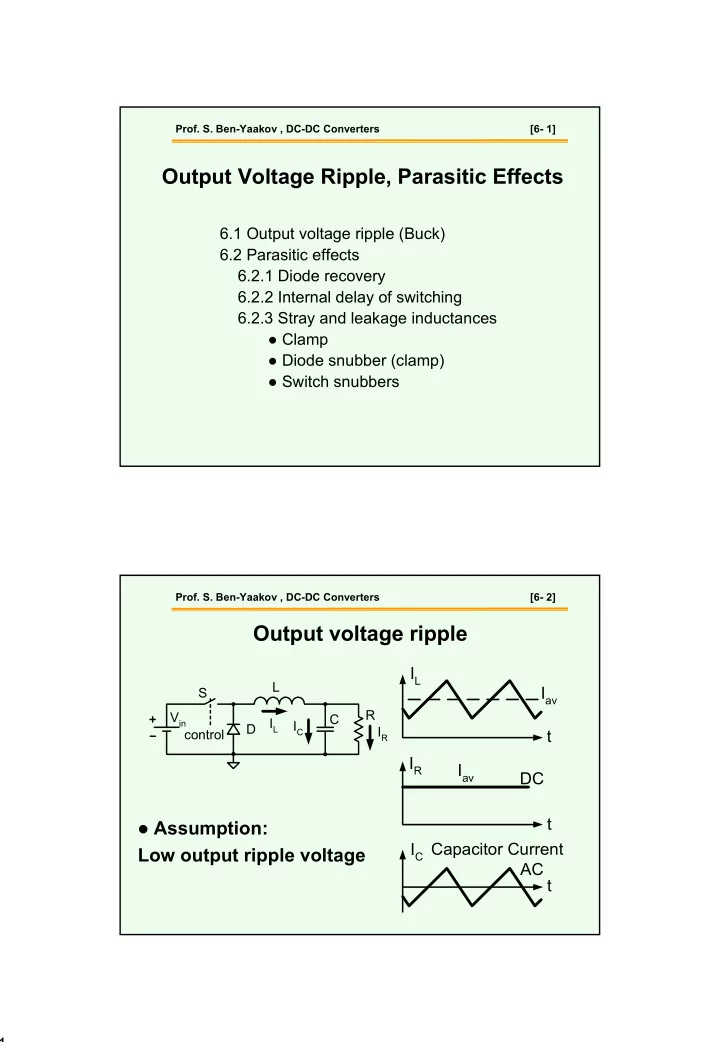

Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 1] Output Voltage Ripple, Parasitic Effects 6.1 Output voltage ripple (Buck) 6.2 Parasitic effects 6.2.1 Diode recovery 6.2.2 Internal delay of switching 6.2.3 Stray and leakage inductances ● Clamp ● Diode snubber (clamp) ● Switch snubbers Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 2] Output voltage ripple I L L I av S R V in C I L I C D I R control t I R I av DC t � Assumption: I C Capacitor Current Low output ripple voltage AC t 1
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 3] Ripple I C ∆ I L t 2 ∆ I t 1 t 2 L T s V C ∆ V t c t ∆ Q 2 ∫ ∆ = ∆ = Q I dt ; V C ; L ∆ I 1 C ∆ = t V L 1 C 8 C f ∆ ∆ I T 1 I s L T ∆ = L ⋅ s ⋅ ∆ = Q ; Q s 2 2 2 8 Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 4] V V D Ripple ∆ L = ∆ = = I o D T o off I V t / L L off s o off L Lf s V D 1 V D ∆ = o off = o off V C 2 CLf 8 f 8 CLf s s s V D ∆ I = The effect of f s o off Lf s ∆ I L; f s can be traded for same ∆ I ∆ = L V C 8 f C s C;f s can be traded for same ∆ I& ∆ V C V D o off ∆ = V C 2 if f s is increased for given L, C 8 LCf s ∆ V C goes down -40 db/dec (second order) 2
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 5] Example L S ∆ I L = 1 A R V in C = µ C 47 F I L I C D I R control = µ T s 10 S = Ω ESR 10 m ∆ Find the output voltage ripple V ⋅ µ 1 A 10 S ∆ = = V C 25 mV ⋅ µ 8 47 F ∆ = Ω ⋅ = V ESR 10 m 1 A 10 mV � Approximate (upper limit) of total ripple) ∆ = ∆ + ∆ = + = V V V 25 mV 10 mV 35 mV C ESR Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 6] Application of Simulation 10meg R4 D1 out Dbreak L1 L2 V1 {L1} C1 RL {Vin} {L1*(n*n)} 220u {Load} IC = 6 out_gnd drain S1 K K1 0 gate PARAM ET ERS: K_Linear + + COUPLING = 1 n = 0.5 - - L1 = l1 Vin = 12 V1 = 0 Sbreak L1 = 300u V2 L2 = l2 V2 = 15 Load = 10 TD = 0 0 TR = 0.01u TF = 0.01u PW = 10u PER = 20u 0 Modify circuit to include ESR=100m Ω Find ripple at output 3
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 7] Diodes Recovery – Implications L V x V o V in Reverse current at R C switch turn on � Soft and hard recovery Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 8] Stages in diode recovery Diode voltage L stray L stray V D t ESR V O L stray V Dmax L stray L stray ESR 4
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 9] Turn “off” of transistor L main L main L stray L stray C o V o L stray L stray ESR L stray V DS V O t Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 10] Diode forward recovery I +V C L I t V D V PK clamp V F t 5
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 11] Parasitic effects: Internal delay To turn “on” R L R G V ′ (real) C GS gs R L V gs L S V gs L S C gs = Q V' gs Depend on Q + R R L G Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 12] Clamps V in ∗ limiting maximum voltage V ′ o V O I pk V in L lkg V ds C dss V DS L lkg V O C dss t 6
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 13] Solutions n:1 n:1 V O V O V in V in Very fast diode L lkg L lkg R c C c C dss V z > V in + V o ’ = V in + nV o Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 14] Simple Example V in Clamp B is better A from the point of view V in of efficiency. = + ′ V ( A ) V V C in o B But ... 7
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 15] Parasitic inductance L 1 V in Energy of L 1 L 2 L 3 L 4 will cause high spike on C (FET). The FET is not protected! C L 4 L 2 L 3 Rule: Connect clamps and snubbers directly to the elements to be protected Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 16] To protect FET V in Line D L D R G Line Still: G L S S 8
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 17] Designing the Snubber Components V in R c C c L lkg Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 18] Snubber ∆ V V V Cc av T s L Parasitic energy I + lkg pav I ' p V R V C o Cc C C V C R Cc c c V Cc > V o ’ 9
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 19] Leakage discharge dI I I p dt pk I p av · R c = V Cc av R c · C c = T > T s t p − dI V V ' p = Cc av o dt L lkg L I = lkg pk t p − V V ' Cc av o Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 20] Leakage average current ⋅ I t = pk p ⋅ I f p av s 2 Procedure 1. Select V Cc av 2. Calculate I p av V R = Cc av 3. Select c I p av 4. Select C c T > T s 5. Trim in-circuit 10
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 21] Simulation Exercise 10meg R4 D1 out Dbreak L1 L2 V1 {L1} C1 RL {Vin} {L1*(n*n)} 220u {Load} IC = 6 out_gnd drain S1 K K1 0 gate PARAM ET ERS: K_Linear + + COUPLING = 1 n = 0.5 - - L1 = l1 Vin = 12 V1 = 0 Sbreak L1 = 300u V2 L2 = l2 V2 = 15 Load = 10 TD = 0 0 TR = 0.01u TF = 0.01u PW = 10u PER = 20u 0 � Add 1uH leakage to Flyback converter. Design a clamp and check it by simulation. Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 22] Diode Snubber (clamp) V o C D L stray L stray Diode Snubber 11
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 23] Snubber waveforms V D no snubber bad snubber C S R S V o V O C D L stray V D C S is very l arg e good snubber V O C s > C D 2 V C Energy lost to snubber S 2 Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 24] Snubber design Design - use simulation in circuit tuning C S R S Needed information I pk ( Reverse ) L stray V O I pk L stray 2 L I stray pk ⇒ ⇒ + ∆ moves to C V V s o 2 R s ⇒ damping 12
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 25] Switch Snubbers control V GS t V V S S I S t J d P switching t Switching losses due to overlap P d linear with f S ! Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 26] Snubber types dV dI Snubbers = control of or dt dt dV snubbers dt dI snubbers dt 13
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 27] Snubber types Passive (dissipative) snubber ∗ Energy lost to heat Non-dissipative (lossless) snubber ∗ Energy recovered Passive Snubbers ∗ by passive network Active snubbers ∗ by auxiliary active devices Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 28] Switching overlap control V GS t dV V S dI dt I S dt t J p t 14
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 29] Switch Snubber V o C dV (at turn off) can be slow down by adding external dt snubber capacitor C V o At turn off C C dss Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 30] dV/dt dV I = + dt C C dss C dss - output capacitance of FET I = 1 Amp C + C dss = 1nF 3 dV 1 10 kV = = = 1 µ S − − 9 6 dt 10 10 15
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 31] Capacitor losses V o C 2 2 CV CV Problem at turn on ! = = ⋅ E O ( J ) P O f C d s 2 2 Example : V O = 400 V C = 1 nF f s = 100 kHz − 9 4 ⋅ ⋅ 10 16 10 5 = ⋅ = P 10 8 W d 2 Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 32] Solution V O C S R S V O C S Snubbing 16
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 33] Reset V O If R ds on < R s most energy will be lost to R s → Heat C S R DSon Selection of C s → R S Selection of R s → to ensure reset 1 = << ≈ T t t 4 R C on on s s R C s s Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 34] CV 2 Losses 2 C 2 C V dss dss max → f lost to heat s 2 Linear with f s ! Switching losses (overlap) also linear with f s ! 17
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 35] Lossless snubbing (simple example) Q 1 V C t C 1 L 2 Q 2 delay t V C I C 2 L 2 t V DS 1 C 1 , C 2 of transistor t plus external (if any) V DS 2 t Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [6- 36] Dead time requirement Q 1 t Q 2 delay t I L t V DS 1 t V DS 2 t 18
Recommend
More recommend