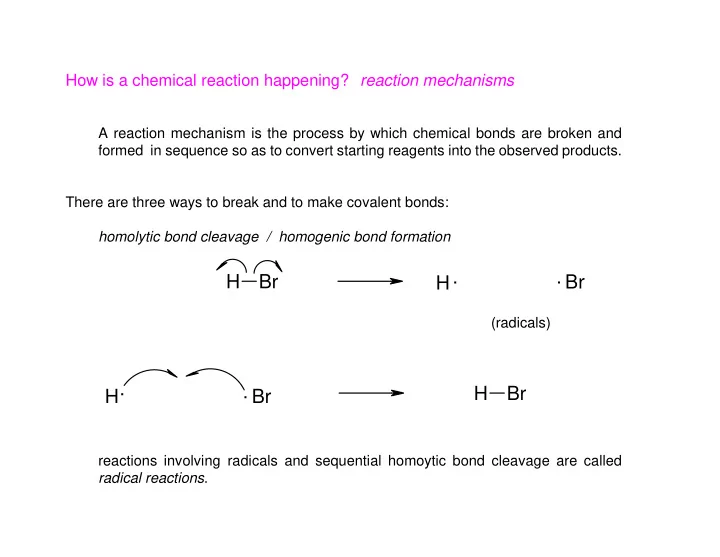

How is a chemical reaction happening? reaction mechanisms A reaction mechanism is the process by which chemical bonds are broken and formed in sequence so as to convert starting reagents into the observed products. There are three ways to break and to make covalent bonds: homolytic bond cleavage / homogenic bond formation . . H Br Br H (radicals) . . H Br H Br reactions involving radicals and sequential homoytic bond cleavage are called radical reactions .
Radical mechanisms The steps of radical mechanisms fall into one of three categories: Initiation Initiations are mechanism steps in which radicals are created from nonradical precursors Propagation Propagations are mechanism steps in which precursor radicals form new radicals Termination Terminations are mechanism steps in which nonradical products form from precursor radicals There are six characteristic steps in radical mechanisms.
Radical mechanisms (Initiation) Six characteristic patterns: 1. Homolytic bond cleavage to form radicals
Radical mechanisms (Propagation) Six characteristic patterns: 2. Radical addition to a pi bond
Radical mechanisms (Propagation) Six characteristic patterns: 3. Hydrogen abstraction by a radical
Radical mechanisms (Propagation) Six characteristic patterns: 4. Halogen abstraction by a radical
Radical mechanisms (Propagation) Six characteristic patterns: 5. Elimination of a radical
Radical mechanisms (Termination) Six characteristic patterns: 5. Coupling of 2 radicals
Recommend
More recommend