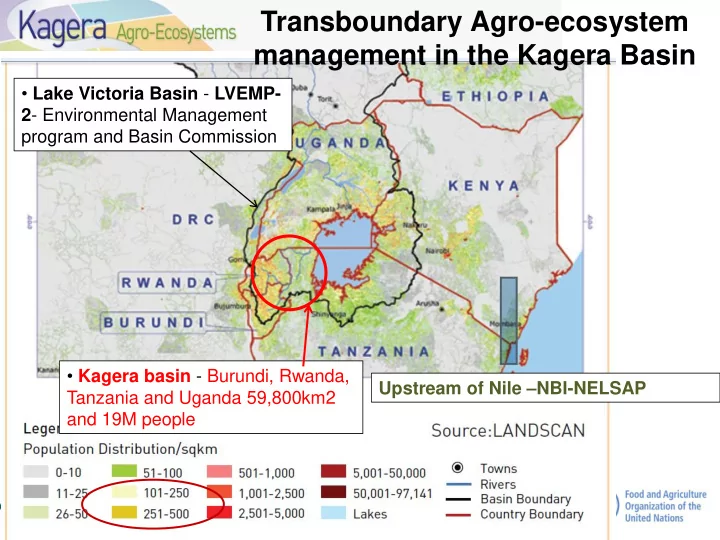

Transboundary Agro-ecosystem management in the Kagera Basin • Lake Victoria Basin - LVEMP- 2 - Environmental Management program and Basin Commission • Kagera basin - Burundi, Rwanda, Upstream of Nile – NBI-NELSAP Tanzania and Uganda 59,800km2 and 19M people
Pressures on land resources in the Kagera basin Bush burning
Kagera Basin Challenges State: Degradation (soil erosion & fertility loss, less water quality & flow, loss of vegetation cover, biodiversity & ecosystem functions) Impacts: poverty, food insecurity, conflict over resources, youth out-migration (labour shortage) To treat these symptoms we need to address the cause ses Direct Pressures : reduced farm size, fragmented, poor land use/ management practices, differential access (herds; land) conflict Drivers: population growth, market driven crop/ livestock intensification (urban demand), low knowledge base, lack of support (policy, incentives)
Theory of change f rom a degradation scenario to adoption and buy in of integrated SLaM 1. Support for SLM adoption for range of land uses and land user types (FFS approach grants, facilitation/extension, technical support teams, investment) 2. Capacity developed at all levels : farmers, technicians, decision makers. 3. Participatory Land Planning: farm-catchment-community bye laws, district 4. Transboundary Cooperation & harmonisation • to restore degraded lands and improve productivity • to sequester carbon and adapt to climate change • to conserve agro-biodiversity and ensure its sustainable use • to improve food security and rural livelihoods • and thereby, contribute to the protection of international waters
Diagnostics using DPSIR Framework Build understanding of the interactions RESPONSES for each land use type and for each land user group IMPACTS DRIVING (on FORCES livelihood (indirect causes) assets) PRESSURES (direct causes) IMPACTS (on ecosystem services) STATE OF THE LAND Vegetation, soil, water (processes) Drivers Pressures Status and Impacts Responses trends
LADA local assessment- Characterize the area/catchment, status and trends of vegetation, soil, water Compare good and poor land use and management practices Transect Responses & their Impacts on ES Z A Vegetation Soil erosion / soil properties Water resources
Key Informant & land user typology and HH livelihoods assessment Interviews with sample households in catchment Score each asset for interviewed households • Natural assets- land area, land quality, trees, … • Physical assets- access to transport, market … • Human assets- education level, knowledge • Social assets- water users organisation, FFS … • Financial assets- capital, access to credit/bank Draw asset pentagons to compare the assets (& capacities) of the different land user profiles and trends Better off Average Poor
Field visits to select best practices (Tanzania) Visits with locals and extension and FFS study plots to select and adapt existing crop, grazing, tree, forest and livestock management practices
Identify, Assess and Document SLM Technologies and Approaches using WOCAT
FFS Learning & Experimentation Range of SLAM interventions Well made ridges on a radical terrace planted with Round potato for Umurava FFS group field Ballet box to assess knowledge FFS group agroforestry tree change nursery, Kamonyi district FFS group dynamics
Integrated landscape/production systems for multiple benefits and • Bring together FFS approach, catchment resilience planning & management and bye laws/ local governance • Identify, assess and document best practices using WOCAT tools (QA, QT), • Share best practices through WOCAT database and pilot QW and QC • Asses and raise awareness understanding on multiple benefits of SLM: • Productivity , • CC A&M, short and long term resilience • Agro-biodiversity (diverse genetic resources, species and habitats- pollination, pest control etc) • Food security and nutrition • Sustaining ecosystem services (C, nutrients water, flood & drought management) http://www.fao.org/in-action/kagera/home/en/a www.fao.org/landandwater
Recommend
More recommend