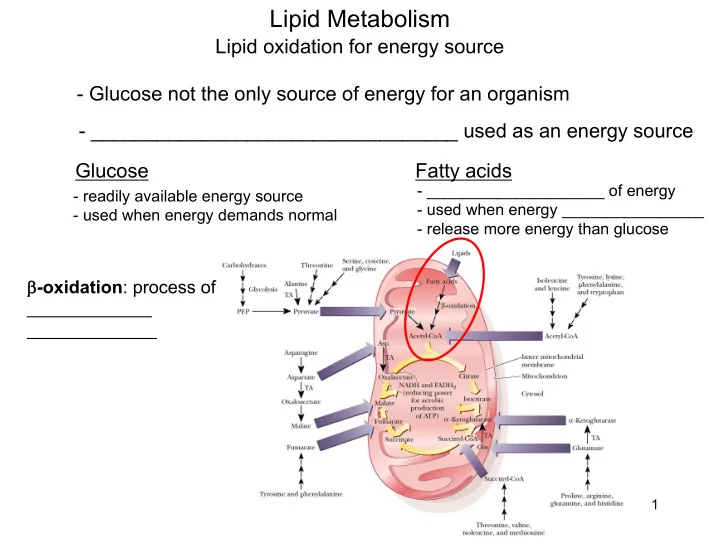

Lipid Metabolism Lipid oxidation for energy source - Glucose not the only source of energy for an organism - _________________________________ used as an energy source Glucose Fatty acids - ____________________ of energy - readily available energy source - used when energy ________________ - used when energy demands normal - release more energy than glucose b -oxidation : process of 1
Lipid Metabolism Lipid synthesis Acetyl-CoA from TCA cycle used to _____________________________ _____________________ converted to acetyl-CoA 2
Lipid Metabolism Cellular localization of lipid metabolism b -oxidation - ____________ Acetyl-CoA formation - ______ Fatty acid chain elongation - ___ 3
Fatty Acids amphipathic lipid -carboxyl group polar end (hydrophilic) -hydrocarbon chain nonpolar tail (hydrophobic) - even # of carbon atoms - hydrocarbon chain unbranched - saturated: no C - C double bonds - unsaturated: C - C double bonds - double bonds almost always cis 4
Triacylglycerols (triglycerides) Triacylglycerols - ester linkage of a fatty acid to each OH of glycerol Generally, same F.A. esterified to all three positions on glycerol Not found in membranes but act to store F.A.’s for metabolic energy source polar nonpolar 5
Phosphoacylglycerols (phospholipids) Phosphatidyl esters 6
Lipid Metabolism Release of fatty acids from triacylglycerols and phospholipids triacylglycerols phospholipids - ______________ - _____________________ - breaks bonds between ____ - breaks bonds between F.A. _______________________ and OH of glycerol - not so often _______________ - most often _______________ 7
Lipid Metabolism Release of fatty acids from triacylglycerols - Epinephrine hormone activates _________________________. - Each F.A. released from glycerol - F.A. has _____________________ Why do distance athletes drink coffee before event? - caffeine ______________________ - induces F.A. __________________ - saves carbohydrates for later in the event 8
Lipid Metabolism Oxidation of F.A. Activation of F.A. - bonding of F.A. carboxyl group ____________________ - general term of ______________________ - exact name depends ______________________ - ___________________________________ - energy, by hydrolysis of two phosphate bonds - takes place in cytoplasm 9
Lipid Metabolism b -oxidation - acyl-CoA moved from cytoplasm to ____________________________ - ___________ units removed from F.A. in 4 rxn cycle - carbons removed from _________ ___________________ - b carbon becomes carboxyl carbon - cycle repeats until F.A. _____________ in successive 2 carbon acetyl-CoA removals - produced acetyl-CoA put into ________________ 10
Lipid Metabolism b -oxidation Step 1: oxidation of C a - C b bond to ____________________ - acyl-CoA __________________ - FAD reduced to FADH 2 - double bond in __________ configuration - product: trans - D 2 -Enoyl-CoA 11
Lipid Metabolism b -oxidation Step 2: C a - C b double bond hydrated _______________________ - enoyl-CoA __________________ - uses H 2 O - product: b -hydroxyacyl-CoA 12
Lipid Metabolism b -oxidation Step 3: C b _______________________ - hydroxyacyl-CoA ______________ - reduces NAD+ to NADH - product: b -ketoacyl-CoA - set up for C b to become __________________ 13
Lipid Metabolism b -oxidation Step 4: C a - C b ___________________ - ___________________ - product: acetyl-CoA - requires CoA, added to remaining F.A. - C a goes with acetyl-CoA - C b becomes - _____________________ undergoes a new round of b -oxidation - acetyl-CoA enters ________ 14
Lipid Metabolism b -oxidation - b -oxidation of even # F.A. gives __________________________ - C-18 stearic acid = ____________________________ - requires ____________________ of b -oxidation 15
Lipid Metabolism b -oxidation energy production __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ 16
Lipid Metabolism b -oxidation energy production 3 Glucose = 18 carbons = __________ 1 stearic acid = 18 carbons = ________ Why the difference in ATP production? A more ______________ can donate more e- for ATP production 17
Lipid Metabolism b -oxidation H 2 O production Metabolic H 2 O - _____________________________ aerobic metabolism Large amount of water from b -oxidation can be used ___________________ _____________________________________ Kangaroo rats Camels - hump contains stored lipids - diet of seeds high in lipids - live indefinitely with out external H 2 O 18
Lipid Metabolism Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Acetyl-CoA is transported to the ___________________ Once in cytoplasm, converted _____________ 19
Lipid Metabolism Fatty Acid Biosynthesis 2 Priming events: 1. Acetate transferred to ___________________________________ 2. Acetate transferred to b -ketoacyl-S-ACP-synthase (_____________) - acetyl-KSase combined with ____________, forming acetoacetyl-ACP - ___________ malonyl lost malonyl - carboxylated acetate 20
Lipid Metabolism Fatty Acid Biosynthesis - next three steps are exact ___________________ - reduces ketone from acetate - ____________________ - dehydration to double bond - reduction to __________________ - produces butyrl-ACP - process requires ______________ - uses 2 NADH 21
Lipid Metabolism Fatty Acid Biosynthesis - butyrl-ACP added _________________ malonyl-ACP - same 3 reactions take place to _______________________ - process repeated until required length achieved 16:0 palmitate 22
Lipid Metabolism Fatty Acid Biosynthesis F.A. synthesis takes ___________________ Fatty acid synthase - large protein complex containing all the _______________ _________________ - double bonds introduced by enzymes in the _________________________ As with glycolysis and gluconeogenesis b -oxidation and F.A. synthesis are ____ _______________________________ But, are opposites in terms of end products 23
Lipid Metabolism Triacylglycerol Biosynthesis Generally, free F.A. _____________________ F.A. added to OH groups of ___________ 24
Lipid Metabolism Phospholipid Biosynthesis - 2 F.A. added to ____________________ - polar head group ___________________________ FA 1 FA 2 25
Lipid Metabolism Cholesterol Biosynthesis - essential part of __________________ - used to make __________________ - major contributor ___________________ -synthesized through ______________________________ Isoprenoid pathway - use of ___________ to produce _______ compounds Isoprene Isoprene units can be condensed to form intermediates 26 with carbons ____________________________
Lipid Metabolism Cholesterol Biosynthesis Isoprenoid pathway involved in synthesis of: Chlorophyll a - ________________ (coenzyme Q, e - transport) - ________________ - ________________ Vitamin A ubiquinone 27
Lipid Metabolism Cholesterol Biosynthesis Plants make many isoprenoids, > 20,000 - __________________ - _______________________ carotenoids capsidiol - ________________ b -carotene used by mammals to make vitamin A, ______________________ b -carotene in tomatoes Vitamin A 28
Lipid Metabolism Cholesterol Biosynthesis Isoprenoid pathway general scheme: ____ ____ ____ isopentenyl geranyl farnesyl acetate mevalonate ….C 50 x 3 diphosphate diphosphate diphosphate (acetyl-CoA) ____ (_____) (_____) (_____) ____ ____ ____ ____ O OH S-CoA OPP OPP OPP HO OH O Isopentenyl geranyl farnesyl acetyl-CoA mevalonate diphosphate diphosphate diphosphate Intermediates can be used for ______________ ____________________________________. 29
Lipid Metabolism Cholesterol Biosynthesis Isopentenyl geranyl farnesyl diphosphate diphosphate diphosphate acetyl-CoA mevalonate C 2 C 6 C 5 C 10 C 15 O OH S-CoA x 3 OPP OPP OPP HO OH O x 2 ___________ _____ or ___________ _____ HO 30
Lipid Metabolism Cholesterol Biosynthesis C 30 Squalene is cyclized to _____________ 19 reactions by 19 enzymes convert C 30 lanosterol to C 27 cholesterol 3 carbons lost _____________ - _______________________ of liver cells. 31
Lipid Metabolism Cholesterol Metabolism - cholesterol converted to _____________ Steroid hormone production - pregnenolone to __________________ - sex hormones - glucocorticoids _______________ cortisone _______________ carbohydrate, protein, F.A. metabolism - mineralcorticoids aldosterone _______________________ 32
Lipid Metabolism Cholesterol Metabolism Atherosclerosis - condition of blocked artery by __________________ ____________________ Cholesterol is transported in the blood in the form of __________________________ - cholesterol - phospholipids - proteins LDL - ____________________ lipoprotein HDL - ____________________ lipoprotein Density determined by amount of protein 33
Lipid Metabolism Cholesterol Metabolism - LDL internalized to a cell by binding __________________________ - LDL broken down into ___________________________ - cholesterol used in membranes - oversupply of cholesterol turns off ________________________. What type of regulation is this? - also stops production _____________ - LDL can not be internalized, builds up in arteries, clogged arteries 34
Recommend
More recommend