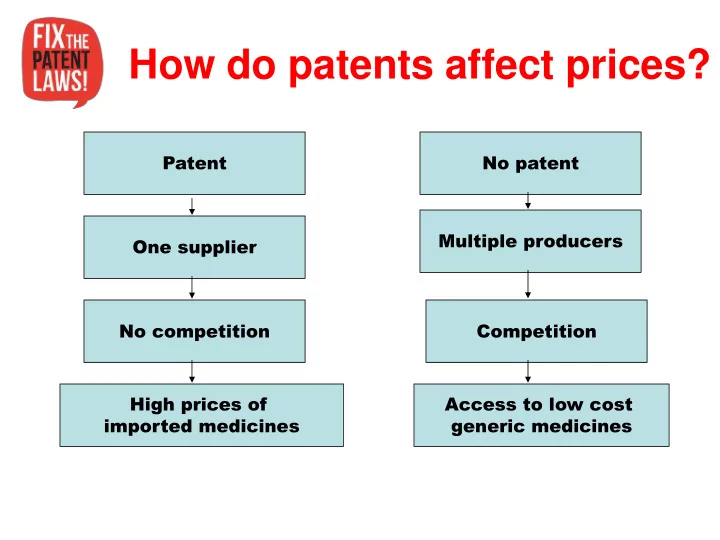

How do patents affect prices? Patent No patent Multiple producers One supplier No competition Competition High prices of Access to low cost imported medicines generic medicines
How to bring down prices? Source: MSF Untangling the Web of Antiretroviral Price Reductions, 15 th Edition, July 2012
What is Evergreening?
What Reforms Could SA Enact? Other countries have used these reforms to make their patent systems work in the interest of public health: – Stricter patentability criteria – Patent search & examination system – Patent opposition – Broad research exception – Improve Compulsory Licensing & Parallel Importation mechanisms – Publicly financed R&D, de-linkage principles The Dept. of Trade & Industry released a “Draft National Policy on IP” for public comment in September 2013, expressing the need for most of these reforms. A closer look…
Economic cost • Pharmaceuticals are 5 th largest driver of SA trade deficit / R5billion spent on procuring pharmaceuticals by DOH in 2012 • Cost driven by branded products – despite the fact that in quantity the majority of medicines are imported from India and majority of API from China. • Every Rand spent on branded medicines is money diverted from the wider health system
Related work: Regulatory Reform Recommendations for Medicines and Related Substances Amendment Bill: S15(2)b: Specific timelines of registration (6 months) for priority treatments, with explicit penalties of Authority for non compliance S 21: Formally allow Section 21 exemption on the grounds of affordability restricting access to life saving treatments S 22: Require the Authority to make public the date of application submission, name of medicine in question, expected price and current status of application S 2B(2)(a): Other Stringent Regulatory Authorities’ findings can be utilised in order to speed up registration
Linezolid: IP and Price Challenges MSF started including linezolid in strengthened regimens of DR-TB patients in 2011 — 6-month supply of Pfizer product cost over R123,000 per patient Pfizer product under patent in SA until August 2014 Globally, more affordable generics receive quality approval from stringent regulatory authorities from mid-2013 Source Cost (per pill) Comment Pfizer originator USD 65 18-month course = USD 35 568 South Africa Antibiotic USD27 Pfizer has not bid on Tender (now expired) TB drugs tender Hetero (generic USD8 MSF price--not yet manufacturer) available in South Africa
South Africa pays the price
Lin inezoli lid Redux?: New DR-TB dru rugs • Bedaquiline – US FDA Approval in 2012 – SA registration fast-tracked in Dec. 2012 — approved Oct. 2014 – Clinical access program recently ended following full registration — limited number of sites. Wider national rollout planned (goal of 3,000 patients in 2015) – SA price unknown…but lowest announced price for any country $900 for a course of treatment – At least 4 patents granted in SA (expire between 2025- 2027) — including use for treating DR-TB in combination with other TB drugs • Delamanid – Registered by the EMA in 2013 – Will Otsuka register in South Africa? At what price? – At least 7 patents in SA (expire between 2025-2032) — including on use with other TB drugs **Will combination patents hinder research into better regimens??**
Unaffordable Why are some medicines so expensive?
Effect of Secondary Patents Cancer drug Imatinib Mesylate Patents: Evergreening Trend 1993 + 20 1997 + 20 2002 + 20 (2013) (2017) (2022) Imanitib compound New Use of Imatinib and all its salts Mesylate salt of (GIST) Patented patented. (This imatinib patent expired in SA patented Granted in S. Africa 2013)
Before generic competition in SA
Imatinib: Still Priced Too High • Novartis charges 39% less in India than in SA • Cipla’s price in India is 91% less than in SA • Least expensive option: Cipla in SA is almost 20 times more than Glenmark in India Manufacturer India ppy South Africa (ZAR) ppy (ZAR) Novartis R 237,549 R 387,834 Cipla R 17, 816 R 208,780 Sun Pharma R160,982 Natco R 20,902 -- Glenmark R 10,694 -- Will further competitors (and lower prices) be blocked in South Africa by Novartis’ secondary patents?
How many times do we pay? Novartis’ Gleevec: 1. Early Research Costs: – 50% National Cancer Institute – 30% Leukemia and Lymphoma Society – 10% Oregon Health Sciences university; – Only 10% Novartis 2. Tax Credits: Orphan Drug Credit for Novartis 3. Product costs: Sales of Gleevec in 2012: $4.6 billion Estimated Novartis Investment in R&D: $38-$96 million Full return on investment every 13 days!!!
Aripiprazole • Aripiprazole - anti-psychotic (for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder) — one of the top-10 selling drugs globally • Could have been off-patent in U.S. in 2009 (extensions run to 2015) — South African multiple pending patents (Otsuka, BMS) could run until 2033. • Cost of a 10mg tablet R35.60 in South Africa over 35x higher than generics available in India. • SA price (R3.56/mg) 20% higher than in Japan (R2.84/mg ) • If SA had India’s prices, over R29 million in savings annually that could be realized on one drug alone
Oral contraceptive (DSP+EE) • Bayer holds multiple patents on drospirenone clathrate/ethinyl estradiol (Yasmin/Yaz). • Initial Yasmin patent expired 2011 in SA, secondary patents expire 2022 (size of synthetic hormone) and 2024 (dissolution profile). • Ruby is a generic version of Yasmin, by manufacturer Pharmadynamics
Oral contraceptive (DSP+EE), continued • Pharmadynamics 2011 launch of generic product at ~30% lower price was halted through an interdict over secondary patent • SA court case continues, even though generics available elsewhere, patent in question has been struck down in Europe and US. • Secondary patents on Yasmin run to 2024 • Pharmadynamics has incurred over R10million in legal fees, millions of rand in lost sales — will make it difficult to realize lower prices even if they are given right to launch product
Oral contraceptive (DSP+EE) Sales Manufacturer Brand Units Sold Annual Price per pack Name in SA revenue of pills in in ZAR private sector* (Oct 2012- (Oct. Sept. 2012- 2013)^ Sept. 2013)^ Bayer Yaz 793 559 89 404 R139.80 172 Bayer Yasmi 903 531 84 196 R115.62 n 100 Pharmadynam Ruby 0 0 R80.93 ics If everyone on Yasmin had made the switch to Ruby, South African women would have saved over R11 million per year in total.
Entecavir for Hepatitis B • Hepatitis B chronic infection affects approximately 8% of the population in Sub-Saharan Africa • Entecavir used for those who don’t tolerate tenofovir, have kidney impairment. Not available in public sector, nor on private formularies for HepB • R4,700-R5,500 per month in SA (Bristol-Myers Squibb only manufacturer). In India, generics cost around R400-R800 per month! • Initial patent expired 2011 in SA. Three secondary patents were granted, one still in force (expires 2022). • Patent overturned in the U.S. can be filed in SA up until end 2014
How can we strengthen the campaign? • Organisations endorse/sign up to campaign • Encourage patient voices • Find/be an “expert doctor” to be campaign spokesperson • Join public actions, meetings with decision makers, conferences • Sign on to letters, parliament submissions, petitions, social media actions, etc. • Feedback on ideas (e.g. poster) • Google group to share activities, open source campaign materials • Other ideas?
http://www.fixthepatentlaws.org @FixPatentLaw Thank you!
Recommend
More recommend