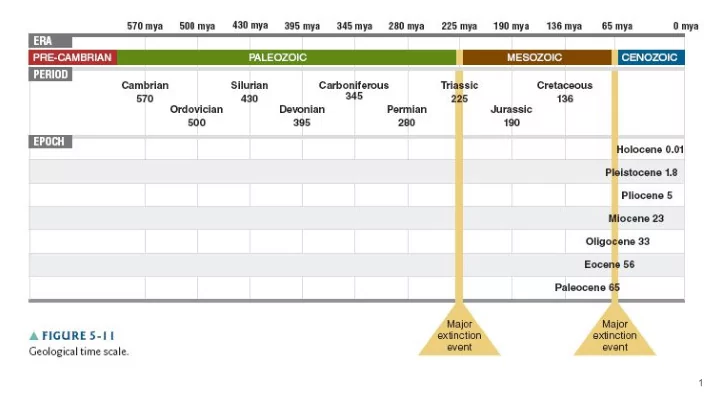

Paleozoic era (570-225 mya) -first vertebrates emerged -first mammal-like reptiles -Pangaea formed Mesozoic era (225-65 mya) -Age of dinosaurs Cenozoic era (65-0 mya) -Age of mammals 1
Continental drift: movement of continents on Earth's surface -plate tectonics moved organisms around the globe during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras 2
Mesozoic to Cenozoic Late Mesozoic era: Age of Dinosaurs -earliest mammals Cenozoic era: age of the mammals 3
Three modern mammalian subgroups Monotremes: most ancestral mammals, e.g., they lay eggs 4
Three modern mammalian subgroups Marsupials: immature birth; development continues in mother's pouch 5
Three modern mammalian subgroups Placental: in utero development 6
Mammalian shared derived homologies -Endothermic -Heterodont dentition -Placental -Complex brains and f lexible behavior 7
Overview of the primates -native to tropics and semi-tropics Four categories of Primate homologies 1. Limbs and locomotion 2. Diet and dentition 3. Senses and brain 4. Maturity and behavior Rhesus macaque 8
Overview of the primates 1. Limbs and locomotion 9
Overview of the primates 2. Diet and dentition -generalized; omnivorous Dental formulas: 10
Overview of the primates 3. Senses and brain -color vision and diurnal -stereoscopic vision - eyes are located in front of face -decreased reliance on sense of smell 11
Overview of the primates 4. Maturity and behavior -long life span -long gestation period -few offspring -delayed maturation Behavior -depend more on learned, flexible behavior over pre-packaged instinct -highly social 12
Recommend
More recommend