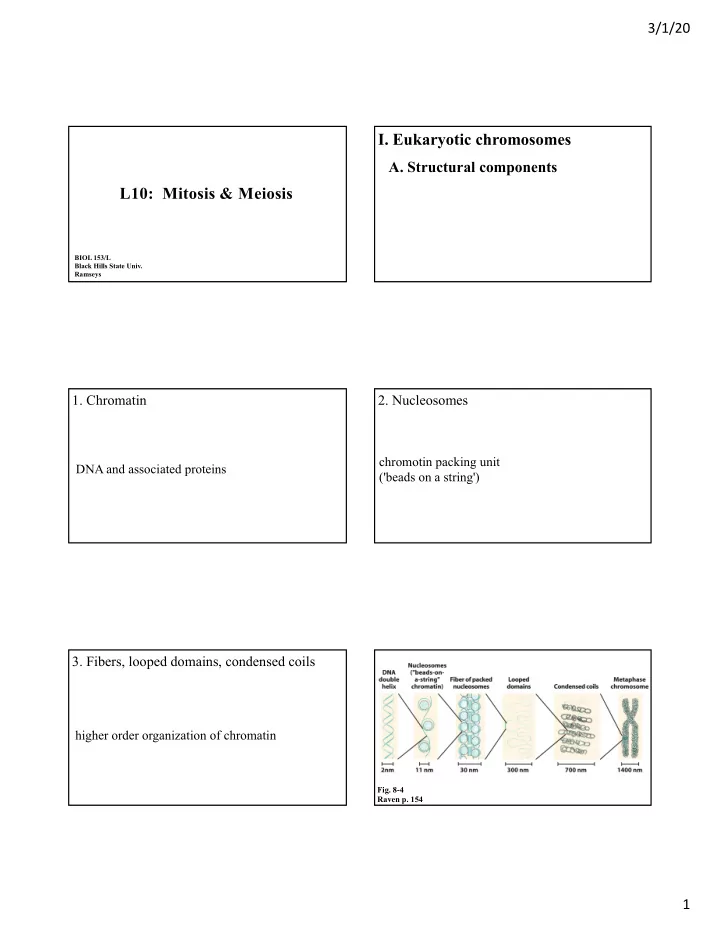

3/1/20 I. Eukaryotic chromosomes A. Structural components L10: Mitosis & Meiosis BIOL 153/L Black Hills State Univ. Ramseys 1. Chromatin 2. Nucleosomes chromotin packing unit DNA and associated proteins ('beads on a string') 3. Fibers, looped domains, condensed coils higher order organization of chromatin Fig. 8-4 Raven p. 154 1
3/1/20 I. Eukaryotic chromosomes 1. In nucleus B. Location 1. In nucleus 1. In nucleus interphase and early prophase interphase and early prophase 2. Across cell 1. In nucleus 1. In nucleus interphase and early prophase interphase and early prophase 2. Across cell 2. Across cell late prophase, metaphase, anaphase late prophase, metaphase, anaphase chromosomes spend most time in nucleus (interphase) 2
3/1/20 I. Eukaryotic chromosomes C. Size and content nuclear envelope degrades during prophase nuclear envelope reforms during telophase 1. Nucleotides: huge variation in base pairs • flowering plants: very high • mammals: kinda high • birds: low Wake-robin Trillium 1. Nucleotides: huge variation in base pairs • flowering plants: very high • mammals: kinda high • birds: low ~68 m of DNA 2. Length: 0.5 g DNA stretches earth to sun! 3
3/1/20 Homo sapiens I. Eukaryotic chromosomes D. Genes ~2 m of DNA I. Eukaryotic chromosome 1. A gene specifies amino acid order in a protein E. Ploidy 2. Allele = alternate version of gene 3. Locus = specific gene location on chromosome 4. Homologous chromosomes 1 1. Haploid: set of chromosomes chromosomes with same genes, in same order 2 2. Diploid : sets of chromosomes (may have different alleles) 3. Polyploid: >2 sets of chromosomes 4
3/1/20 hypothetical organism with only three chromosomes: Haploid Diploid Triploid Tetraploid Haploid Diploid Haploid Diploid Triploid Tetraploid Polyploid homologous homologous homologous homologous Triploid Tetraploid Triploid Tetraploid Haploid Diploid Haploid Diploid Polyploid Polyploid 5
3/1/20 one particular chromosome in hypothetical diploid organism: homologous chromosomes homologous chromosomes 2 different alleles 2 different alleles 1 allele (only) 2 different alleles II. Mitosis overview A. Location somatic (body) cells 6
3/1/20 B. Goal C. Examples make exact chromosome replicates (occurs with cell division) C. Examples animal development chicken egg plant growth ash seedling if mitosis makes exact copies... how do bloody blobs become chicks? how do seeds become trees? 7
3/1/20 III. Meiosis overview A. Location gametic (reproductive) cells B. Goal C. Examples testes à sperm reduce (half) chromosome number (occurs with cell division) ovary à egg anther à pollen IV. Shared features of mitosis & meiosis A. Naming of stages [I]P-MAT 8
3/1/20 A. Naming of stages B. DNA replication [Interphase] Prophase Interphase [I]P-MAT Metaphase Anaphase Telophase C. DNA condensing D. Lining up of chromosomes Prophase Metaphase E. Separation (chromatids/chromosomes) V. Particular features of meiosis Anaphase 9
3/1/20 A. Two rounds of division A. Two rounds of division P-MAT I P-MAT II P-MAT I P-MAT II "Reductional Division" "Equational Division" "Reductional Division" "Equational Division" reduces chromosome # in half divides chromatids Meiosis I Meiosis II "Reductional Division" "Equational Division" B. Crossing over of homologous chromosomes (recombination) Prophase I 10
3/1/20 C. Separation of homologous chromosomes (reduction) Anaphase I & Telophase I 11
Recommend
More recommend