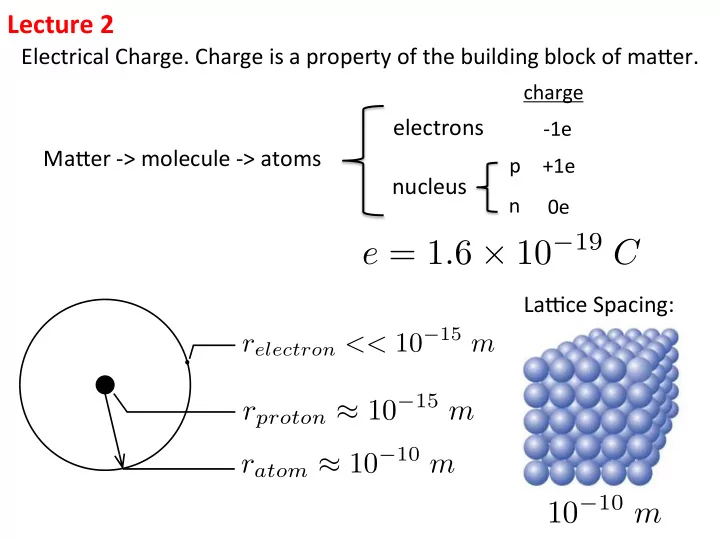

Lecture ¡2 ¡ Electrical ¡Charge. ¡Charge ¡is ¡a ¡property ¡of ¡the ¡building ¡block ¡of ¡ma9er. ¡ charge ¡ electrons ¡ -‑1e ¡ Ma9er ¡-‑> ¡molecule ¡-‑> ¡atoms ¡ p ¡ +1e ¡ nucleus ¡ ¡ ¡ n ¡ 0e ¡ e = 1 . 6 × 10 − 19 C LaAce ¡Spacing: ¡ r electron << 10 − 15 m r proton ≈ 10 − 15 m r atom ≈ 10 − 10 m 10 − 10 m
F = kq 1 q 2 r 2 ≈ 9 × 10 9 Nm 2 1 k = C 2 4 ⇡✏ 0 4 ⇡ k = 8 . 85 × 10 − 12 C 2 1 ✏ 0 = Nm 2 k ¡is ¡the ¡conversion ¡factor: ¡ 1 C 2 m 2 = 9 × 10 9 N Electric ¡Field ¡ a. ¡Causal ¡DescripFon ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡Coulombs ¡law ¡is ¡a ¡descripFon ¡of ¡acFon ¡at ¡distance. ¡ ¡ ¡(acausal ¡descripFon) ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡A ¡causal ¡descripFon ¡can ¡be ¡achieved ¡in ¡2 ¡steps. ¡
Spider-‑Fly ¡Analogy ¡ A9racFon ¡between ¡spiders ¡ and ¡fly ¡ q ¡ Q ¡ E ¡ ✓ kQ ◆ F = q ≡ Eq Test ¡charge ¡ Source ¡charge ¡ Field ¡ r 2 E = F Descrip9on ¡of ¡the ¡field: ¡Field ¡line ¡ q + - NegaFve ¡charges ¡a ¡source ¡ PosiFve ¡charges ¡a ¡source ¡ of ¡field ¡lines ¡ of ¡field ¡lines ¡
Electric ¡Force ¡Vectors ¡ Combine ¡gravitaFonal ¡force ¡vector ¡with ¡electric ¡force: ¡ due to q 2 = kq 1 q 2 F q 1 0 q 2 q 1 r 2 F m on F m = mg Adding ¡electric ¡force ¡vector ¡to ¡gravitaFonal ¡force ¡vector. ¡ E = kq 1 F = kq 1 q 2 ~ ~ r = ~ r Eq 2 r 2 ˆ ˆ r 2 NoFce ¡E ¡depends ¡on ¡the ¡source ¡charge ¡q1 ¡and ¡the ¡posiFon ¡of ¡the ¡observaFon ¡ point ¡in ¡relaFon ¡to ¡the ¡source ¡charge, ¡r. ¡E ¡is ¡independent ¡of ¡q2. ¡
Recommend
More recommend