Lecture series on 3d gravity Lecture 1: Geometry of Classical 3d - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Lecture series on 3d gravity Lecture 1: Geometry of Classical 3d Gravity Quantum Structure of Spacetime and Gravity 2016 August 21-28 2016 Belgrade, Serbia Catherine Meusburger Department Mathematik, Universitt Erlangen-Nrnberg
Lecture series on 3d gravity Lecture 1: Geometry of Classical 3d Gravity Quantum Structure of Spacetime and Gravity 2016 August 21-28 2016 Belgrade, Serbia Catherine Meusburger Department Mathematik, Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg
Motivation Why 3d gravity? • toy model for quantum gravity in higher dimensions • non-commutative structures and mathematical structures of NC geometry: Hopf algebras, (co)module algebras, twists,… • relates them to classical geometry: Lorentz and hyperbolic geometry, Teichmüller theory,… Content • Lecture 1: Geometry of classical 3d gravity • Construction of spacetimes • Classification results • Relation to Teichmüller and hyperbolic geometry • Lecture 2: Phase space and symplectic structure • Phase space of 3d gravity • Symplectic structure in terms of Poisson-Lie groups • Phase space as cotangent bundle of Teichmüller space • Lecture 3: Quantisation • Quantum 3d gravity as a Hopf algebra gauge theory • Construction of the quantum theory • Relation to models from condensed matter physics
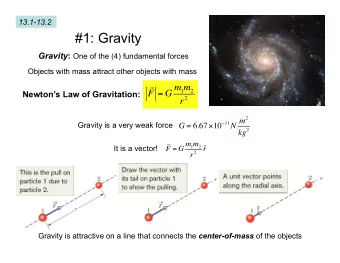
1. Gravity in 3 dimensions Ric µ ν − 1 Einstein equations 2 g µ ν R + Λ g µ ν = − 8 π GT µ ν • in 3d: Ricci curvature ➩ Riemann curvature R µ νρσ Ric µ ν • no local gravitational degrees of freedom • spacetimes locally isometric to model spacetimes X Λ • global degrees of freedom from matter (point particles) and topology • vacuum solutions ( ) ➩ constant curvature ➩ Einstein spacetimes Λ T µ ν = 0 • constructed as quotients of model spacetimes model spacetimes spacetime X Λ isometry group G Λ Lorentzian Λ > 0 dS 3 PSL(2 , C ) ( − 1 , 1 , 1) PSL(2 , R ) ⊂ G Λ = PSL(2 , R ) n R 3 Λ = 0 M 3 Iso(2 , 1) ∼ X Λ = G Λ / PSL(2 , R ) Λ < 0 AdS 3 PSL(2 , R ) × PSL(2 , R ) S 3 Λ > 0 SU(2) × SU(2) Euclidean (1 , 1 , 1) = SU(2) n R 3 Λ = 0 E 3 Iso(3) ∼ SU(2) ⊂ G Λ H 3 Λ < 0 PSL(2 , C ) X Λ = G Λ / SU(2)
2. Unified description of model spacetimes isometry groups of Lorentzian model spacetimes • commutative real algebra : notation : with ` 2 = − Λ R Λ = ( R 2 , + , · Λ ) ( a, b ) = a + ` b a = Re ` ( a + ` b ) ( a, b ) · Λ ( c, d ) = ( ac − Λ bd, ad + bc ) b = Im ` ( a + ` b ) a + ` b = a − ` b • analytic continuation analytic function ➩ analytic function f : R Λ → R Λ f : R → R ∂ Re ` f = ∂ Im ` f f ( x ) + ` f 0 ( x ) y Λ = 0 ∂ x ∂ y ➩ 2 (1 + ` ) f ( x + y ) + 1 1 f ( x + ` y ) = 2 (1 − ` ) f ( x − y ) Λ = − 1 ∂ Re ` f = − Λ ∂ Im ` f f ( x + i y ) Λ = 1 ∂ y ∂ x • isometry groups of model spacetimes Iso(2 , 1) Λ = 0 G Λ = { M ∈ Mat(2 , R Λ ) : det( M ) = 1 } = SL(2 , R ) × SL(2 , R ) Λ < 0 SL(2 , C ) Λ > 0 • Lie algebras of isometry groups iso (2 , 1) Λ = 0 g Λ = { M ∈ Mat(2 , R Λ ) : tr( M ) = 0 } = sl (2 , R ) ⊕ sl (2 , R ) Λ < 0 sl (2 , C ) Λ = 0 Λ > 0
Lorentzian model spacetimes: M 3 , dS 3 , AdS 3 ✓ ¯ ✓ a ◆ � ¯ ◆ b d b • involution � : Mat(2 , R Λ ) ! Mat(2 , R Λ ) 7! c d c a � ¯ ¯ X Λ = { M ∈ Mat(2 , R Λ ) : M � = M, det( M ) = 1 } • model spacetimes for Λ ∈ { 0 , ± 1 } • action of isometry group B : G Λ × X Λ → X Λ G B M = G · M · G � • metric h M, M i = � det(Im ` ( M ) + ` Re ` ( M )) • geodesics for , g ( t ) = M exp( t ` X ) X ∈ sl (2 , R ) M ∈ X Λ • standard future lightcone L = { exp( ` X ) : X ∈ sl (2 , R ) , tr( X 2 ) < 0 } • foliation of lightcone by 2d hyperbolic space ✓ 1 ◆ ✓ − Re( z ) ◆ + ` s Λ ( t ) | z | 2 0 H : R × H 2 → X Λ H ( z, t ) = c Λ ( t ) H ( t, z ) 0 1 − 1 Re( z ) Im( z ) 8 8 1 Λ = 0 Λ = 0 t ∞ ∞ t 2 k Λ k t 2 k +1 Λ k > > < < X X c Λ ( t ) = (2 k )! = cos( t ) Λ = − 1 s Λ ( t ) = (2 k + 1)! = sin( t ) Λ = − 1 > > k =0 cosh( t ) Λ = 1 k =0 sinh( t ) Λ = 1 : : ➩ compatible with -action: H ( g B z, t ) = g · H ( z, t ) · g � SL(2 , R ) action on upper half-plane by Möbius transformations
3. Construction and classification of spacetimes maximal globally hyperbolic Lorentzian spacetimes with compact Cauchy surface S M ➩ homeomorphic to R × S M ➩ universal cover globally hyperbolic ˜ M ⊂ X Λ M = ˜ π 1 ( S ) y ˜ ➩ , via group homomorphism ρ : π 1 ( S ) → G Λ M/ π 1 ( S ) M universal cover ρ ( a ) = e 1 ∈ R 3 • Ex: torus universe for Λ =0 π 1 ( S ) = Z × Z spacelike translation ρ ( b ) ρ ( a ) , ρ ( b ) ∈ R 3 ρ ( b ) = u ∈ SO(2 , 1) e 1 u ρ ( a ) spacelike translations Lorentz boost stabilising e 1 ˜ M = M 3 ˜ M = I + ( R e 1 ) future of a line • Cauchy surface of genus g>1, general Λ [Mess, Benedetti, Bonsante] • is convex, open, future complete region in , future of a spacelike graph ˜ X Λ M • initial singularity ∂ ˜ M • cosmological time function t : ˜ t ( p ) = sup { l ( c ) : c past directed causal curve with c (0) = p } M → R • foliation by surfaces of constant cosmological time (cct) M = ∪ T ˜ ˜ ˜ M T = t − 1 ( T ) M T π 1 ( S ) y ˜ • and M = ∪ T ˜ M T M T / π 1 ( S )
conformally static spacetimes of genus g>1 π 1 ( S ) = h a 1 , b 1 , ..., a g , b g | [ a g , b g ] · · · [ a 1 , b 1 ] = 1 i • group homomorphism ρ : π 1 ( S ) → PSL(2 , R ) • universal cover ˜ - interior of standard lightcone M = L • cosmological time - geodesic distance from tip of lightcone t : ˜ M → R • cct surfaces ˜ - rescaled copies of M T = H ( H 2 , T ) ∼ = s Λ ( T ) H 2 H 2 • action of π 1 ( S ) action of Fuchsian group on H 2 Γ ⊂ PSL(2 , R ) ➩ tesselation of by geodesic arc 4g-gons H 2 ➩ M → g · ˜ ˜ ρ → g · ρ · g � covariant: corresponds to ➩ PSL(2 , R ) M · g � v x b 1 • spacetime M = ∪ T ˜ M T / π 1 ( S ) = ∪ T s Λ ( T ) H 2 / Γ conformally static v − 1 b’ v x x 1 a 2 a 1 a’ 1 g M = − dT 2 + s Λ ( T ) 2 g H 2 / Γ a 2 v b 1 v − 1 v x b x v − 1 a 2 x 2 b 1 b v for all values of Λ : b 1 2 a 1 v b 2 v x a 2 v − 1 x a’ { conformally static MGH spacetimes of genus g > 1 } / Di ff 0 ( M ) a 1 a 1 2 b’ 2 v x b 2 = { Fuchsian groups Γ ⊂ PSL(2 , R ) of genus g > 1 } / PSL(2 , R ) = T ( S ) Teichmüller space
geometry change via earthquake and grafting ingredients ⇔ cocompact Fuchsian group Γ ⊂ PSL(2 , R ) • hyperbolic surface Σ = H 2 / Γ ⇔ conformally static spacetime • weighted multicurve finite set of closed, non-intersecting geodesics on { ( c i , w i ) } i ∈ I Σ c i with weights w i > 0 construction • lift geodesics to H 2 and embed into foliated lightcone • select basepoint • cut lightcone along geodesics q p grafting earthquake n • for each geodesic : • for each geodesic : c i c i apply to the right exp( ` w i X c i ) ∈ G Λ apply to the right exp( w i X c i ) ∈ PSL(2 , R ) ~ imaginary earthquake Lorentz boost, hyperbolic distance w i translation, distance w i X c i ∈ sl (2 , R ) stabilises exp( sX c i ) ∈ PSL(2 , R ) c i tr( X 2 c i ) = 1 2 moves to the left w q’ q +w n p p q +w n w p
earthquake grafting • universal cover • remains standard lightcone • deformed lightcone • future of a point • future of a graph • cosmological time • geodesic distance from tip • geodesic distance from graph of lightcone • rescaled copies of H 2 • deformed copies of H 2 • ccT surfaces • action of π 1 ( S ) • via group homomorphism • via group homomorphism ρ : π 1 ( S ) → G Λ ρ : π 1 ( S ) → PSL(2 , R ) Static spacetime Grafted spacetime • spacetime • remains conformally static • evolves with cosmological time w w T w w
earthquake and grafting - transformation of holonomies • group homomorphism ⇔ Fuchsian group of genus g ρ 0 : π 1 ( S ) → PSL(2 , R ) Γ = im( ρ 0 ) • weighted multicurve on Σ = H 2 / Γ { ( c i , w i ) } i ∈ I transformation of group homomorphism given by cocycles grafting earthquake B gr : H 2 × H 2 → G Λ B qu : H 2 × H 2 → PSL(2 , R ) q Y B gr ( p, q ) = exp( ` w i X c i ) Y B qu ( p, q ) = exp( w i X c i ) ( p,q ) ∩ c i ( p,q ) ∩ c i ~ imaginary earthquake X c i ∈ sl (2 , R ) stabilises exp( sX c i ) ∈ PSL(2 , R ) c i p c 3 c 2 c 1 tr( X 2 c i ) = 1 2 moves to the left • - covariant PSL(2 , R ) g ∈ PSL(2 , R ) B ( g B p, g B q ) = g · B ( p, q ) · g � • - invariant g ∈ Γ B ( g B p, g B q ) = B ( p, q ) Γ transformation of holonomies ρ : π 1 ( S ) → G Λ ρ ( λ ) = ρ 0 ( λ ) · B ( p, ρ 0 ( λ ) B p )
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.