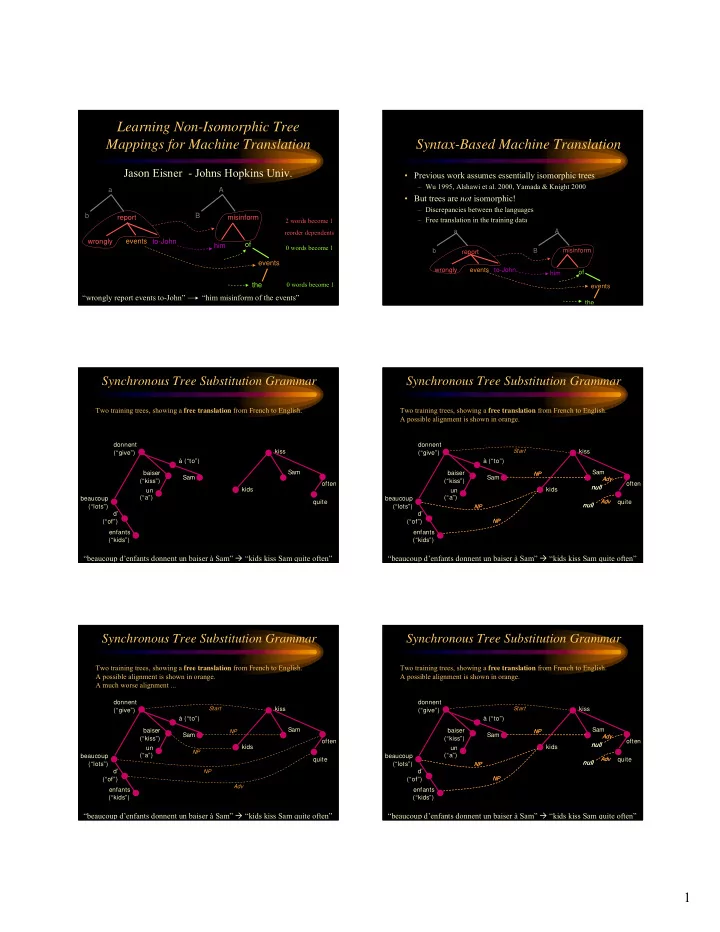

Learning Non-Isomorphic Tree Mappings for Machine Translation Syntax-Based Machine Translation Jason Eisner - Johns Hopkins Univ. • Previous work assumes essentially isomorphic trees – Wu 1995, Alshawi et al. 2000, Yamada & Knight 2000 a A • But trees are not isomorphic! – Discrepancies between the languages b B report misinform – Free translation in the training data 2 words become 1 reorder dependents a A wrongly events to-John of him 0 words become 1 b B misinform report events wrongly events to-John him of 0 words become 1 the events “wrongly report events to-John” “him misinform of the events” the Synchronous Tree Substitution Grammar Synchronous Tree Substitution Grammar Two training trees, showing a free translation from French to English. Two training trees, showing a free translation from French to English. A possible alignment is shown in orange. donnent donnent kiss Start kiss (“give”) (“give”) à (“to”) à (“to”) baiser Sam baiser Sam NP NP Sam Sam Adv Adv (“kiss”) (“kiss”) often often null null kids kids un un (“a”) (“a”) beaucoup beaucoup quite Adv Adv quite null null (“lots”) (“lots”) NP NP d’ d’ NP (“of”) (“of”) NP enfants enfants (“kids”) (“kids”) “beaucoup d’enfants donnent un baiser à Sam” � “kids kiss Sam quite often” “beaucoup d’enfants donnent un baiser à Sam” � “kids kiss Sam quite often” Synchronous Tree Substitution Grammar Synchronous Tree Substitution Grammar Two training trees, showing a free translation from French to English. Two training trees, showing a free translation from French to English. A possible alignment is shown in orange. A possible alignment is shown in orange. A much worse alignment ... donnent donnent Start kiss Start kiss (“give”) (“give”) à (“to”) à (“to”) baiser Sam baiser Sam NP NP NP Sam Sam Adv Adv (“kiss”) (“kiss”) often often null null kids kids un un NP (“a”) (“a”) beaucoup beaucoup quite Adv Adv quite null null (“lots”) (“lots”) NP NP d’ NP d’ NP NP (“of”) (“of”) Adv enfants enfants (“kids”) (“kids”) “beaucoup d’enfants donnent un baiser à Sam” � “kids kiss Sam quite often” “beaucoup d’enfants donnent un baiser à Sam” � “kids kiss Sam quite often” 1
Synchronous Tree Substitution Grammar Grammar = Set of Elementary Trees donnent Two training trees, showing a free translation from French to English. Start kiss (“give”) A possible alignment is shown in orange. à (“to”) Alignment shows how trees are generated synchronously from “little trees” ... baiser NP Adv (“kiss”) donnent idiomatic null Start Start kiss (“give”) un translation à (“to”) (“a”) NP baiser Sam NP NP Sam Adv Adv (“kiss”) often null null un kids (“a”) beaucoup Adv Adv quite null null (“lots”) NP NP d’ kids NP (“of”) NP enfants enfants (“kids”) NP (“kids”) “beaucoup d’enfants donnent un baiser à Sam” � “kids kiss Sam quite often” NP Sam Sam Grammar = Set of Elementary Trees Grammar = Set of Elementary Trees donnent donnent Start kiss Start kiss (“give”) (“give”) à (“to”) à (“to”) baiser baiser NP NP NP Sam Sam Adv Adv (“kiss”) (“kiss”) idiomatic null null kids un un translation (“a”) (“a”) enfants (“kids”) NP NP NP beaucoup (“lots”) NP d’ “beaucoup d’” deletes kids (“of”) NP inside the tree kids enfants (“kids”) NP NP enfants NP (“kids”) NP Sam Sam Sam Sam Grammar = Set of Elementary Trees Grammar = Set of Elementary Trees donnent donnent Start kiss Start kiss (“give”) (“give”) à (“to”) à (“to”) baiser baiser NP NP Adv Adv (“kiss”) (“kiss”) null null un un kids (“a”) (“a”) beaucoup beaucoup (“lots”) NP NP (“lots”) NP NP d’ d’ “beaucoup d’” deletes “beaucoup d’” matches (“of”) inside the tree NP (“of”) nothing in English NP NP enfants (“kids”) kids kids NP NP enfants enfants NP NP (“kids”) (“kids”) Sam Sam Sam Sam 2
Grammar = Set of Elementary Trees Probability model similar to PCFG donnent Start kiss (“give”) à (“to”) Probability of generating training baiser NP trees T1, T2 with alignment A Adv (“kiss”) P(T1, T2, A) = ∏ p(t1,t2,a | n) null un adverbial subtree (“a”) matches nothing in French NP probabilities of the “little” Adv beaucoup trees that are used often null (“lots”) NP d’ p( | ) Adv kids (“of”) NP null report misinform VP VP Adv quite wrongly NP null NP NP enfants is given by a maximum entropy model (“kids”) NP Sam Sam Form of model of big tree pairs Maxent model of little tree pairs p( | ) Joint model P θ (T1,T2). report misinform VP VP Wise to use noisy-channel form: P θ (T1 | T2) * P θ (T2) But any joint model will do. wrongly NP NP could be trained on zillions train on paired trees of target-language trees (hard to get) FEATURES • verb incorporates adverb child? report+wrongly ↔ misinform? • • verb incorporates child 1 of 3? In synchronous TSG, aligned big tree pair is generated (use dictionary) • children 2, 3 switch positions? by choosing a sequence of little tree pairs: report ↔ misinform? (at root) • • common tree sizes & shapes? P(T1, T2, A) = ∏ p(t1,t2,a | n) wrongly ↔ misinform? • • ... etc. .... Inside Probabilities Inside Probabilities a a A A o n l y O b B b B ( misinform misinform n 2 report VP report VP ) wrongly events to-John wrongly events to-John of of him him NP events events NP the the β ( ) = ... p( | ) β ( ) = ... p( | ) misinform misinform VP misinform VP VP report report report VP VP NP wrongly NP * β ( ) * β ( ) + ... * β ( ) * β ( ) + ... events NP of to-John NP him 3
Recommend
More recommend