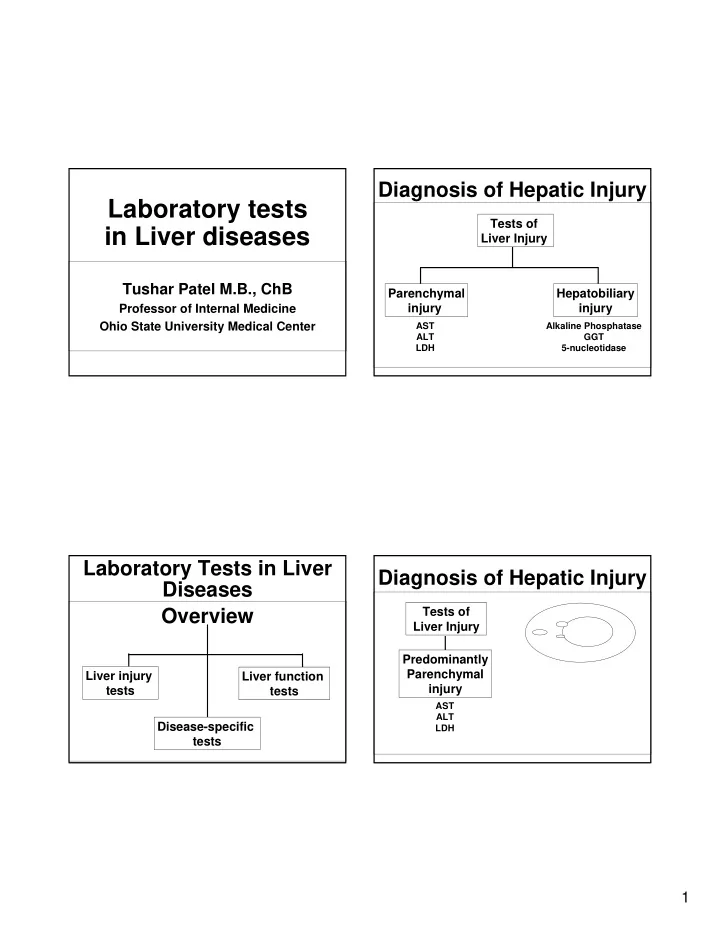

Diagnosis of Hepatic Injury Laboratory tests Tests of in Liver diseases Liver Injury Tushar Patel M.B., ChB Parenchymal Hepatobiliary Professor of Internal Medicine injury injury Ohio State University Medical Center AST Alkaline Phosphatase ALT GGT LDH 5-nucleotidase Laboratory Tests in Liver Diagnosis of Hepatic Injury Diseases Tests of Overview Liver Injury Predominantly Parenchymal Liver injury Liver function injury tests tests AST ALT Disease-specific LDH tests 1
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) Diagnosis of Hepatic Injury Glutamate-Oxaloacetate Transaminase Tests of • Ubiquitous, and found in all tissues Liver Injury • Highest activity in heart, with significant activity in the liver, brain, gastric mucosa, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and kidneys. Predominantly • In mild hepatocellular injury when the plasma Parenchymal but not the mitochondrial membrane is injury damaged, cytoplasmic form of AST is released into the blood. With more severe hepatocellular AST injury, mitochondrial damage may result in the ALT Enzymes leak out release of mitochondrial AST. LDH of damaged cells • CPK or aldolase may be useful to exclude a muscle source of abnormal AST Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) Increased AST/ALT Glutamate Pyruvate Transaminase • Increased ALT or AST usually imply hepatic parenchymal injury but can occur in other organ • As a group, the aminotransferases catalyze the damage interconversion of amino acids and alpha-keto � ALT is more “liver” specific . acids by transfer of amino groups. • Highest activity in the liver, with decreasing • Reflect hepatic injury not hepatic function – and concentrations in the kidney, heart, skeletal can be normal in advanced liver disease or muscle, pancreas, spleen, and lung. cirrhosis • The enzyme is mainly located in the cytoplasm and escapes into the blood circulation during • Can occur with damage to other organs the cellular injury. (myocardial infarction, muscular dystrophy, etc) 2
AST/ALT Ratio Alkaline Phosphatase • The ratio of AST to ALT activity in the • Present in several tissues, including bile blood is helpful in the diagnosis of liver ducts, bone, kidney, intestine and diseases. placenta. • In patients with most hepatic disorders, including acute or chronic viral hepatitis, • Exists as isoenzymes that are specific for ALT is increased more than AST. various tissues. • However, in alcoholic liver disease, AST is • The bulk of the alkaline phosphatase in increased much more than ALT, and the normal humans is made up of liver and ratio is greater than 2 bone isoenzymes Increased Alkaline Diagnosis of Hepatic Injury Phosphatase Tests of • Identify tissue source by isoenzyme analysis, or measure either 5’-nucleotidase or gamma Liver Injury glutamyl transpeptidase. • Levels may rise in persons with blood Predominantly groups O and B, who are ABH secretors and Lewis antigen-positive, esp after a fatty meal. Hepatobiliary Thus, measure alkaline phosphatase in the injury fasting state. • Note: Alk Phos may be normal even with Alkaline Phosphatase extensive hepatic metastases or complete GGT bile duct obstruction. Patients with 5-nucleotidase Wilson’s disease may have normal values. 3
γ -Glutamyl Increased Alkaline Phosphatase Transferase • Cholestasis • Present in almost all tissues, but highest • Intrahepatic or Extrahepatic biliary activity in bile ducts, kidney and pancreas obstruction (from biliary stones, cholangitis, billiary cirrhosis, cancers etc.) • In the liver present in biliary tract cells • Hypernephroma and Hodgkin’s disease have elevated levels in the absence of liver involvement Alk phos can be increased Clinical significance of increased γ GT in non-hepatic conditions � Some malignancies • Very sensitive indicator of liver disease. • Patients with malignancies may have • Rarely normal in the presence of hepatic increased levels not caused by liver or disease. bone metastases (Regan isoenzyme) • However, it is not very specific for liver � Bone or intestinal disease in the absence of diseases. liver disease. • Levels may be increased in • In normal children with active bone growth, � Persons who take drugs such as influx of enzyme from osteoid tissue may phenytoin, phenobarbital, or alcohol result in threefold increase in serum levels. � Persons with renal failure, myocardial � Pregnancy infarction, pancreatic disease etc. • In the third trimester of pregnancy, the serum level may double as a consequence • GGT is a sensitive screening test for occult of placental contribution. alcoholism 4
Albumin Tests of Liver Function • 60% of the total serum protein • The liver synthesizes 120 mg/kg of albumin daily. • Serum half-life of about 20 days. Synthetic Excretory or Detoxifying • Reflects relatively long term synthetic Function Function function. Prothrombin time • Can be lowered by renal or GI losses Albumin Bilirubin (excretory) Pseudocholinesterase which exceed the capacity of hepatic Ammonia (detoxifying) synthesis even with a normal liver Prothrombin Time Serum Protein Electrophoresis • Prothrombin time is prolonged when • The major proteins in serum are separated in an electric clotting factor levels are decreased. field and their concentrations determined • Increased in chronic liver diseases if � Albumin, Alpha-globulins, Beta-globulins , Gamma- cirrhosis is present and there is fairly globulins significant liver damage • Cirrhosis: albumin may be decreased, globulins may • Useful prognostic marker in acute liver be increased injury • Auto-immune hepatitis: gamma globulins can be markedly increased � It is increased with severe damage, and improves as the patient recovers. • Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency: alpha-globulins may be low • Can be increased in Vitamin K deficiency, drugs (warfarin) 5
Sources of Heme Clotting Factors 250-350 mg/day • All coagulation factors, except factor VIII and von Willebrand factor are made in the liver. The half-life of these factors is short (few hours to a few days). • Factor VIII levels may be normal or increased in severe hepatic injury. • This may help distinguish between the coagulopathy of liver disease from that due to disseminated intravascular coagulation (where factor VIII levels are decreased). • Synthesis of several factors requires vitamin K. This fat-soluble vitamin is absorbed from the gut as a RBCs complex with bile salts. In patients with biliary obstruction, the absorption of a vitamin K is inadequate 70% which results in the decreased synthesis of these factors (II, VII, IX, X). Sources of Heme Bilirubin 250-350 mg/day • Useful for evaluating degrees of jaundice • Useful for the diagnosis of liver disease • Useful for the detection of hemolytic anemia Hepatic • Bilirubin is mostly formed by the Hemoproteins RBCs reticuloendothelial system during the Cytochrome p450 Catalase destruction of red blood cells. 70% 23-37% 6
Unconjugated Sources of Heme Hyperbilirubinemia 250-350 mg/day • > 80% of the total bilirubin level is unconjugated or indirect • Consider � Criggler-Najjar syndrome � Mild changes also seen in Hepatic • Gilbert’s disease, Hemoproteins RBCs Non-Hepatic Cytochrome p450 • uncomplicated hemolytic disorders Hemoproteins Catalase • Congestive heart failure. 70% 23-37% <10% • Neonates Increased Bilirubin Gilbert’s Syndrome Conjugated (direct) or unconjugated (indirect) Total bilirubin – direct bilirubin = Indirect bilirubin � Common! Affects 3-7 % of population � Males > Females (7:1) • Virtually 100% of serum bilirubin in health is � Bilirubin levels increased by fasting unconjugated, whereas conjugated hyperbilirubinemia occurs only in hepatobiliary conditions � Bilirubin levels decreased by: • Delta bilirubin, an albumin-linked bilirubin fraction, represents a significant fraction of total serum bilirubin � Phenobarbital (UGT induction?) in hepatobiliary disorders, but not in health, neonates, or with hemolysis. � Steroids (increased storage proteins) • The clearance of delta bilirubin is slow, 12 to 24 days, vs non-albumin bound conjugated bilirubin 7
Recommend
More recommend