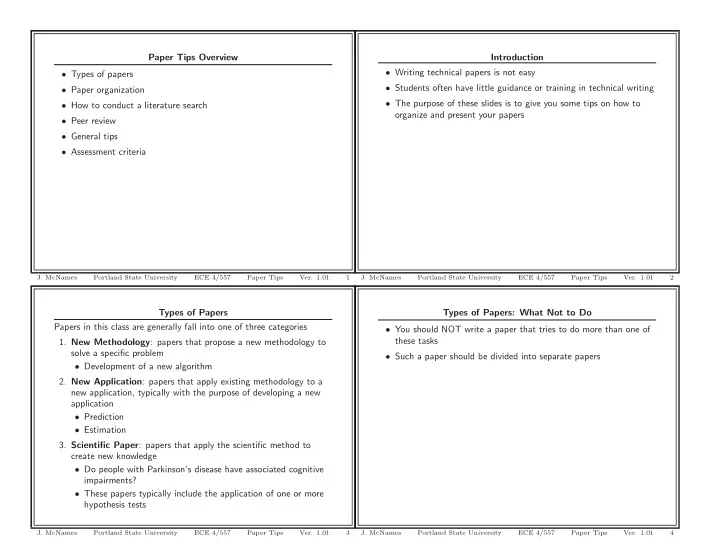
Paper Tips Overview Introduction Writing technical papers is not easy Types of papers Students often have little guidance or training in technical writing Paper organization The purpose of these slides is to give you some tips
Paper Tips Overview Introduction • Writing technical papers is not easy • Types of papers • Students often have little guidance or training in technical writing • Paper organization • The purpose of these slides is to give you some tips on how to • How to conduct a literature search organize and present your papers • Peer review • General tips • Assessment criteria J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 1 J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 2 Types of Papers Types of Papers: What Not to Do Papers in this class are generally fall into one of three categories • You should NOT write a paper that tries to do more than one of these tasks 1. New Methodology : papers that propose a new methodology to solve a specific problem • Such a paper should be divided into separate papers • Development of a new algorithm 2. New Application : papers that apply existing methodology to a new application, typically with the purpose of developing a new application • Prediction • Estimation 3. Scientific Paper : papers that apply the scientific method to create new knowledge • Do people with Parkinson’s disease have associated cognitive impairments? • These papers typically include the application of one or more hypothesis tests J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 3 J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 4
Paper Organization Introduction The introduction should meet the following objectives, usually in this Papers typically consist of the following sections order • Abstract: Should be written last • Define the problem to be solved/question to be answered • Introduction • Explain the practical significance of solving the problem. • Methodology/Design – Who will be affected by the answer? • Results • Summarize the prior, published work of other people who have attempted to solve this problem • Discussion • Distinguish your work from prior work • Conclusion/Summary – Your problem is different, or – Your solution is better (more accurate, or more robust, or requires fewer conditions and assumptions, etc.) • If the paper has objectives other than solving the stated problem, they should be stated here as well • Optionally, describe how the paper is organized J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 5 J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 6 Algorithm Design Methodology: Scientific Papers • This section is only included in papers that propose a new • This section describes how the experiment was conducted to test algorithm the hypothesis • Typically this section completely describes the algorithm • Includes – How the data was collected • If the algorithm is especially complicated, mathematical proofs and other lengthy details are sometimes included in an appendix – How the data was analyzed – What type of hypothesis test was used • The goal of this section is to completely and clearly describe the new algorithm – The level of significance • Do not describe components of your algorithm elsewhere • Essentially, all of the details of what you did to collect and analyze the data belong in this section J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 7 J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 8
Methodology: New Algorithm, Application Results • Typically, this section is also full of detail stating the results of • This section describes how you assessed the performance of your your work algorithm or new application • For this class, results will often be plots, tables, or the results of • Assessment often doesn’t receive sufficient attention hypothesis tests • Must think carefully about how to demonstrate your algorithm works better than one of the following: – Previous techniques published by others – The best current practice • Whenever possible, the assessment should be prospective – Use new data to measure performance – Reduces favorable bias J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 9 J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 10 Discussion Conclusion/Summary • The objectives of this section are • This section should concisely summarize the final results of the – To interpret the results paper – To discuss possible explanations for any anomalies in the results • For scientific paper, typically one or more conclusions can be – To speculate about the impact of the results drawn • In scientific papers, this section is also used to compare the results • For new methodologies, a summary section may be more with those of other studies and suggest possible explanations appropriate that summarizes (hypotheses) for any discrepancies – What was proposed – How well it performed – What other advantages & good features it has J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 11 J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 12
Abstract Organization • The abstract should be a concise summary of the entire paper • Required: Abstract, Introduction, Results, Conclusions, & References (if any) • It is not an introduction • Optional: Acknowledgments and Appendices • Should include a statement of the problem, summary of the methods and key results, and the conclusions that you made • Prohibited: Source code and raw data in printed form • This is usually easy to write once you have written the rest of the paper J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 13 J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 14 Literature Search General Tips • You should conduct a literature search for your project • Readership • Purpose: to determine what other people have written about your – Should be written for someone that understands the key topic concepts and methods covered in this class • Literature only includes PUBLISHED papers – You may assume the reader is a first year graduate student in an engineering program • It does not usually include web pages or textbooks • In general, try to avoid passive sentence construction • You cannot conduct a literature search with Google or any other – If you don’t like using first person pronouns (“I”), you can web search engine often use “this paper” or “this report” as the subject • The PSU library has web access to several literature databases – For example, “This paper describes an analysis of. . . ” that you can use to find papers on your topic – Not “An analysis of . . . is described” or “I describe an analysis • Probably the best ones for this class are of . . . ” – Web of Science (http://isi4.isiknowledge.com) • Try to use simple declarative sentences, “The model achieved an – Compendex via Engineering Village 2 MSE=3.27 (1.75–8.83 with 95% confidence).” (http://www.engineeringvillage2.org) – IEEE Xplore (http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/Xplore) J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 15 J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 16
General Tips Continued • Figures – Label your axes. – Describe the figures in words using a caption below the figure – Be sure to use the IEEE format for the caption. • Tables – Remember to use units – The captions go above the tables • Citations – Include relevant citations – Use review articles to avoid a lengthy literature search – Each reference number should be enclosed in square brackets – Do not begin a sentence with a reference number J. McNames Portland State University ECE 4/557 Paper Tips Ver. 1.01 17
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.