
Defining the Potency of Sox2-Positive Taste Epithelial Cells Using Lingual Organoid Culture Benjamin Tiano Barlow Lab-UC Denver ITTSD Conference 2018
What we know already LGR5-EGFP/ Sox2/LGR5-EGFP/ Sox2 KCNQ1 KCNQ1 • Single LGR5+ cells generate renewing lingual organoids (Ren et al., 2014) • Basal proliferative Sox2+ cells give rise to all types of taste bud cells (Ohmoto et al., 2017) • Sox2 is expressed in LGR5+ Ohmoto et al., 2017 cells (Ohmoto et al., 2017) • Sox2 deletion in lingual progenitors disrupts taste Sox2 bud renewal (Castillo-Azofeifa et al., 2018) * * Suzuki, 2008
What we know already • Single LGR5+ cells generate Low-GFP renewing lingual organoids (Ren et al., 2014) • Basal proliferative Sox2+ MedLo- Sox2-GFP cells give rise to all types of GFP Circumvallate taste bud cells (Ohmoto et al., Papilla HiMed-GFP 2017) • Sox2 is expressed in LGR5+ High-GFP cells (Ohmoto et al., 2017) • Sox2 deletion in lingual Collect tongues and Dissociate into single FACS sort progenitors disrupts taste epithelia cell suspension based on GFP bud renewal (Castillo-Azofeifa expression level et al., 2018)
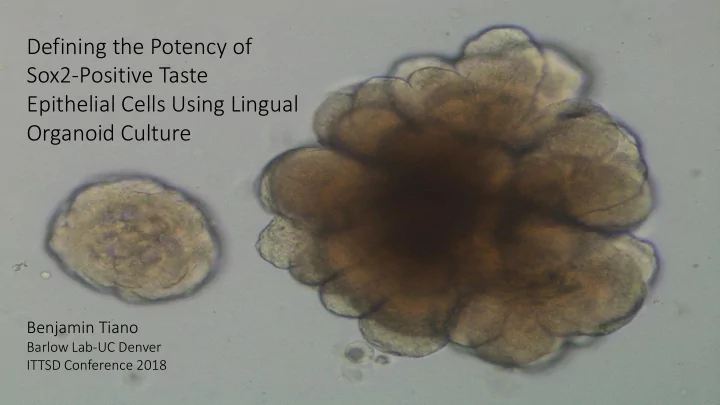
Do they grow?
Do different Sox2+ populations exhibit different growth potentials? 1000 cells/well 500 cells/well
LGR5 is differentially expressed by organoids from different Sox2 expression bins
Acknowledgements Barlow Lab Linda Barlow Dany Gaillard Erin Golden Jenn Scott Lauren Shechtman Kelly Zaccone
Recommend
More recommend