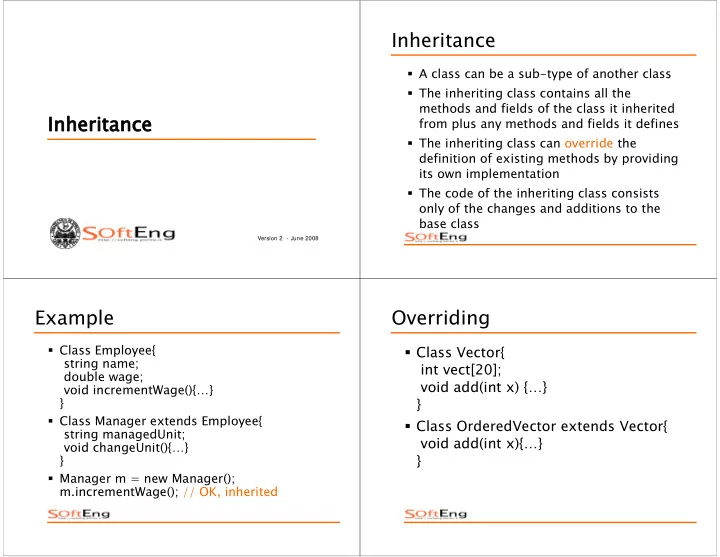

Inheritance � A class can be a sub-type of another class � The inheriting class contains all the methods and fields of the class it inherited Inheritance Inheritance from plus any methods and fields it defines � The inheriting class can override the definition of existing methods by providing its own implementation � The code of the inheriting class consists only of the changes and additions to the base class Version 2 - June 2008 Example Overriding � Class Employee{ � Class Vector{ string name; int vect[20]; double wage; void add(int x) {…} void incrementWage(){…} } } � Class Manager extends Employee{ � Class OrderedVector extends Vector{ string managedUnit; void add(int x){…} void changeUnit(){…} } } � Manager m = new Manager(); m.incrementWage(); // OK, inherited
Why inheritance Inheritance in real Life � Frequently, a class is merely a modification � A new design created by the of another class. In this way, there is modification of an already existing minimal repetition of the same code design � Localization of code � The new design consists of only the � Fixing a bug in the base class automatically fixes changes or additions from the base it in the subclasses design � Adding functionality in the base class � CoolPhoneBook inherits PhoneBook automatically adds it in the subclasses � Add mail address and cell number � Less chances of different (and inconsistent) implementations of the same operation Example of inheritance tree Inheritance terminology Living species � Class one above � Parent class � Class one below Animal vegetal � Child class Human being � Class one or more above Flower Professor � Superclass, Ancestor class, Base class SalesMan � Class one or more below Student � Subclass, Descendent class Travel Agent
Inheritance and polymorphism Inheritance and polymorphism Class Employee{ private string name; Employee e1 = new Employee(); � Employee e1 = new Employee(); public void print(){ Employee e2 = new Manager(); � Employee e2 = new Manager(); //ok, is_a System.out.println(name); e1.print(); // name � e1.print(); // name } e2.print(); // name and unit } � e2.print(); // name and unit Class Manager extends Employee{ private string managedUnit; public void print(){ //overrides System.out.println(name); //un-optimized! System.out.println(managedUnit); } } Inheritance in few words Inheritance in Java: extends class Car { � Subclass class Car { String color; String color; Car � Inherits attributes and methods boolean isOn; boolean isOn; String licencePlate; color String licencePlate; � Can modify inherited attributes and isOn licencePlate void paint(String color) { void paint(String color) { methods (override) this.color = color; this.color = color; turnOn } paint } class ElectricCar extends Car � Can add new attributes and methods class ElectricCar extends Car { void turnOn() { { void turnOn() { isOn=true; isOn=true; boolean cellsAreCharged; } boolean cellsAreCharged; } } ElectricCar void recharge() { } void recharge() { cellsAreCharged = true; cellsAreCharged = true; cellsAreCharged } } recharge void turnOn() { void turnOn() { turnOn if(cellsAreCharged ) if(cellsAreCharged ) isOn=true; isOn=true; } } } } 11 12
Inheritance in Java: extends ElectricCar class Car { class Car { � Inherits String color; String color; Car � attributes (color, isOn, licencePlate) boolean isOn; boolean isOn; String licencePlate; color String licencePlate; � methods (paint) isOn licencePlate void paint(String color) { void paint(String color) { � Modifies (overrides) this.color = color; this.color = color; turnOn } paint } class ElectricCar extends Car class ElectricCar extends Car � turnOn() { void turnOn() { { void turnOn() { isOn=true; isOn=true; � Adds boolean cellsAreCharged; } boolean cellsAreCharged; } } ElectricCar void recharge() { } void recharge() { � attributes (cellsAreCharged) cellsAreCharged = true; cellsAreCharged = true; cellsAreCharged } } � Methods (recharge) recharge void turnOn() { void turnOn() { turnOn if(cellsAreCharged ) if(cellsAreCharged ) isOn=true; isOn=true; } } } } 13 14 Example class Employee { private String name; private double wage; } Visibility (scope) Visibility (scope) class Manager extends Employee { void print() { System.out.println(“Manager” + name + “ ” + wage ); } } Not visible 16
Protected In summary � Attributes and methods marked as Method of Method of another Method in another Method � public public are always accessible public class the same class in the of in the � private private are accessible within the class class class same subclass subclass outside only package package world world � protected protected are accessible within the class � private and its subclasses � � package � � � protected � � � � public 17 Super (reference) Example class Car { � “ this ” is a reference to the current class Car { String color; object String color; Car boolean isOn; boolean isOn; String licencePlate; color String licencePlate; � “ super ” is a reference to the parent isOn licencePlate void paint(String color) { void paint(String color) { class this.color = color; turnOn this.color = color; } paint } class ElectricCar extends Car{ class ElectricCar extends Car{ void turnOn() { void turnOn() { boolean cellsAreCharged; boolean cellsAreCharged; isOn=true; isOn=true; } } void recharge() { } void recharge() { ElectricCar } cellsAreCharged = true; cellsAreCharged = true; } cellsAreCharged } was was void turnOn() { recharge void turnOn() { if(cellsAreCharged) turnOn if( cellsAreCharged ) if( cellsAreCharged ) isOn = true; super.turnOn(); super.turnOn(); } } } } 19 20
Attributes redefinition � Class Parent{ protected int attr = 7; } Inheritance and Inheritance and � Class Child{ protected String attr = “hello”; constructors constructors void print(){ System.out.println(super.attr); System.out.println(attr); } public static void main(String args[]){ Child c = new Child(); c.print(); } } 21 Construction of child objects Construction of child objects � Since each object “contains” an � Execution of constructors proceeds instance of the parent class, the latter top-down in the inheritance hierarchy must be initialized � Java compiler automatically inserts a � In this way, when a method of the call to default constructor (no params) child class is executed (constructor of parent class included), the super-class is � The call is inserted as the first completely initialized already statement of each child constructor 23 24
Example Example (cont’d) class ArtWork { class ArtWork { ArtWork() { ArtWork() { Cartoon obj = new Cartoon(); System.out.println(“New ArtWork”); } System.out.println(“New ArtWork”); } } } class Drawing extends ArtWork { class Drawing extends ArtWork { new ArtWork new ArtWork Drawing() { Drawing() { new Drawing System.out.println(“New Drawing”); } new Drawing System.out.println(“New Drawing”); } } new Cartoon } new Cartoon class Cartoon extends Drawing { class Cartoon extends Drawing { Cartoon() { Cartoon() { System.out.println(“New Cartoon”); } System.out.println(“New Cartoon”); } } } 25 26 A word of advice Super � Default constructor “disappears” if � If you define custom constructors custom constructors are defined with arguments � and default constructor is not defined class Parent{ class Parent{ explicitly Parent(int i){} Parent(int i){} } } class Child extends Parent{ } class Child extends Parent{ } // error! � the compiler cannot insert the call // error! class Parent{ class Parent{ automatically Parent(int i){} Parent(int i){} Parent(){} //explicit default Parent(){} //explicit default } } class Child extends Parent { } class Child extends Parent { } // ok! // ok! 27 28
Super Example � Child class constructor must call the class Employee { class Employee { right constructor of the parent class, private String name; private String name; private double wage; private double wage; explicitly ??? ??? Employee(String n, double w){ Employee(String n, double w){ name = n; name = n; wage = w; wage = w; � Use super() to identify constructors of } } class Manager extends Employee { class Manager extends Employee { parent class } private int unit; } private int unit; Manager(String n, double w, int u) { Manager(String n, double w, int u) { super(); ERROR !!! super(); ERROR !!! � First statement in child constructors unit = u; unit = u; } } } } 29 30 Example class Employee { class Employee { private String name; private String name; Dynamic binding/ Dynamic binding/ private double wage; private double wage; polymorphism polymorphism Employee(String n, double w){ Employee(String n, double w){ name = n; name = n; wage = w; wage = w; } } class Manager extends Employee { class Manager extends Employee { } private int unit; } private int unit; Manager(String n, double w, int u) { Manager(String n, double w, int u) { super(n,w); super(n,w); unit = u; unit = u; } } } } 31
Recommend
More recommend